SwRI-led eclipse projects shed new light on solar corona
2024-04-22
SAN ANTONIO — April 22, 2024 —Teams led by Southwest Research Institute successfully executed two groundbreaking experiments — by land and air — collecting unique solar data from the total eclipse that cast a shadow from Texas to Maine on April 8, 2024. The Citizen Continental-America Telescopic Eclipse (CATE) 2024 experiment engaged more than 200 community participants in a broad, approachable and inclusive attempt to make a continuous 60-minute high-resolution movie of this exciting event. A nearly simultaneous investigation used unique equipment installed in NASA’s WB-57F research aircraft to chase the ...
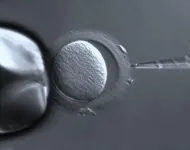
Analyzing the impact of ovulation-inducing agents on the quality of embryo
2024-04-22
Low birth rates have become a serious problem in many developed countries throughout the world, with Japan being a prime example. In Japan particularly, aging and stress have led to a massive rise in infertility, which now affects one in every 4.4 couples. To find a workaround this condition, many couples have now turned to assisted reproduction technologies (ARTs) and in vitro fertilization (IVF) for conception. However, even though ARTs and IVF methods are well-established and have been widely used for over four decades, birth rates post IVF in Japan are still critically low, peaking at a meager 10.2%.
One of the reasons ...
Prognostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma based on serine and glycine metabolism-related genes
2024-04-22
Background and Aims
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy have emerged as treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in recent years. The significance of serine and glycine metabolism in various cancers is widely acknowledged. This study aims to investigate their correlation with the prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) of HCC.
Methods
Based on the public database, different subtypes were identified by cluster analysis, and the prognostic model was constructed through regression analysis. The gene expression omnibus (GEO) data set was used as the ...
In psychedelic therapy, clinician-patient bond may matter most
2024-04-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Drug effects have dominated the national conversation about psychedelics for medical treatment, but a new study suggests that when it comes to reducing depression with psychedelic-assisted therapy, what matters most is a strong relationship between the therapist and study participant.
Researchers analyzed data from a 2021 clinical trial that found psilocybin (magic mushrooms) combined with psychotherapy in adults was effective at treating major depressive disorder.
Data included depression outcomes and participant reports about their experiences ...
Family learning environments in Scandinavia: dimensions, types and socioeconomic profiles
2024-04-22
Do children have regular bedtimes and do parents enforce strict screen time policies? And do parents take their children to museums so that they can learn from an early age? Or is everyday life more about having fun together, without clear rules and any ambition to ‘develop’ children in any particular way?
Family life can be lived in many different ways, and what children bring with them from the home environment has a substantial impact on their opportunities and development later in life.
A new study from the Department of Sociology, University of Copenhagen, and VIVE - The Danish Center for Social Science Research ...
People think 'old age' starts later than it used to, study finds
2024-04-22
Middle-aged and older adults believe that old age begins later in life than their peers did decades ago, according to a study published by the American Psychological Association.
“Life expectancy has increased, which might contribute to a later perceived onset of old age. Also, some aspects of health have improved over time, so that people of a certain age who were regarded as old in the past may no longer be considered old nowadays,” said study author Markus Wettstein, PhD, of Humboldt University in Berlin, Germany.
However, the study, which was published in the journal Psychology and Aging, also found evidence that the trend of later perceived old age has slowed ...
Afib more common and dangerous in younger people than previously thought
2024-04-22
PITTSBURGH, April 22, 2024 – Atrial fibrillation (Afib), a common type of arrhythmia that is on the rise in people under the age of 65, is more dangerous in this increasingly younger population than previously thought, according to a new study published today in Circulation Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology and authored by physician-scientists at the UPMC Heart and Vascular Institute.
The study, which is among the first to examine a large group of Afib patients younger than 65 in the U.S., found that these younger patients were more likely to be hospitalized for heart failure, stroke or heart ...
To accelerate biosphere science, reconnect three scientific cultures
2024-04-22
Researchers who study Earth’s biosphere tend to operate from one of three scientific cultures, each with distinct ways of conducting science, and which have been operating mostly independently from one another, find the authors of a Perspective published in PNAS on April 19, 2024. SFI Professors Christopher Kempes and Geoffrey West, together with External Professor Brian Enquist (University of Arizona) identify and explain the three cultures, and suggest that reconnecting them could help accelerate ...
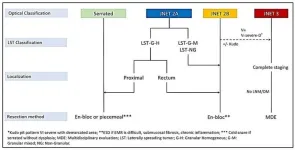
Endoscopic techniques for removing large colorectal polyps
2024-04-22
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second most common cancer in the United States. This highlights the importance of early detection and treatment of precancerous lesions like large polyps. Endoscopy offers a minimally invasive approach to removing these polyps, reducing the need for traditional surgery.
This review, published in eGastroenterology, explores advancements in endoscopic resection techniques, specifically Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) and Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD).
Complete removal of large polyps (>10 mm) is crucial to prevent progression to CRC. Piecemeal resection during endoscopic procedures can increase the risk ...
Speech Accessibility Project now sharing recordings, data
2024-04-22
The Speech Accessibility Project, which aims to make automatic speech recognition technology more accessible to people with speech differences and disabilities, is now sharing some of its voice recordings and related data with universities, nonprofits and companies.
The project team is accepting signed data use agreements and one-page proposals for 211 recordings of people with Parkinson’s. The download also includes text of the original speech prompts and a transcript of the participants’ responses. A subset includes annotations ...
Scientists in Missouri, Virginia receive pediatric heart transplantation research grants
2024-04-22
DALLAS, April 22, 2024 — Scientific researchers in Missouri and Virginia have been awarded nearly $1.4 million each in grants to study ways to extend the life expectancy and improve the quality of life for children with a transplanted heart. These two research awards mark the latest round of funding for a joint $3 million scientific research initiative between the American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, and Enduring Hearts, the only non-profit organization solely dedicated ...
Same species, different sizes: rare evolution in action spotted in island bats
2024-04-22
A University of Melbourne researcher has spotted a rare evolutionary phenomenon happening rapidly in real time in bats living in the Solomon Islands.
Dr Tyrone Lavery reports in a paper published in Evolution that two groups of leaf-nosed bats with vastly different body sizes that were thought to be separate species are an example of a rare type of parallel evolution. Parallel evolution is when different populations living in similar environments evolve similar features independently.
The smaller bat, Hipposideros diadema, is found across its six main islands and many smaller islands. It is ...
New technology uncovers mechanism affecting generation of new COVID variants
2024-04-22
The SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID has the unsettling ability of often generating variants of itself. Other viruses also mutate, but as SARS-CoV-2 quickly spread throughout the entire human population during the pandemic, killing millions, the virus’ dynamic evolution posed a serious problem: it repeatedly challenged our bodies’ immune response fighting the virus and hindered the process of getting updated vaccines ready.
Understanding the genetic mechanism fueling SARS-CoV-2’s ability to generate variants can go a long way in keeping COVID at bay. In this study published in Nature Microbiology, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions developed ...
Planning at multiple scales for healthy corals and communities
2024-04-22
Governments in the Mesoamerican Reef region are exploring the use of nature-based solutions to strengthen coral health and societal benefits for coastal communities. A new study led by Stanford researchers in collaboration with scientists from the World Wildlife Fund, the Healthy Reefs Initiative, and others from the Smart Coasts project quantified the outcomes of different watershed interventions to support coral health at regional versus national scales, and identified target areas that could improve both ecosystem and societal benefits nationally and across the region.
The nature-based approaches evaluated as key ...
U of T researchers map protein network dynamics during cell division
2024-04-22
An international team led by researchers at the University of Toronto has mapped the movement of proteins encoded by the yeast genome throughout its cell cycle. This is the first time that all the proteins of an organism have been tracked across the cell cycle, which required a combination of deep learning and high-throughput microscopy.
The team applied two convolutional neural networks, or algorithms, called DeepLoc and CycleNet, to analyze images of millions of live yeast cells. The result was a comprehensive map identifying where proteins are located and how they move and change in abundance ...
Pressure in the womb may influence facial development
2024-04-22
Physical cues in the womb, and not just genetics, influence the normal development of neural crest cells, the embryonic stem cells that form facial features, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study published in Nature Cell Biology found that an increase in hydrostatic pressure sensed by the embryo can hinder the healthy development of facial features in mouse and frog embryos and in human embryoids (cell structures grown in the lab from human stem cells), suggesting that differences in pressure might affect the risk of facial malformations.
The ...
AI weather forecasts captured Ciaran’s destructive path
2024-04-22
Artificial intelligence (AI) can quickly and accurately predict the path and intensity of major storms, a new study has demonstrated.
The research, based on an analysis of November 2023’s Storm Ciaran, suggests weather forecasts that use machine learning can produce predictions of similar accuracy to traditional forecasts faster, cheaper, and using less computational power.
Published in npj Climate and Atmospheric Science, the University of Reading study highlights the rapid progress and transformative potential of AI in weather prediction.
Professor Andrew Charlton-Perez, ...
Feedback loop that is melting ice shelves in West Antarctica revealed
2024-04-22
Feedback loop that is melting ice shelves in West Antarctica revealed
New research has uncovered a feedback loop that may be accelerating the melting of the floating portions of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, pushing up global sea levels.
The study, published in Science Advances, sheds new light on the mechanisms driving the melting of ice shelves beneath the surface of the ocean, which have been unclear until now.
The West Antarctic Ice Sheet has been losing mass in recent decades, contributing to global sea level rise. If it were to melt entirely, global sea levels would rise by around five meters.
It’s known that Circumpolar Deep Water (CDW), ...
How does aspirin help prevent colorectal cancer development and progression?
2024-04-22
Long-term daily use of aspirin can help to prevent the development and progression of colorectal cancer, but the mechanisms involved have been unclear. New research has revealed that aspirin may exert these protective effects by boosting certain aspects of the body’s immune response against cancer cells. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
To investigate the effects of aspirin (a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) on colorectal cancer, investigators in Italy obtained tissue samples from 238 patients who underwent surgery for colorectal cancer in 2015–2019, 12% of whom were aspirin ...
3 in 5 parents play short order cook for young children who don’t like family meal
2024-04-22
While most parents of preschool and elementary aged children strive to give their children a balanced, nutritional diet, some of their strategies to promote healthy eating may backfire, a national poll suggests.
A top example from the report: Three in five parents customize meals if their child doesn’t like what everyone else is eating.
Meanwhile, one in eight parents require children to eat everything on their plate, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health. And while just one in three believe the standard American diet is healthy for kids, few have tried alternative, potentially more nutritional ...
Japan’s premodern concept of nature at root of distinctive mindset in early childhood education
2024-04-22
Osaka, Japan — Observers of Japanese early childhood education and care have pointed to the mindset of educators watching over and waiting on preschoolers as being an intriguing tendency. This mimamoru approach has its roots in a premodern concept of nature, according to Professor Yosuke Hirota at the Graduate School of Literature and Human Sciences of Osaka Metropolitan University.
Professor Hirota looked into the works of Sozo Kurahashi (1882-1955) and Kitaro Nishida (1870-1945) to see how this concept of nature from the past made its way into education in the present day. Kurahashi’s writing on ...
First Nations patients leave ED without completing treatment more than comparable non–First Nations patients
2024-04-22
First Nations patients in Alberta leave emergency departments (EDs) without completing treatment more often than comparable non–First Nations patients, due in part to anti-Indigenous racism expressed by providers, found new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231019.
Higher proportions of incomplete ED care for First Nations patients compared with non–First Nations patients occurred even in cases of serious diagnosis, and were found across all parts of Alberta. Provincially, 6.8% of First Nations visits end without completing ...
What do you know about measles and vaccination?
2024-04-22
With measles cases rising in Canada and internationally, it is important for clinicians to understand the disease and the role of vaccination against measles. Two practice articles in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240415 https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240371
provide succinct overviews of this highly infectious disease. Many clinicians may not have direct experience with measles diagnosis and treatment as Canada achieved measles elimination status in 1998.
“The increase in measles activity globally and in Canada is a reminder of the importance of immunization. ...
Giant galactic explosion exposes galaxy pollution in action
2024-04-22
A team of international researchers studied galaxy NGC 4383, in the nearby Virgo cluster, revealing a gas outflow so large that it would take 20,000 years for light to travel from one side to the other.
The discovery was published today in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Lead author Dr Adam Watts, from The University of Western Australia node at the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR), said the outflow was the result of powerful stellar explosions in the central regions of the galaxy that could eject enormous amounts of hydrogen and heavier elements.
The ...
Understanding ‘how’ pupils learn is key to tackling wandering focus in a digital age
2024-04-22
School attendance figures are dwindling, there are more pupils than ever before needing additional support, and a demanding legion of exams – all of which mean pupils are struggling to learn, an education expert has warned.
But, he suggests, with a renewed focus on the techniques of learning, pupils can be guided to success.
In a difficult environment for teachers, it is clear they need support. Failure might be inevitable in a classroom, former teacher Alex Quigley argues, but if teachers can understand why learning has failed, they can address ...
[1] ... [1227]
[1228]
[1229]
[1230]
[1231]
[1232]
[1233]
[1234]
1235
[1236]
[1237]
[1238]
[1239]
[1240]
[1241]
[1242]
[1243]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.