Higher BMI is significantly associated with worse mental health, especially in women, per study of middle-aged and older adults which adjusted for lifestyle and demographic factors
2024-03-06
Higher BMI is significantly associated with worse mental health, especially in women, per study of middle-aged and older adults which adjusted for lifestyle and demographic factors
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299029
Article Title: Associations between adiposity measures and depression and well-being scores: A cross-sectional analysis of middle- to older-aged adults
Author Countries: Ireland
Funding: This research was funded by the Irish Health Research Board, grant number: HRC/2007/13. The funder had no role in the ...
This injectable hydrogel mitigates damage to the right ventricle of the heart
2024-03-06
An injectable hydrogel can mitigate damage to the right ventricle of the heart with chronic pressure overload, according to a new study published March 6 in Journal of the American College of Cardiology: Basic to Translational Science.
The study, by a research team from the University of California San Diego, Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University, was conducted in rodents. In 2019, this same hydrogel was shown to be safe in humans through an FDA-approved Phase 1 trial in people who suffered a heart attack. As a result of the new preclinical ...
Giant dinosaur was “heron from hell,” not a deep diver, says new analysis
2024-03-06
For years, controversy has swirled around how a Cretaceous-era, sail-backed dinosaur—the giant Spinosaurus aegyptiacus—hunted its prey. Spinosaurus was among the largest predators ever to prowl the Earth and one of the most adapted to water, but was it an aquatic denizen of the seas, diving deep to chase down its meals, or a semiaquatic wader that snatched prey from the shallows close to shore?
A new analysis led by paleontologists from the University of Chicago reexamines the density ...
New deep-sea worm discovered at methane seep off Costa Rica
2024-03-06
Greg Rouse, a marine biologist at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography, and other researchers have discovered a new species of deep-sea worm living near a methane seep some 50 kilometers (30 miles) off the Pacific coast of Costa Rica. Rouse, curator of the Scripps Benthic Invertebrate Collection, co-authored a study describing the new species in the journal PLOS ONE that was published on March 6.
The worm, named Pectinereis strickrotti, has an elongated body that is flanked by a row of feathery, gill-tipped appendages called ...
Nanosurgical tool could be key to cancer breakthrough
2024-03-06
The high-tech double-barrel nanopipette, developed by University of Leeds scientists, and applied to the global medical challenge of cancer, has - for the first time - enabled researchers to see how individual living cancer cells react to treatment and change over time – providing vital understanding that could help doctors develop more effective cancer medication.
The tool has two nanoscopic needles, meaning it can simultaneously inject and extract a sample from the same cell, expanding its potential uses. And the platform’s high level of semi-automation has sped ...
Genetic mutation in a quarter of all Labradors hard-wires them for obesity
2024-03-06
New research finds around a quarter of Labrador retriever dogs face a double-whammy of feeling hungry all the time and burning fewer calories due to a genetic mutation.
This obesity-driving combination means that dog owners must be particularly strict with feeding and exercising their Labradors to keep them slim.
The mutation is in a gene called POMC, which plays a critical role in hunger and energy use.
Around 25% of Labradors and 66% of flatcoated retriever dogs have the POMC mutation, which researchers previously showed causes increased interest in food ...
MIT scientists use a new type of nanoparticle to make vaccines more powerful
2024-03-06
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Many vaccines, including vaccines for hepatitis B and whooping cough, consist of fragments of viral or bacterial proteins. These vaccines often include other molecules called adjuvants, which help to boost the immune system’s response to the protein.
Most of these adjuvants consist of aluminum salts or other molecules that provoke a nonspecific immune response. A team of MIT researchers has now shown that a type of nanoparticle called a metal organic framework (MOF) can also provoke a strong immune response, by activating the innate immune system — the body’s first line of defense against ...
A noninvasive treatment for “chemo brain”
2024-03-06
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Patients undergoing chemotherapy often experience cognitive effects such as memory impairment and difficulty concentrating — a condition commonly known as “chemo brain.”
MIT researchers have now shown that a noninvasive treatment that stimulates gamma frequency brain waves may hold promise for treating chemo brain. In a study of mice, they found that daily exposure to light and sound with a frequency of 40 hertz protected brain cells from chemotherapy-induced damage. The treatment also helped to prevent memory loss and impairment of other ...
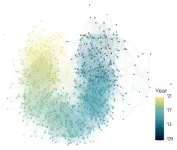
Film festivals are becoming more diverse in several ways, new study reports
2024-03-06
A group of Tallinn University researchers has published an innovative study that sheds light on the intricate dynamics of the global film festival circuit, revealing insights into diversity and public value creation within the industry. The research demonstrates that festival programming has become more thematically diverse, and the inclusion of films by women creatives has increased between 2012–2021.
The study “Quantifying the global film festival circuit: Networks, diversity, and public value creation,” published open access in the PLOS ONE journal, provides a comprehensive analysis of over 600 film festivals worldwide, spanning a period ...
New hydrogen producing method is simpler and safer
2024-03-06
Researchers in Sweden unveiled a new concept for producing hydrogen energy more efficiently, splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen without the dangerous risk of mixing the two gases.
Developed at KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, the new method decouples the standard electrolysis process for producing hydrogen gas, which splits water molecules by applying an electric current. In contrast with prevailing systems it produces the resulting oxygen and hydrogen gases separately rather than simultaneously in the same cell, where they need to be separated by membrane barriers
That separation eliminates the possibility of the gases mixing with the risk of explosions, says ...
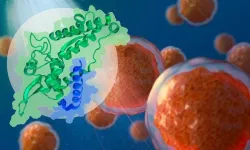
Studying the relationship between cancer-promoting proteins
2024-03-06
By Simonne Griffith-Jones, Predoctoral Fellow, EMBL Grenoble
Researchers from the Bhogaraju Group at EMBL Grenoble have gained new insights into how a cancer-relevant family of proteins bind their targets. The results of the study, published in The EMBO Journal, could potentially help in the development of drugs against certain chemotherapy- and radiotherapy-resistant cancers.
The Melanoma Antigen Gene (MAGE) family consists of more than 40 proteins in humans, most of which are only present in the ...
UTA educating schoolchildren about solar eclipse
2024-03-06
The University of Texas at Arlington has received a grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to support educational activities related to the upcoming eclipse.
UTA faculty and graduate students are visiting elementary, middle and high schools in the DFW area in March to give talks to about 4,000 students explaining the natural phenomena occurring during the eclipse and the physics behind it. UTA will also provide special eclipse glasses for students to use to avoid eye damage.
The $50,000 grant will also provide for about 1,500 students to take field trips to the UTA Planetarium, one of the three largest in Texas, to learn ...
Espresso yourself: Wearable tech measures emotional responses to coffee
2024-03-06
Researchers in Italy have introduced a novel approach for assessing the quality of coffee. In a pioneering new study, they have demonstrated the feasibility of using wearable technology to measure the emotional responses of coffee experts during tastings.
Published in SCI’s Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, the study provides an innovative solution for reducing judgement biases that can result from traditional and more subjective methods of coffee quality assessment.
Coffee is one of the most popular and widely consumed beverages in the world, ...
What drives ‘drug-induced homicide’ prosecutions in North Carolina?
2024-03-06
A new study finds that prosecutors in North Carolina believe “drug-induced homicide” (DIH) laws are effective at both reducing drug overdoses in a community and curtailing the distribution of illicit drugs. These beliefs are worth noting because there is no evidence to support them, while there is evidence that DIH prosecutions make people in affected communities less likely to call 911 – and may actually increase the number of overdoses in a community.
DIH laws, also called “death by distribution” or “delivery resulting in death” laws, ...
Psychosocial stressors linked to higher inflammation in Black pregnant women
2024-03-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Living in neighborhoods with more white residents and greater lifetime experiences of racial discrimination are linked to increased systemic inflammation during pregnancy among Black women, according to new research led by a team from Penn State. The study, published in the February issue of the journal Brain, Behavior, & Immunity – Health, found that these social-environmental factors were associated with higher levels of a protein that has been connected to chronic stress and an elevated risk of ...
Amyloid blood levels associated with brain changes in Alzheimer's study
2024-03-06
New research published today suggests there is a link between abnormal blood levels of amyloid — a protein associated with Alzheimer’s disease — and subtle changes in brain microstructures on a type of MRI, findings that could lead to a new way to detect Alzheimer’s earlier in people with no clinical signs.
Researchers analyzed the results of 128 human participants with and without dementia from the 1Florida Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center who underwent imaging scans using an established diagnostic tool called positron emission tomography, or PET, which can detect amyloid plaques in the brain, a hallmark ...
Linkage case management and posthospitalization outcomes in people with HIV
2024-03-06
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial that involved 500 hospitalized people with HIV, a linkage case management intervention did not reduce 12-month mortality outcomes. These findings may help inform decisions about the potential role of linkage case management among hospitalized people with HIV.
Authors: Robert N. Peck, M.D., Ph.D., of Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.2177)
Editor’s ...
Study quantifies dramatic rise in school shootings and related fatalities since 1970
2024-03-06
Key Takeaways
Incidence of school shootings increasing dramatically: In the 53 years leading up to May 2022, the number of school shootings annually increased more than 12 times.
Children more likely to be victims. The likelihood of children being school shooting victims has increased more than fourfold, and the rate of death from school shootings has risen more than sixfold.
A total of 2,056 school shooting incidents were analyzed: The incidents involved 3,083 victims, including 2,033 children ages 5-17 years, and 1,050 adults ages 18-74 years.
CHICAGO: The ...
New microscopy tech answers fundamental questions
2024-03-06
The mammalian brain is a web of densely interconnected neurons, yet one of the mysteries in neuroscience is how tools that capture relatively few components of brain activity have allowed scientists to predict behavior in mice. It is hard to believe that much of the brain’s complexity is irrelevant background noise. “We wondered why such a redundant and metabolically costly scheme would have evolved,” says Rockefeller’s Alipasha Vaziri.
Now, a new study in Neuron—which presents an unprecedented simultaneous recording of the activity of one million neurons in mice—offers a surprising answer to this fundamental question: technological limitations ...
Moffitt’s Dr. Tiffany Carson joins Global Cancer Grand Challenges team to tackle cancer inequities
2024-03-06
TAMPA, Fla. — An international interdisciplinary team of researchers, including Moffitt Cancer Center’s Tiffany Carson, Ph.D., has been selected to receive a Cancer Grand Challenges award. Co-founded by the National Cancer Institute and Cancer Research UK, Cancer Grand Challenges supports a community of diverse, global teams to come together, think differently and take on some of cancer’s toughest challenges.
Carson is part of the SAMBAI (Societal, Ancestry, Molecular and Biological Analyses of Inequalities) team led by Melissa Davis, Ph.D., from Morehouse School of Medicine. The team will receive up to $25 million over the next five ...
Cancer Grand Challenges selects five new global, interdisciplinary teams to take on four challenges
2024-03-06
Cancer Grand Challenges has selected five new global research teams that will address the following challenges in cancer: reducing cancer inequities, understanding the mechanisms of early-onset cancers, developing drugs for solid tumors in children, and broadening our knowledge about how T cells recognize cancer cells. The winning teams were announced at the Cancer Grand Challenges Summit on March 6, 2024, in London.
Cancer Grand Challenges is a global funding initiative cofounded in 2020 by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), ...
25 million US dollars for International Cancer Research
2024-03-06
The team is co-led by Martin Eilers, Chair of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the University of Würzburg (JMU). “Our research project is called KOODAC,” he explains. “That stands for ‘Knocking-Out Oncogenic Drivers and Curing Childhood Cancer’”. Our goal is to develop well-tolerated drugs that can target and eliminate cancer cells in children.” The current standard of care for childhood cancer is chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which, even when successful, are associated with severe side effects. “These ...
3D reflector microchips could speed development of 6G wireless
2024-03-06
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have developed a semiconductor chip that will enable ever-smaller devices to operate at the higher frequencies needed for future 6G communication technology.
The next generation of wireless communication not only requires greater bandwidth at higher frequencies – it also needs a little extra time. The new chip adds a necessary time delay so signals sent across multiple arrays can align at a single point in space-- without disintegrating.
The team’s paper, ...
Adverse childhood experiences and adult mental health outcomes
2024-03-06
About The Study: The results of this study using twin data support an association between adverse childhood experiences and poor mental health in adulthood, notwithstanding evidence for familial confounding from shared genetic and environmental factors. These findings suggest that targeted interventions may be associated with reduced risks of future psychopathology.
Authors: Hilda Björk Daníelsdóttir, M.Sc., of the University of Iceland in Reykjavík, Iceland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Symptoms of cognitive impairment among children with atopic dermatitis
2024-03-06
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that pediatric atopic dermatitis (AD) was generally associated with greater odds of reported difficulties in learning and memory. However, this association was primarily limited to children with neurodevelopmental comorbidities, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder or learning disabilities. These results may improve the risk stratification of children with AD for cognitive impairments and suggest that evaluation for cognitive difficulties should be prioritized among children with AD and neurodevelopmental disorders.
Authors: Joy ...
[1] ... [1293]
[1294]
[1295]
[1296]
[1297]
[1298]
[1299]
[1300]
1301
[1302]
[1303]
[1304]
[1305]
[1306]
[1307]
[1308]
[1309]
... [8791]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.