Using AI to find the polymers of the future
2024-08-20
Nylon, Teflon, Kevlar. These are just a few familiar polymers — large-molecule chemical compounds — that have changed the world. From Teflon-coated frying pans to 3D printing, polymers are vital to creating the systems that make the world function better.
Finding the next groundbreaking polymer is always a challenge, but now Georgia Tech researchers are using artificial intelligence (AI) to shape and transform the future of the field. Rampi Ramprasad’s group develops and adapts ...
Salk Professor Rusty Gage awarded 2024 Taylor International Prize in Medicine
2024-08-20
LA JOLLA (August 14, 2024)—Professor Rusty Gage has been awarded the 2024 J. Allyn Taylor International Prize in Medicine by the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry and the Robarts Research Institute at Western University. One of the most prestigious medical research awards in Canada, the Taylor Prize recognizes scientists for transformative, career-defining work in basic sciences, translational research, and medical innovations.
This year’s prize specifically honors a research leader in aging-related medical science and research—a long-term focus of Gage and his lab. Gage will receive $50,000 and be celebrated at a Robarts Research ...
Heart data unlocks sleep secrets
2024-08-20
We know that quality sleep is as essential to survival as food and water. Yet, despite spending a third of our lives in slumber, it largely remains a scientific mystery.
Not that experts haven’t tried.
Sleep analysis, also known as polysomnography, is used to diagnose sleep disorders by recording multiple types of data, including brain (electroencephalogram or EEG) and heart (electrocardiogram or ECG). Typically, patients are hooked up to dozens of sensors and wires in a clinic, tracking brain, ...
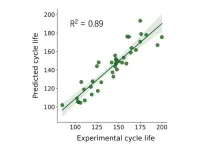
Development of a model capable of predicting the cycle lives of high-energy-density lithium-metal batteries
2024-08-20
1. NIMS and SoftBank Corp. have jointly developed a model capable of predicting the cycle lives of high-energy-density lithium-metal batteries by applying machine learning methods to battery performance data. The model proved able to accurately estimate batteries’ longevity by analyzing their charge, discharge and voltage relaxation process data without relying on any assumption about specific battery degradation mechanisms. The technique is expected to be useful in improving the safety and reliability of devices powered by lithium-metal batteries.
2. Lithium-metal ...
UVA Engineering Professor’s $600,000 grant set to innovate pediatric brain tumor treatment
2024-08-19
Natasha Sheybani, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Virginia School of Engineering, will collaborate with researchers at Children’s National Hospital to study the combination of two therapies for pediatric brain cancer.
High-risk brain tumors in children often don’t respond well to existing chemotherapy and radiation treatments, but Sheybani and her collaborators hope their fusion of therapies will offer a better option.
Over the two-year project, researchers ...
Illinois researchers develop index to quantify circular bioeconomy
2024-08-19
URBANA, Ill. – As the world faces the challenges of mitigating climate change and providing resources for a growing population, there is increasing focus on developing circular economies for sustainable production. But to evaluate strategies and impacts, it is necessary to have reliable metrics. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a Circularity Index that provides a comprehensive method to quantify circularity in bioeconomic systems. In a new paper, they outline the method and apply it to two case studies – a corn/soybean farming operation and the entire U.S. food and agriculture system.
“The ...
Less severe forest fires can reduce intensity of future blazes
2024-08-19
Not all forest fires have devastating effects. Low- and moderate-severity forest wildfires can reduce the intensity of future conflagrations for as long as 20 years in certain climates, according to new research by the University of California, Davis.
The extent of reduced severity of these second fires, or reburns, and the duration of the moderating effect, varies by climate, forest type and other factors. But initial fires continue to mitigate future severity even during extreme weather, such as wind, high temperatures and drought, research published in the journal Ecological ...
Electric reactor could cut industrial emissions
2024-08-19
Currently, industrial processes in the U.S. account for approximately a third of the country’s carbon dioxide emissions – even more than the annual emissions from passenger vehicles, trucks, and airplanes combined. Decarbonizing this sector is a challenging but vital step in mitigating impacts on our future climate.
Researchers at Stanford Engineering have designed and demonstrated a new type of thermochemical reactor that is capable of generating the immense amounts of heat required for many industrial processes using electricity instead of burning fossil fuels. The design, published Aug. ...
Causal relationship between PECAM-1 level and cardiovascular diseases
2024-08-19
https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/CVIA.2024.0032
Announcing a new article publication for Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications journal. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1) is present in the vascular endothelium and plays important roles in various biological processes. Several recent studies have reported associations between PECAM-1 and certain subtypes of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). However, further research is necessary to clarify the causal effects of PECAM-1 on CVDs.
To determine whether PECAM-1 and CVDs are causally ...
The plausible role of vascular adhesion molecules in cardiovascular diseases
2024-08-19
https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/CVIA.2024.0046
Announcing a new article publication for Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications journal. Vascular Adhesion Molecules (VAMs) appear to play important roles in the development of Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD). The roles of these molecules in mediating inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and plaque formation suggest that they may be important as both biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Understanding and targeting these molecules are hoped to substantially contribute to ...
Whole-exome sequencing identifies three novel TTN variants in Chinese families with dilated cardiomyopathy
2024-08-19
https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/CVIA.2024.0040
Announcing a new article publication for Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications journal. Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), a severe heart disease, is the leading cause of heart failure and sudden cardiac death worldwide. DCM is defined by a dilated and deficient systolic left ventricle (LV) and is a major risk factor for morbidity and mortality worldwide. DCM progression can be ascribed to genetic and non-genetic factors, including hypertension, infectious agents, toxins, and drugs.
Sarcomere genes play crucial roles in myocardial cells’ physical structure and physiological function. Various cardiomyopathies ...
Key biofuel-producing microalga believed to be a single species is actually three
2024-08-19
MEDIA INQUIRES
WRITTEN BY
Laura Muntean
Ashley Vargo
laura.muntean@ag.tamu.edu
601-248-1891
FOR ...
Simple alternative criteria identify people with the most to gain from lung cancer screening
2024-08-19
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 19 August 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives ...
For some older adults with kidney failure, dialysis may not be the best option
2024-08-19
Whether dialysis is the best option for kidney failure and, if so, when to start, may deserve more careful consideration, according to a new study.
For older adults who were not healthy enough for a kidney transplant, starting dialysis when their kidney function fell below a certain threshold — rather than waiting — afforded them roughly one more week of life, Stanford Medicine researchers and their colleagues found.
More critically, perhaps, they spent an average of two more weeks in ...
UC Davis Health develops a real-time action plan to help patients with lung disease cope with wildfire smoke
2024-08-19
A multidisciplinary team of UC Davis Health experts are calling on health systems to create wildfire preparedness action plans to support patients with preexisting respiratory diseases. They are urging providers to proactively put in place interventions to mitigate the effects of poor air quality from smoke.
Their article, published in the Journal of the COPD Foundation, identifies the needs of high-risk populations when affected by wildfire smoke. It outlines an action plan for health systems to help these groups with the burdens of poor air quality from wildfires.
“Patients ...
MIT study explains why laws are written in an incomprehensible style
2024-08-19
Legal documents are notoriously difficult to understand, even for lawyers. This raises the question: Why are these documents written in a style that makes them so impenetrable?
MIT cognitive scientists believe they have uncovered the answer to that question. Just as “magic spells” use special rhymes and archaic terms to signal their power, the convoluted language of legalese acts to convey a sense of authority, they conclude.
In a study that will appear in the journal of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers found that even non-lawyers use this type of language when asked to write laws.
“People seem to understand that there’s ...
Understanding of early life ecosystems highlighted in new publication
2024-08-19
STARKVILLE, Miss.—With a new understanding of past life on the planet through fossils, a Mississippi State biological sciences faculty member is helping researchers better predict Earth’s future.
In a new paper published in July in the esteemed peer-reviewed journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Donald L. Hall Professor of Biology Matthew Brown unearths a specific area of under-studied fossils: microbial eukaryotes—more specifically, testate amoebae from 750 million ...
New research finds scalable mindfulness interventions delivered via telehealth improve pain and well-being for veterans with chronic pain
2024-08-19
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (08/19/2024) — Mindfulness-based interventions delivered via telehealth in a scalable format can improve pain and overall well-being among veterans with chronic pain, according to new research published today in JAMA Internal Medicine.
In a randomized clinical trial, researchers aimed to test the effectiveness of two eight-week telehealth mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) designed to be scalable and widely implemented in healthcare systems. MBIs help people pay attention non-judgmentally in the present moment and often involve practices like meditation, breathing exercises or gentle movement.
“Although mindfulness interventions are evidence-based ...
Current HIV prevention medication users often stigmatize other PrEP users as ‘promiscuous’
2024-08-19
Novel findings attend to attitudes of the stigmatized, rather than stigmatizers
Past research identified perception of promiscuity and assumptions that PrEP users are HIV-positive as key drivers of perceived stigma
Perception of stigma is highest among those who believe their sexual behavior puts them at risk for HIV
Knowing others who use PrEP does not influence one’s fear of potential discrimination
CHICAGO --- Public health messaging that drives stigma around Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), a medication that can reduce HIV risk by up to 99%, appears to play a role in uptake of the medication. While the potential mismarketing of the drug is well-understood and ...
How "winner and loser effects" impact social rank in animals - and humans
2024-08-19
Research has shown that in many animals, the winners of a fight are more likely to win subsequent contests, while the losers tend to lose their following fights. In experiments where male stickleback fish were randomly introduced to another fish, 65% of the winning fish won the second match, while all losing fish lost the second contest.
Such winner and loser effects can greatly influence individual behavior and fitness. This effect happens in humans as well. In "Winner and Loser Effects and Social Rank in Humans," recently published in The Quarterly Review of Biology, authors Noah M. T. Smith and Reuven ...
Research study examines Alzheimer’s disease drug on tissue samples from people with Down syndrome
2024-08-19
People with Down syndrome are likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease at a young age, with autopsy studies showing that by age 40 years, the brains of individuals with Down syndrome have amyloid plaques. Yet people with Down syndrome have been excluded from or underrepresented in clinical trials of new therapies for treating AD. Lecanemab, which has been shown to target and remove beta-amyloid plaques, has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat AD early in the disease’s progression. ...
International Society of Biomechanics recommendations for wearables-based motion capture
2024-08-19
Dr. Reed Gurchiek, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, and an Early-stage Investigator, was a co-first author of a recent publication in the Journal of Biomechanics titled “International Society of Biomechanics recommendations on the definition, estimation, and reporting of joint kinematics in human motion analysis applications using wearable inertial measurement technology”. A collaborative effort that incorporated feedback from the biomechanics community has produced recommendations in five categories: sensor characteristics ...
Rutgers researchers discover new way to control the sense of touch
2024-08-19
Rutgers researchers have found a new way to manage the receptors that control the sense of touch, which could lead to treating chronic pain more effectively.
“Identifying a natural molecule that specifically reduces pain sensitivity offers hope for new therapeutic strategies in the management of pain,” said Tibor Rohacs, a professor in the Department of Pharmacology, Physiology and Neuroscience at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School and a member of the Rutgers Brain Health Institute. “Our goal is to translate these findings into effective treatments that improve the quality of life for people suffering from chronic ...
New UH study targets early signs of vision loss in diabetic patients
2024-08-19
A $3.3 million study at the University of Houston College of Optometry will track the health of patients with prediabetes and diabetes to find out who might develop eye problems and be at risk for future vision loss. The study is being led by Wendy Harrison, associate professor, and is underwritten by the National Eye Institute.
Vision loss in type 2 diabetes results from diabetic retinopathy, caused by damage to blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye. The disease can appear without warning.
“The ...
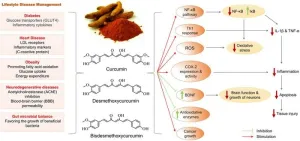
Herbal-based nutraceuticals in management of lifestyle diseases: Experience from Indian population
2024-08-19
Lifestyle diseases, also known as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), have emerged as a major health burden globally, including in India. These diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders, are primarily caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices like sedentary behavior, poor dietary habits, and stress. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), NCDs are responsible for 41 million deaths annually, accounting for 74% of all global deaths. Notably, 86% of these premature deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries.
The increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases ...
[1] ... [993]
[994]
[995]
[996]
[997]
[998]
[999]
[1000]
1001
[1002]
[1003]
[1004]
[1005]
[1006]
[1007]
[1008]
[1009]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.