Charge fractionalisation observed spectroscopically
2024-03-06
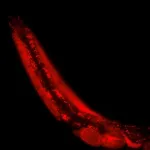
A research team led by the Paul Scherrer Institute has spectroscopically observed fractionalisation of electronic charge in an iron-based metallic ferromagnet. Experimental observation of the phenomenon is not only of fundamental importance. Since it appears in an alloy of common metals at accessible temperatures, it holds potential for future exploitation in electronic devices. The discovery is published in the journal Nature.
Basic quantum mechanics tells us that the fundamental unit of charge is unbreakable: the electron charge is quantised. Yet, we have come to understand that exceptions exist. In some situations, ...
Bee-2-Bee influencing: Bees master complex tasks through social interaction
2024-03-06
In a groundbreaking discovery, bumblebees have been shown to possess a previously unseen level of cognitive sophistication. A new study, published in Nature, reveals that these fuzzy pollinators can learn complex, multi-step tasks through social interaction, even if they cannot figure them out on their own. This challenges the long-held belief that such advanced social learning is unique to humans, and even hints at the presence of key elements of cumulative culture in these insects.
Led by Dr Alice Bridges and Professor Lars Chittka , the research team designed a two-step puzzle box requiring ...
New study may broaden the picture of the consequences of childhood adversity
2024-03-06
A research team has examined the link between adverse childhood experiences and the risk of mental health problems later in life, according to a study in JAMA Psychiatry. The researchers from Karolinska Institutet and University of Iceland have found that the risk of suffering from mental illness later in life among those experiencing significant adversity in childhood can be partly explained by factors shared by family members, such as genetics and environment.
Several previous studies have shown that people who have experienced ...
Revealing the evolutionary origin of genomic imprinting
2024-03-06
Some of our genes can be expressed or silenced depending on whether we inherited them from our mother or our father. The mechanism behind this phenomenon, known as genomic imprinting, is determined by DNA modifications during egg and sperm production. The Burga Lab at the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences uncovered a novel gene regulation process, associated with the silencing of selfish genes, that could represent the first step in the evolution of imprinting. Their discovery, reported in Nature, ...
Universal tool for tracking cell-to-cell interactions
2024-03-06
One of the fundamental goals of basic biology is understanding how diverse cell types work in concert to form tissues, organs, and organ systems. Recent efforts to catalog the different cell types in every tissue in our bodies are a step in the right direction, but only one piece of the puzzle. The great mystery of how those cells communicate with one another remains unsolved.
Now, a new paper in Nature describes uLIPSTIC, a tool capable of laying the groundwork for a dynamic map tracking the physical interactions between different cells—the elusive cellular interactome. The authors have been perfecting the technology since 2018 and the latest iteration ...
Synthetic DNA sheds light on mysterious difference between living cells at different points in evolution
2024-03-06
“Random DNA” is naturally active in the one-celled fungi yeast, while such DNA is turned off as its natural state in mammalian cells, despite their having a common ancestor a billion years ago and the same basic molecular machinery, a new study finds.
The new finding revolves around the process by which DNA genetic instructions are converted first into a related material called RNA and then into proteins that make up the body’s structures and signals. In yeast, mice, and humans, the first step in a gene’s expression, transcription, proceeds as DNA molecular “letters” (nucleobases) are read in one direction. While 80% of the human genome ...
AI can speed design of health software
2024-03-06
Artificial intelligence helped clinicians to accelerate the design of diabetes prevention software, a new study finds.
Publishing online March 6 in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, the study examined the capabilities of a form of artificial intelligence (AI) called generative AI or GenAI, which predicts likely options for the next word in any sentence based on how billions of people used words in context on the internet. A side effect of this next-word prediction is that the generative AI “chatbots” like chatGPT can generate replies to questions in realistic language, and produce clear summaries of complex texts.
Led ...
Shrinking technology, expanding horizons
2024-03-06
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and its collaborators have delivered a small but mighty advancement in timing technology: compact chips that seamlessly convert light into microwaves. This chip could improve GPS, the quality of phone and internet connections, the accuracy of radar and sensing systems, and other technologies that rely on high-precision timing and communication.
This technology reduces something known as timing jitter, which is small, random changes in the timing of microwave signals. Similar to when a musician is trying to keep a steady beat in music, the timing of these signals can sometimes waver a bit. The researchers ...
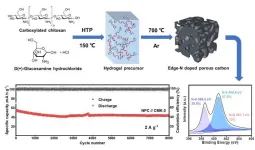
Edge-nitrogen doped porous carbon for energy-storage potassium-ion hybrid capacitors
2024-03-06
They published their work on March. 4th in Energy Material Advances, a Science Partner Journal (https://spj.science.org/journal/energymatadv).
"The development of cost-effective and high-performance electrochemical energy storage devices is imperative," said paper's corresponding author Wei Chen, a professor in the School of Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC). "Currently, lithium-ion batteries still dominate the market, but they are limited in both lithium as a resource and in their power densities."
Chen ...
Revolutionary elephant iPSC milestone reached in Colossal’s Woolly Mammoth Project
2024-03-06
Dallas, TX – March 06, 2024 - Colossal Biosciences (“Colossal”), the world’s first de-extinction company, announces today that their Woolly Mammoth team has achieved a global-first iPSC (induced pluripotent stem cells) breakthrough. This milestone advancement was one of the primary early goals of the mammoth project, and supports the feasibility of future multiplex ex utero mammoth gestation.
iPSC cells represent a single cell source that can propagate indefinitely and give rise to every other type of cell in a body. As such, the progress with elephant iPSCs extends far beyond ...
JAMA study finds facilities treating poor patients penalized by CMS payment model
2024-03-06
INDIANAPOLIS – A new study of more than 2,000 dialysis facilities randomized to a new Medicare payment model aimed to improve outcomes for patients with end-stage kidney disease has found that facilities that disproportionately serve populations with high social risk have lower use of home dialysis and transplant waitlisting and fewer kidney transplants. These facilities thus received reduced performance scores and reimbursement from Medicare.
A high proportion of non-Hispanic Blacks and of those initiating dialysis while uninsured or Medicaid-covered also was found to be an indicator of lower use of home dialysis and transplant waitlisting and fewer kidney ...
For Boston College professor, research into "high latitude" reaches of the seas led to improving accurate access to real-time ocean data
2024-03-06
Chestnut Hill, Mass (03/06/2024) – Boston College Assistant Professor of Earth and Environmental Sciences Hilary Palevsky has been awarded a nearly $1-million National Science Foundation CAREER Award for her work to make remote ocean monitoring data accessible and accurate in real time and produce a series of educational videos to guide students using the data.
Palevsky, whose research focuses on marine biogeochemistry and the mechanisms that enable the ocean to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, said the funding will allow her to build upon the work she has done to help scientists use the ...
Microbes impact coral bleaching susceptibility, new study shows
2024-03-06
Washington, D.C. – March 6, 2024 – A new study provides insights into the role of microbes and their interaction as drivers of interspecific differences in coral thermal bleaching. The study was published this week in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“The diversity, community dynamic and interaction of coral associated microorganisms play important roles in the health state and climate change response pattern of coral reefs,” said lead study author Biao ...
Study: Black boys are less likely to be identified for special education when matched with Black teachers
2024-03-06
WASHINGTON, March 6, 2024—Black male elementary school students matched to Black teachers are less likely to be identified for special education services, according to new research published today. The relationship is strongest for economically disadvantaged students. The study, by Cassandra Hart at the University of California, Davis, and Constance Lindsay at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill appeared in the American Educational Research Journal, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
The researchers also found that the connection is ...
A new genus of fungi on grasses
2024-03-06
While ecologically important, small mushrooms on monocots (grasses and sedges) are rarely studied and a lack of information about their habitat and DNA sequences creates difficulties in determining their presence or absence in ecological studies and their genetic relationships to other mushroom taxa.
This study led by Drs. Karen W. Hughes and Ronald H. Petersen (University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA) examined a mushroom species, Campanella subdendrophora, (also known as Tetrapyrgos subdendrophora), which fruits on grasses in the US Pacific Northwest.
The researchers evaluated its phylogenetic position concerning both Campanella and Tetrapyrgos ...
Allen Institute joins the Weill Neurohub
2024-03-06
SEATTLE, WASH.—March 6, 2024—The Allen Institute has officially become the newest member of the Weill Neurohub, a collaborative research network advancing treatments for neurological diseases.
Founded in 2003 by philanthropist Paul G. Allen, the Allen Institute focuses on big questions in biology through a team-based, open science approach, and currently has moonshot projects in neuroscience, cell biology, and immunology institutes.
The new partnership will integrate the Allen Institute’s expertise ...
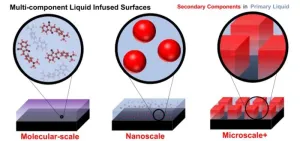
Revolutionizing surface technology: Introducing multi-component liquid-infused surfaces for adaptive and functional coatings
2024-03-06
Surface coatings have long been essential in various industries, offering protection and functionality. In recent years, liquid-infused surfaces (LIS) have emerged as a groundbreaking technology, revolutionizing how we approach surface coatings. In a review article recently published in Industrial Chemistry & Materials on Feb. 23, 2024, authors Zachary Applebee and Dr. Caitlin Howell explore a novel approach in surface technology that could significantly impact various industries, including healthcare and environmental conservation. A new frontier is emerging: multi-component ...
Nanodevices can produce energy from evaporating tap or seawater
2024-03-06
Evaporation is a natural process so ubiquitous that most of us take it for granted. In fact, roughly half of the solar energy that reaches the earth drives evaporative processes. Since 2017, researchers have been working to harness the energy potential of evaporation via the hydrovoltaic (HV) effect, which allows electricity to be harvested when fluid is passed over the charged surface of a nanoscale device. Evaporation establishes a continuous flow within nanochannels inside these devices, which act as passive pumping mechanisms. This effect is also seen in the microcapillaries of plants, where ...
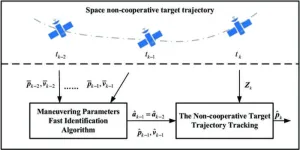
Scientist proposed a research on space noncooperative target trajectory tracking based on maneuvering parameter estimation
2024-03-06
Firstly, the authors briefly describe two models for tracking the maneuvering trajectories of non-cooperative space targets: the relative dynamics model and the indirect measurement model. In the relative dynamics model, tracking the maneuvering trajectory of the target is modeled as a problem of tracking the target's position over short discrete time intervals. On the other hand, the indirect measurement model transforms radar-derived values directly into measurements in the Local Vertical Local Horizontal (LVLH) coordinate system.
Next, the authors address the tracking problem of targets ...
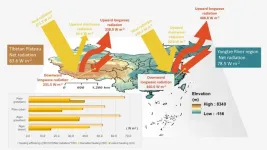
Scientists uncover comparable net radiation between the high-elevation Tibetan Plateau and the low-elevation Yangtze River region
2024-03-06
Land–atmosphere interactions play a crucial role in shaping Earth’s climate system, profoundly influencing weather patterns, climate variables, and ecological processes. Despite being located at similar latitude, the Tibetan Plateau (TP) and Yangtze River region (YRR) represent two distinct climate zones, garnering significant attention in this field. The former, situated in western China at an altitude exceeding 4000 m, is characterized by an arid climate, whereas the latter, located in the eastern Chinese plain, experiences a humid climate. Although both the TP and YRR have ...
Why some RNA drugs work better than others
2024-03-06
Spinal muscular atrophy, or SMA, is the leading genetic cause of infant death. Less than a decade ago, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Adrian Krainer showed this brutal disease can be treated by tweaking a process called RNA splicing. This breakthrough resulted in Spinraza, the first effective treatment for SMA. It also opened a new frontier in drug development. Now, CSHL research could push RNA-splicing drugs even further. CSHL Associate Professor Justin Kinney, Krainer, and postdoc Yuma Ishigami have ...
Scientists-CT scanned thousands of natural history specimens, which you can access for free
2024-03-06
Read the online version (Available 8:00 a.m. ET, March 6, 2024)
Watch the video (Embargoed. Do not distribute before 8:00 a.m. ET, March 6, 2024)
Natural history museums have entered a new stage of scientific discovery and accessibility with the completion of openVertebrate (oVert), a five-year collaborative project among 18 institutions to create 3D reconstructions of vertebrate specimens and make them freely available online.
Researchers published a summary of the project in the journal BioScience in which they review the specimens that have been scanned to date and offer a glimpse of how the data might be used to ask new questions ...
INFUSE workshop gives private and public fusion partners a chance to network and share experiences
2024-03-06
More than 120 people gathered for the 2024 Innovation Network for Fusion Energy (INFUSE) Workshop at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) from Feb. 27-28.
The event, which was sponsored by the DOE’s Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES), is a part of the INFUSE awards program that funds laboratories or universities so they can partner with private sector companies working on the science and technology ...
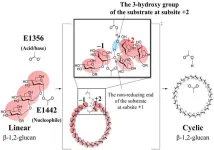
Uncovering the cyclization mechanism of cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase
2024-03-06
The polysaccharide β-1,2-glucan consists of repeating units of glucose linked together by β-1,2-glycosidic bonds. Cyclic β-1,2-glucans (CβGs) occur in different bacterial species and have a role in bacterial infections and symbiotic relationships. CβG biosynthesis is catalyzed by cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase (CGS), an enzyme that catalyzes the cyclization (closed ring formation) of linear β-1,2-glucan (LβG).
Since the method for large-scale enzymatic synthesis of linear β-1,2-glucan has already been established, combining it with this enzyme is technically feasible for efficient ...
Marine algae implants could boost crop yields
2024-03-06
Scientists have discovered the gene that enables marine algae to make a unique type of chlorophyll. They successfully implanted this gene in a land plant, paving the way for better crop yields on less land.
Finding the gene solves a long-standing mystery amongst scientists about the molecular pathways that allow the algae to manufacture this chlorophyll and survive.
“Marine algae produce half of all the oxygen we breathe, even more than plants on land. And they feed huge food webs, fish that get eaten by mammals and humans,” said UC Riverside ...
[1] ... [1294]
[1295]
[1296]
[1297]
[1298]
[1299]
[1300]
[1301]
1302
[1303]
[1304]
[1305]
[1306]
[1307]
[1308]
[1309]
[1310]
... [8791]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.