Tracking down the asteroid that sealed the fate of the dinosaurs
2024-08-16
Geoscientists from the University of Cologne have led an international study to determine the origin of the huge piece of rock that hit the Earth around 66 million years ago and permanently changed the climate. The scientists analysed samples of the rock layer that marks the boundary between the Cretaceous and Paleogene periods. This period also saw the last major mass extinction event on Earth, in which around 70 percent of all animal species became extinct. The results of the study published in Science indicate that the asteroid formed outside Jupiter’s orbit during the ...
IOP Publishing hosts Progress In Physics 2024 – a two-day hybrid conference focused on condensed matter physics
2024-08-16
The Institute of Physics and IOP Publishing (IOPP) are launching Progress In Physics 2024, a two-day hybrid workshop hosted at the Institute of Physics’ office in London from 9-10 October 2024. The event will cover topics on condensed matter and will bring together leading physics researchers to exchange knowledge in both an in-person and online format.
Progress in Physics 2024 aligns with the mission of IOPP’s new Progress In seriesTM of journals. The series builds on the success of IOPP’s flagship journal Reports on Progress in PhysicsTM which celebrates its 90th anniversary this year.
With ...
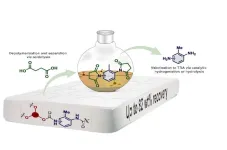
Researchers discover smarter way to recycle polyurethane
2024-08-16
Researchers discover smarter way to recycle polyurethane
Researchers at Aarhus University have found a better method to recycle polyurethane foam from items like mattresses. This is great news for the budding industry that aims to chemically recover the original components of the material – making their products cheaper and better.
Polyurethane (PUR) is an indispensable plastic material used in mattresses, insulation in refrigerators and buildings, shoes, cars, airplanes, wind turbine blades, cables, and much more. It could be called a wonder material if it weren’t also an environmental ...
Right on schedule: Physicists use modeling to forecast a black hole's feeding patterns with precision
2024-08-16
Powerful telescopes like NASA’s Hubble, James Webb, and Chandra X-ray Observatory provide scientists a window into deep space to probe the physics of black holes. While one might wonder how you can “see” a black hole, which famously absorbs all light, this is made possible by tidal disruption events (TDEs) - where a star is destroyed by a supermassive black hole and can fuel a “luminous accretion flare.” With luminosities thousands of billions of times brighter than the Sun, accretion events enable astrophysicists to study supermassive black holes (SMBHs) at cosmological distances.
TDEs occur when a star is violently ripped ...
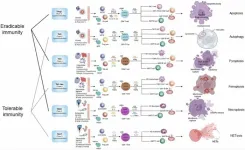
Cell death types and their relations to host immune pathways
2024-08-16
“We have proposed a framework encompassing all discovered host immunological pathways, such as TH1, TH2a, TH2b, TH3, TH9, TH17, TH22, TH1-like, and THαβ immune reactions”
BUFFALO, NY- August 16, 2024 – A new review was published as the cover paper of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 15, entitled, “Types of cell death and their relations to host immunological pathways”.
Various ...
Perceived parental distraction by technology and mental health among emerging adolescents
2024-08-16
About The Study: In a cohort study of 1,300 emerging adolescents ages 9 to 11 across three assessments, higher levels of anxiety symptoms were associated with higher levels of perceived parental technoference later in development. Higher levels of perceived parental technoference were associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity symptoms later in development. The findings of this study speak to the need to discuss digital technology use and mental health with parents and emerging adolescents as a part of routine care.
Corresponding Author: To contact ...
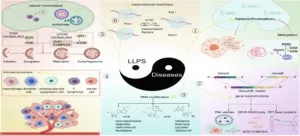
Liquid-liquid phase separation in diseases
2024-08-16
This paper, led by Professor Wu (Wenzhou Institute University, Wenzhou Medical University) and Professor Huang (Northeastern University), explores LLPS, a phenomenon closely associated with various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. As a frontier research area, LLPS plays a significant role in cancer through its regulation of multiple facets, including signaling pathways, gene expression, and tumor microenvironment. Dysregulation of LLPS leads to the formation of various aggregates, such as amyloid proteins, suggesting that modulating LLPS in ...
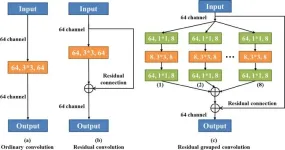
Advanced U-net segmentation model using residual grouped convolution and attention mechanism for brain tumor MRI image segmentation
2024-08-16
The brain is responsible for the "general command" of human thinking and coordination of the body. Thus, various brain diseases can cause great damage to the human body and nervous system. Brain tumors are caused by abnormal cells that grow and multiply irregularly within the brain. Glioma is one of the most common malignant tumors in adults. It originates from glial cells and the surrounding infiltrating tissue, compresses other normal tissues in the brain during the growth process, and blurs the boundary of the tumor. ...
PolyU develops versatile fluidic platform for programmable liquid processing
2024-08-16
Society relies heavily on diverse fluidic technologies. The ability toprecisely capture and release various chemical and biological fluids plays a fundamental role in many fields.A long-standing challenge is to design a platform that enables the switchable capture and release of liquids with precise spatial and temporal control and accurate volumes of the fluid. Recently, researchers at The Polytechnic University of Hong Kong (PolyU) have invented a new method to effectively overcome this challenge.
Led by Prof. WANG Liqiu, Otto Poon Charitable Foundation Professor in Smart and Sustainable Energy, Chair ...
MIT engineers design tiny batteries for powering cell-sized robots
2024-08-16
A tiny battery designed by MIT engineers could enable the deployment of cell-sized, autonomous robots for drug delivery within in the human body, as well as other applications such as locating leaks in gas pipelines.
The new battery, which is 0.1 millimeters long and 0.002 millimeters thick — roughly the thickness of a human hair — can capture oxygen from air and use it to oxidize zinc, creating a current of up to 1 volt. That is enough to power a small circuit, sensor, or actuator, the researchers showed.
“We think this is going to be very enabling ...
New tool simplifies cell tracking data analysis
2024-08-16
Studying cell migration is vital because it plays a crucial role in many biological processes, including immune response, wound healing, and cancer metastasis. Understanding how cells move and behave can lead to breakthroughs in treating diseases, developing new drugs, and creating innovative therapies. For example, in cancer research, tracking how cancer cells migrate can reveal how tumors grow and spread through the human body. This insight can led to the discovery of more efficient and targeted treatments to stop or even prevent metastasis.
Scientists have introduced CellTracksColab, a tool that simplifies cell tracking data analysis. This free platform leverages advanced ...
Exploring Huntington’s disease, researchers discover that protein aggregates poke holes in nuclear membrane
2024-08-16
Researchers at Utrecht University in the Netherlands have identified a new way in which the toxic protein aggregates associated with Huntington’s disease may damage nerve cells and cause them to die. The study, to be published August 16 in the Journal of Cell Biology (JCB), suggests that the aggregates can poke holes in the membrane that separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell, damaging the DNA inside the nucleus and changing the activity of neuronal genes.
Huntington’s disease is a devastating neurogenerative disorder caused by a mutation in the HTT gene that results in cells producing abnormally large versions of the huntingtin protein. These ...
Why isn't Colorado's snowpack ending up in the Colorado River? New research suggests the problem might be the lack of spring rainfall
2024-08-16
The Colorado River and its tributaries provide water for hydropower, irrigation and drinking water in seven U.S. states and Mexico. Much of this water comes from the snowpack that builds up over the winter and then melts each spring. Every year in early April, water managers use the snowpack to predict how much water will be available for the upcoming year.
But since 2000, these predictions have been incorrect, with the actual streamflow being consistently lower than the predicted streamflow. That’s left water managers ...
New research shows unprecedented atmospheric changes during May's geomagnetic superstorm
2024-08-16
On May 11, a gorgeous aurora surprised stargazers across the southern United States. That same weekend, a tractor guided by GPS missed its mark.
What do the visibility of the northern lights have in common with compromised farming equipment in the Midwest?
A uniquely powerful geomagnetic storm, according to two newly published papers co-authored by Virginia Tech's Scott England.
“The northern lights are caused by energetic, charged particles hitting our upper atmosphere, which are impacted by numerous factors in space, including the sun,” said England, associate professor in the Kevin T. Crofton Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering. “During ...
How some states help residents avoid costly debt during hard times
2024-08-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new national study provides the best evidence to date that generous unemployment insurance benefits during the COVID-19 pandemic helped reduce reliance on high-cost credit use.
Researchers found that lower-income residents of states with more generous benefits were significantly less likely than those living in less-generous states to take out new credit cards, personal finance loans and payday loans or other alternative financial service offerings.
The study, published recently in the journal ...
Same person. Different place. Twice the odds of a dementia diagnosis.
2024-08-16
With new medications on the market or in the works for Alzheimer’s disease and other kinds of dementia, a new study suggests that getting the diagnosis needed to access these new treatments may depend on where you live.
The percentage of people who get a new dementia diagnosis each year varies a lot across regions of the U.S., the study finds.
And the differences between regions of the country are even larger for people on the young end of the dementia-risk age range, ages 66 to 74, and for those who are Black ...
The banana apocalypse is near, but UMass Amherst biologists might have found a key to their survival
2024-08-16
August 16, 2024
The Banana Apocalypse is Near, but UMass Amherst Biologists Might Have Found a Key to Their Survival
Discovery of molecular mechanisms used by the banana-destroying microbe brings hope to the breakfast table
AMHERST, Mass. – The bananas in your supermarket and that you eat for breakfast are facing functional extinction due to the disease Fusarium wilt of banana (FWB) caused by a fungal pathogen called Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense (Foc) tropical race 4 (TR4). However, thanks to recent research from an ...
Rethinking the dodo
2024-08-16
Rethinking the Dodo
Review of 400 years of scientific literature corrects the record on icon of extinction
Researchers are setting out to challenge our misconceptions about the Dodo, one of the most well-known but poorly understood species of bird.
In a paper published today [16 August 2024] in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society researchers from the University of Southampton, Natural History Museum (NHM) and Oxford University Museum of Natural History have undertaken the most comprehensive review of the taxonomy of the Dodo and its closest relative, the Rodriguez ...
Arts and crafts improves your mental health as much as having a job, scientists find
2024-08-16
Could arts and crafts help protect the public’s mental health? A new study in Frontiers in Public Health provides evidence that indulging our creative side could provide everyone with a significant wellbeing boost. Because arts and crafts are relatively affordable and accessible, promoting the public’s access to artistic activities could provide a major boost to public mental health.
“Crafting and other artistic activities showed a meaningful effect in predicting people’s ...
It’s a rave – underground acoustics amplify soil health
2024-08-16
Barely audible to human ears, healthy soils produce a cacophony of sounds in many forms – a bit like an underground rave concert of bubble pops and clicks.
Special recordings made by Flinders University ecologists in Australia show this chaotic mixture of soundscapes can be a measure of the diversity of tiny living animals in the soil, which create sounds as they move and interact with their environment.
With 75% of the world’s soils degraded, the future of the teeming community of living species that live underground face a dire future without restoration, says microbial ecologist Dr Jake Robinson, from the Frontiers ...
New poll finds 50% of parents believe too much time on technology hinders kids from forming connections in the classroom
2024-08-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio (August 16, 2024) – Building positive connections with teachers and peers in the classroom can be critical to the mental health and academic success of children and adolescents. Yet, a new national poll from The Kids Mental Health Foundation, conducted by Ipsos, finds half of parents believe spending too much time on technology and social media hinder children from making meaningful connections as they head into the upcoming school year.
The poll, conducted by Ipsos on behalf of ...
How policing impacts the homeless
2024-08-16
People who are homeless often endure constant and intrusive police interactions, leaving them feeling intimidated, harassed and stigmatised, a new study finds.
More people of all ages and backgrounds are finding themselves homeless, often due to job loss or illness, as well as a lack of affordable housing. Between 2016 and 2021 homelessness increased by 5.2% in Australia.
Professor of Law Thalia Anthony from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) said the research aimed to give a voice to people experiencing homelessness ...
Scottish and Irish rocks confirmed as rare record of ‘snowball Earth’
2024-08-16
A rock formation spanning Ireland and Scotland may be the world’s most complete record of “snowball Earth”, a crucial moment in planetary history when the globe was covered in ice, finds a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
The study, published in the Journal of the Geological Society of London, found that the Port Askaig Formation, composed of layers of rock up to 1.1km thick, was likely laid down between 662 to 720 million years ago during the Sturtian glaciation – the first of two global freezes thought to have ...
Research provides a roadmap for improving electrochemical performance
2024-08-16
Thomas Edison went through thousands of materials before he finally found the right tungsten filament to create a working lightbulb. This type of trial-and-error research continues today and is responsible for countless inventions that improve our world. Battery systems that help power our lives in many seen (and unseen) ways are one example.
However, improving these materials and devices requires more than experimentation. Modern engineers must also form a deeper understanding of the general principles that govern material performance, from which they can design better materials to achieve challenging product requirements.
In a paper ...
Females’ and males’ muscles differ in sugar and fatty acid handling
2024-08-16
Females’ and males’ muscles differ in glucose and fatty acid handling – but regular physical activity quickly triggers similar beneficial metabolic changes in the muscles of both sexes, new research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (Madrid, 9-13 September) has found.
Exercise has a potent effect on skeletal muscle and is the most effective strategy to prevent weight loss-related muscle loss and type 2 diabetes. ...
[1] ... [996]
[997]
[998]
[999]
[1000]
[1001]
[1002]
[1003]
1004
[1005]
[1006]
[1007]
[1008]
[1009]
[1010]
[1011]
[1012]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.