Tackling cancer from the inside out: A deep dive into immune checkpoint inhibitors
2024-08-13
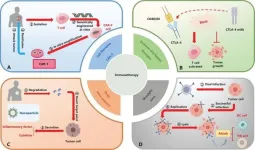
In the past two decades, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized cancer treatment, showing promising results against various solid tumors. This study reviews recent developments in ICIs, focusing on new targets like T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT), T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 (TIM-3), and lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3). These targets aim to overcome resistance mechanisms limiting the effectiveness of current therapies, such as anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4. By identifying and developing these new ...
RPI Physicist Moussa N’Gom is using light to enhance nuclear security
2024-08-13
Our nation’s security depends on the effective detection of nuclear materials at our borders and beyond. To address this challenge, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) physicist Moussa N’Gom, Ph.D., is leading research aimed at developing a quantum sensing probe to detect and characterize special nuclear materials precisely and without contact. Special nuclear materials are only mildly radioactive but can be used in nuclear explosives.
The research is being conducted through RPI’s participation in the Consortium ...
The atmosphere in the room can affect strategic decision-making, study finds
2024-08-13
The atmosphere within a group can influence the outcome of strategic decision-making, according to a new study co-authored by Bayes Business School (formerly Cass).
Paula Jarzabkowski, Professor of Strategic Management at Bayes, along with researchers from University of Queensland, Macquarie University and Leuphana University of Lüneburg, found that different atmospheres led to people speaking and interacting in different ways that changed how they made sense of the strategy.
For instance, when the atmosphere was pensive, people were cautious about the way to proceed, whereas, when it was curious they felt ...
Study uncovers mutated driver genes in colorectal cancer: 9 novel to CRC and 24 previously undetected in any cancer
2024-08-13
The Institute of Intelligent Medical Research (IIMR) of BGI Genomics, in collaboration with Sweden’s Uppsala University, has published the largest multi-omics study of colorectal cancer (CRC) to date. The study aimed to understand the functional and prognostic impact of cancer-causing somatic mutations, revealing new genetic alterations and developing a new molecular classifier of tumor variants. This research was published in the journal Nature on August 7th, 2024.
Unveiling New Genetic Landscapes
The researchers analyzed the whole genomes and transcriptomes ...
Cricket physics: Science behind the modern bowler technique tricking batters
2024-08-13
WASHINGTON, Aug. 13, 2024 – Key to winning a cricket match is tricking the other team’s batters – no small feat as bowlers bowl cricket balls nearly 100 miles per hour. In recent years, a bowling technique that has become popular involves keeping the arm almost entirely horizontal during delivery, notably used by Sri Lankan stars Lasith Malinga and Matheesha Pathirana. The aerodynamics of such deliveries have perplexed sports physicists.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers have started to unravel the mysteries of how ...
Measuring Martian winds with sound
2024-08-13
WASHINGTON, Aug. 13, 2024 – Mars has a notoriously inhospitable environment, with temperatures that fluctuate dramatically over the course of a Martian day and average minus 80 degrees Fahrenheit. Its surface is mostly covered in red dust, with terrain typified by craters, canyons, and volcanoes. And its atmosphere is extremely thin, comprising only about 1% of the density of Earth’s.
Needless to say, measuring wind speeds on the red planet is challenging. Martian landers have been able capture measurements — some gauging the cooling rate of heated materials ...
Posttraumatic stress disorder and type 2 diabetes outcomes in veterans
2024-08-13
About The Study: The findings of this cohort study of patients with comorbid posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and type 2 diabetes suggest that PTSD is a modifiable risk factor associated with a modest reduction in microvascular complications. Further research is needed to determine whether findings are similar in non-Veterans Health Administration health care settings.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jeffrey F. Scherrer, PhD, email jeffrey.scherrer@health.slu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27569)
Editor’s ...
Smartwatch measures of outdoor exposure and nearsightedness in children
2024-08-13
About The Study: In this 1-year prospective cohort study of children with smartwatches, continuous outdoor exposure with at least 15 minutes accompanied with no less than 2,000 lux sunlight intensity was associated with less myopic shift. These findings suggest that future outdoor interventions should focus not only on the overall time outdoors but also on the effective outdoor exposure patterns, as a means to effectively prevent myopia (nearsightedness) in children.
Corresponding Authors: To ...
Lurie Children’s Hospital awarded $12 million by PCORI to study best approach to treat mild pneumonia in young children
2024-08-13
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, in partnership with University of Utah Health, has been approved for $12 million in research funding by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) for a study that will compare two ways to use antibiotics in young children with mild pneumonia, one of the leading reasons children seek acute care, who are well enough to be cared for at home.
The first approach is to prescribe and give antibiotics immediately, which is the current standard of care. The second way is to prescribe an antibiotic but not give it unless the child’s symptoms worsen or ...
PCORI announces $165 million in funding for new health research
2024-08-13
PCORI announces $165 million in funding for new health research
Approved awards support patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER) on telehealth interventions, heart care and various health concerns
Aug. 13, 2024
WASHINGTON, D.C. – The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) today announced the approval of funding awards totaling more than $165 million for new patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER), as well as research to improve methods and strengthen the science of engagement in patient-centered CER. Among the 10 CER studies awarded, three will evaluate the effectiveness of telehealth interventions ...
Study finds emergency department visits by children associated with water beads more than doubled from 2021 to 2022
2024-08-13
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – Researchers from the Center for Injury Research and Policy and Central Ohio Poison Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital have found more than an estimated 8,000 visits to U.S. emergency departments (EDs) associated with water beads from 2007 through 2022, and the number of these visits increased rapidly by more than 130% from 2021 to 2022.
In a study published in American Journal of Emergency Medicine, researchers analyzed 16 years of data and call for a more comprehensive regulatory approach to prevent water bead-associated injuries. The increase in ...
Reduce, reuse, reflycle
2024-08-13
A Macquarie University team proposes using genetically engineered black soldier flies (Hermetia illucens) to address worldwide pollution challenges and produce valuable raw materials for industry, including the USD $500 billion global animal feed market.
In a new paper published on 24 July in the journal Communications Biology, scientists at Macquarie University outline a future where engineered flies could transform waste management and sustainable biomanufacturing, addressing multiple United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Synthetic biologist Dr Kate Tepper is lead author of the paper and a Postdoctoral Research Fellow at Applied BioSciences, Macquarie University.
“One ...
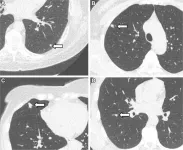
Lung nodules seen in a high percentage of non-smokers
2024-08-13
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new study of more than 10,000 non-smoking adults found that solid lung nodules were present in a considerable portion of study participants. Non-smokers are traditionally thought to be at low risk for lung nodules and lung cancer. The results of the study were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Incidental lung nodules are common findings on chest CT and in high-risk groups are more likely to be a sign of early-stage lung cancer. Because most previous research on the prevalence and size of lung nodules has typically been ...
Study shows text messages help youth at risk for suicide feel supported after discharge
2024-08-13
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – As the nation’s youth mental health crisis continues, providers continue to find ways to help address gaps in care. Patients who receive care for suicidal thoughts and behaviors need extra support as they transition after they are discharged from inpatient care or the emergency department.
Caring Contacts are validating messages sent to patients via text messages, postcards or letters to offer patients ongoing care and support without placing any demands (such as reminders to attend their next appointment). At Nationwide ...
About 10,000 chemistry presentations will happen in Denver soon
2024-08-13
WASHINGTON, Aug. 13, 2024 — The American Chemical Society (ACS) is hosting ACS Fall 2024, its virtual and in-person meeting, with the theme “Elevating Chemistry.” It will take place in Denver on Aug. 18-22.
About 10,000 presentations will feature cutting-edge developments on a range of scientific topics at ACS Fall 2024. Embargoed press releases and videos are available to members of the media on the EurekAlert! website. Reporters can also email newsroom@acs.org to request access to the embargoed content. View the ACS Fall 2024 schedule for a full list of in-person, hybrid ...
Protecting surf breaks mitigates climate change, helps coastal communities, analysis finds
2024-08-13
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Safeguarding places to hang ten and shoot the curl is an opportunity to simultaneously mitigate climate change, fuel tourism and help surrounding ecosystems, new research has shown.
“There is a growing conservation movement regarding coastal areas that host surf breaks,” said Jacob Bukoski of Oregon State University, one of the study’s co-authors. “Earlier research showed that surf breaks tend to be biodiversity hotspots, but no one had looked at the stocks of carbon held within these ecosystems – carbon that could drive climate change if ...
New species of extinct walrus-like mammal discovered in the North Atlantic
2024-08-13
A new discovery by a team of paleontologists, led by Dr. Mathieu Boisville (University of Tsukuba, Japan), has uncovered a new species of the extinct genus Ontocetus from the Lower Pleistocene deposits in the North Atlantic. This species, named Ontocetus posti, displays surprising similarities in feeding adaptations to the modern walrus (Odobenus rosmarus), highlighting an intriguing case of convergent evolution. The research is published in the open access journal PeerJ Life & Environment.
The fossils ...
Empowering women – a key to both sustainable energy and gender justice
2024-08-13
Involving women in implementing solar energy technologies in developing countries not only has great climate impact. A new study published in Nature Energy and carried out by researchers from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, shows that empowering women through energy care work can change unjust, gendered norms and long-lived injustices.
Unlike going from fossil to renewable fuels within the transport sector, transitioning to renewable energy for electricity production is often done at the local level due to decentralised energy providers. Around the world, there are community-led programmes that provide solar, wind and hydro power, as alternative, greener energy sources. ...
Delivery robots’ green credentials make them more attractive to consumers
2024-08-13
PULLMAN, Wash. – The smaller carbon footprint, or wheel print, of automatic delivery robots can encourage consumers to use them when ordering food, according to a Washington State University study.
The suitcase-sized, self-driving electric vehicles are much greener than many traditional food delivery methods because they have low, or even zero, carbon emissions. In this study, participants who had more environmental awareness and knowledge about carbon emissions were more likely to choose the robots as ...
Mayo Clinic offers new innovative therapy to treat atrial fibrillation
2024-08-13
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Cardiologists in Mayo Clinic's Heart Rhythm Clinic are using a new innovative energy source to safely and successfully treat a common type of heart arrhythmia. The therapy, called pulsed field ablation (PFA), has received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval and represents a significant milestone in treating atrial fibrillation (AFib).
The irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm of AFib can lead to blood clots in the heart, increasing a patient's risk of stroke. Clinicians can use medication and therapies to help reset the heart rhythm, but some patients have AFib that ...
Changing food consumers' choices may help cut greenhouse gases
2024-08-13
Planet-warming greenhouse gas emissions associated with the global food supply chains induced by diets could fall by 17% if people change their food choices towards more plant-based diets, a new study reveals.
Researchers believe that a currently over-consuming 56.9% of the global population would save 32.4% of global dietary emissions by changing their diet to the planetary health diet proposed by the EAT-Lancet Commission.
Publishing their findings today (13 Aug) in Nature Climate Change, an international group of researchers note that a diet switch to the planetary health diet would balance the ...
Significant link found between heme iron, found in red meat and other animal products, and type 2 diabetes risk
2024-08-13
Key points:
Researchers identified a significant link between heme iron—iron found in red meat and other animal products —and risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D), as well as the metabolic pathways underlying the link.
Non-heme iron—iron found in plant-based foods—was not associated with risk of T2D.
The study suggests that cutting down on heme iron from red meat and adopting a plant-rich diet can help lower diabetes risk. And it raises concerns about the addition of heme to increasingly popular plant-based meat alternatives.
Boston, MA—Higher intake ...
Older adults’ life satisfaction varies by immigrant status, living arrangement and social disposition
2024-08-13
TORONTO, ON – Do older adults who live alone feel less satisfied with their lives? A new analysis of about 12,000 respondents aged 65 and older reveals that what matters for Canadian older adults’ life satisfaction is not living alone per se. Rather personality-based social dispositions play a key role in how older adults feel about living alone. In addition, the role these dispositions play tend to differ between Canadian-born and immigrant older adults.
The researchers found that despite the existence ...
Say ‘aah’ and get a diagnosis on the spot: is this the future of health?
2024-08-13
A computer algorithm has achieved a 98% accuracy in predicting different diseases by analysing the colour of the human tongue.
The proposed imaging system developed by Iraqi and Australian researchers can diagnose diabetes, stroke, anaemia, asthma, liver and gallbladder conditions, COVID-19, and a range of vascular and gastrointestinal issues.
Engineering researchers from Middle Technical University (MTU) and the University of South Australia (UniSA) achieved the breakthrough in a series of experiments where they used 5260 images to train machine learning algorithms to detect tongue colour.
Two ...
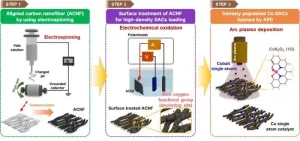
Rapid removal of emerging endocrine disruptors in wastewater using high-performance single-atom catalysts
2024-08-13
Bisphenols are widely used as the main raw material for plastics such as receipts, water bottles, water containers, and vinyl due to their heat-resistant and mechanochemical properties. Among bisphenols, bisphenol A (BPA) that we often refer to as an "endocrine-disrupting chemicals" has been linked to adverse effects on reproduction, development, intelligence, and various metabolic diseases. Bisphenol F (BPF), a recently developed alternative to BPA Bisphenol A has also been reported in the literature to cause neurological disruption and various health risks.
Dr. Jong Min Kim of the Materials Architecturing ...
[1] ... [992]
[993]
[994]
[995]
[996]
[997]
[998]
[999]
1000
[1001]
[1002]
[1003]
[1004]
[1005]
[1006]
[1007]
[1008]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.