Researchers identify distinct sleep types and their impact on long-term health
2024-03-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Poor sleep habits are strongly associated with long-term chronic health conditions, according to decades of research. To better understand this relationship, a team led by researchers in Penn State’s College of Health and Human Development identified four distinct patterns that characterize how most people sleep. These patterns are also predictive of long-term health, the researchers said.
Soomi Lee, associate professor of human development and family studies at Penn State, ...
City of Hope to present new research at the American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2024, highlighting promising data on prostate, colorectal and pancreatic cancer
2024-03-12
This year, City of Hope doctors and scientists will also present data during AACR’s Press Program and a clinical trials plenary session:
Monday, April 8, 2024, at 8:30 a.m.
Research by Ajay Goel, Ph.D., M.S., City of Hope professor and chair, Department of Molecular Diagnostics and Experimental Therapeutics, and Caiming Xu, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in Goel’s lab, will be presented at an AACR press conference. The abstract is titled “An exosome-based liquid biopsy for non-invasive, early detection of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A multicenter ...
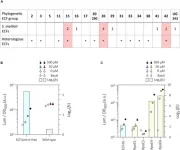
Exploring the transferability of extracytoplasmic function switches across bacterial species
2024-03-12
Extracytoplasmic function sigma factors (ECFs) have been successfully used for constructing predictable artificial gene circuits bacteria like Escherichia coli, but their transferability between species within the same phylum remained unknown. Now, a recent study by a group of researchers from Germany and Australia explored the bacteria Sinorhizobium meliloti and identified ECF switches with cross-species functionality, constructed genetic circuits, and provided a toolbox for universal synthetic biology applications.
In the field of synthetic biology, creating artificial gene circuits with predictable outcomes is both a challenge and a necessity. Extracytoplasmic function sigma factors ...
Cannabis use and its multifaceted impact on the genitourinary system: a scoping review of the literature
2024-03-12
Background and objectives
Cannabis is a commonly used recreational and therapeutic substance in our society. There are a variety of established physical, social, and mental health impacts associated with cannabis use. However, there is no overview of the impact cannabis use has on the genitourinary system. Thus, this scoping review aims to present data on the impact of cannabis on the genitourinary system.
Methods
A scoping review search was undertaken on Embase, Medline, and Web of Science. There were no date restrictions ...
SwRI develops off-road autonomous driving tools focused on camera vision
2024-03-12
SAN ANTONIO — March 12, 2024 — Southwest Research Institute has developed off-road autonomous driving tools with a focus on stealth for the military and agility for space and agriculture clients. The vision-based system pairs stereo cameras with novel algorithms, eliminating the need for lidar and active sensors.
“We reflected on the toughest machine vision challenges and then focused on achieving dense, robust modeling for off-road navigation,” said Abe Garza, a research engineer in SwRI’s Intelligent Systems Division.
Through internal research, SwRI engineers developed a suite of tools known as the Vision for Off-road Autonomy (VORA). The passive ...
Patients with obesity and kidney failure may be newly eligible for kidney transplants
2024-03-12
Key Takeaways
A collaborative study between bariatric and transplant teams has created a viable pathway for patients with obesity who also have end-stage renal disease to become eligible for kidney transplants through weight loss surgery.
Postoperative outcomes indicate significant improvements in BMI, hypertension, and diabetes management, enhancing patients’ overall health and transplant viability.
High drop-off rates emphasize the need for enhanced patient ...
Ultrablack coating could make next-gen telescopes even better
2024-03-12
WASHINGTON, March 12, 2024 – Sometimes, seeing clearly requires complete black. For astronomy and precision optics, coating devices in black paint can cut down on stray light, enhancing images and boosting performance. For the most advanced telescopes and optical systems, every little bit matters, so their manufacturers seek out the blackest blacks to coat them.
In the Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology and the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed an ultrablack thin-film coating for aerospace-grade magnesium alloys. Their coating absorbs 99.3% of light while being ...
Adolescent Δ8-THC and marijuana use in the US
2024-03-12
About The Study: The results of a nationally representative 2023 survey indicate that Δ8- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) use prevalence is appreciable among adolescents and is higher in states without marijuana legalization or existing Δ8-THC regulations. Prioritizing surveillance, policy, and public health efforts addressing adolescent Δ8-THC use may be warranted.
Authors: Adam M. Leventhal, Ph.D., of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.0865)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
ADHD pharmacotherapy and mortality in individuals with ADHD
2024-03-12
About The Study: In this observational, target trial emulation analysis that included 148,000 individuals diagnosed with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in Sweden, initial dispensation of ADHD medication was significantly associated with lower all-cause and unnatural-cause mortality, whereas the association with natural-cause mortality was not significant.
Authors: Zheng Chang, Ph.D., and Lin Li, Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, are the corresponding authors.
To ...
Mortality for time-sensitive conditions at urban vs rural hospitals during the pandemic
2024-03-12
About The Study: In this study of 3,813 hospitals, patient outcomes for time-sensitive conditions (acute myocardial infarction, hip fracture, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, pneumonia, sepsis, and stroke) were worse during the COVID-19 pandemic than before, with different magnitudes of change at urban versus rural hospitals. Mobilizing strategies tailored to the different needs of urban and rural hospitals may help reduce the likelihood of excess deaths during future public health crises.
Authors: H. Joanna Jiang, Ph.D., of the Agency ...
Sex-specific association of alcohol use disorder with suicide mortality
2024-03-12
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis yielded substantive evidence that alcohol use disorder was associated with suicide mortality and that the association was similar across the sexes. The findings underscore the importance of identifying and treating alcohol use disorder as part of a comprehensive suicide prevention strategy.
Authors: Shannon Lange, M.P.H., Ph.D., of the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health in Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.1941)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Delta-8-THC use reported by 11% of 12th graders in 2023
2024-03-12
Approximately 11% of 12th-grade students across the United States reported past-year use of delta-8- tetrahydrocannabinol (delta-8-THC, or delta-8 for short), according to an analysis of data from the 2023 Monitoring the Future survey, which is funded by the National Institutes of Health. Delta-8 is a psychoactive substance that is typically derived from hemp, a variety of the Cannabis sativa plant. Delta-8 has intoxicating effects similar to delta-9-THC (delta-9), the primary THC component responsible for the “high” people may experience from using ...
More than 11% of U.S. 12th graders used psychoactive delta-8-THC last year, study finds
2024-03-12
A new study suggests that delta-8-THC, an intoxicating substance typically made from hemp, is being used by a substantial number of young people across the United States and could potentially pose a significant public health risk.
Delta-8-THC products, which include gummies and vapes, look like marijuana products and have similar mood-altering effects. Delta-8 is often manufactured out of cannabidiol from hemp rather than marijuana, and there is no federal minimum age requirement to purchase delta-8 products. In various states, delta-8-THC is widely sold at gas stations or online, but rates of use among American youth have been unknown.
Now, researchers from ...
Health professionals and laypeople feel differently about allocating scarce lifesaving resources in a crisis
2024-03-12
The pandemic put a spotlight on the challenges that health systems face when deciding how to allocate scarce resources during a time of crisis. To better understand differing opinions on this issue, researchers at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and UC Health conducted a survey of laypeople and healthcare professionals, and found that while both groups have similar priorities for allocating medical resources, they are less aligned on how these priorities should be achieved.
“We did this study in response to concerns in the pandemic that we could run out of critical resources, such as mechanical ventilators, and that health systems ...
PNAS announces six 2023 Cozzarelli prize recipients
2024-03-12
WASHINGTON, DC – The Editorial Board of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) has selected six papers published by PNAS in 2023 to receive the Cozzarelli Prize, an award that recognizes outstanding contributions to the scientific disciplines represented by the National Academy of Sciences (NAS). Papers were chosen from more than 3,000 research articles that appeared in the journal last year and represent the six broadly defined classes under which the NAS is organized. Additionally, the Editorial Board has recognized ...
Association for Psychological Science announces new convention plan to foster global psychological research
2024-03-12
Washington, D.C. (March 12, 2024) — The Association for Psychological Science, the leading global organization dedicated to advancing scientific psychology for the benefit of science and society, is revamping its roster of regularly scheduled events to better foster global scientific collaboration and environmental sustainability.
Starting in 2025, APS will merge its Annual Convention and the biennial International Convention of Psychological Science (ICPS). The new APS Annual Convention will rotate outside of North America ...
Mount Sinai establishes Department of Public Health
2024-03-12
Watch the video announcement here.
New York, NY (March 12, 2024) – The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, fulfilling its commitment to connecting medical care with public health, today established a new Department of Public Health under the visionary leadership of Rosalind J. Wright, MD, MPH, the Horace W. Goldsmith Professor in Children’s Health Research at Icahn Mount Sinai.
The Department of Public Health will bridge the school’s existing excellence in environmental medicine, population health, global health, infectious disease, climate science, digital health, data science and artificial intelligence, community engagement, ...
Who benefits from direct-to-consumer pharmaceutical advertising?
2024-03-12
A new study co-authored by a University of Massachusetts Amherst economist reveals the value of government vaccine recommendations to drugmakers, as well as potential benefits of advertising pharmaceuticals directly to consumers — a practice that is banned in every country apart from the United States and New Zealand. The research is the most comprehensive investigation to date of manufacturer marketing and consumer response to adult vaccine recommendations.
After the U.S. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended in 2014 that people aged 65 and over receive the pneumococcal vaccine Prevnar 13, Medicare and private ...
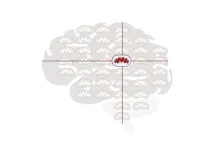
Discovery of a natural protective response in the brain could lead to treatments for concussions
2024-03-12
A team of Medical University of South Carolina researchers, led by Onder Albayram, Ph.D., reports in PNAS Nexus that they have discovered a novel protective response by which the brain naturally repairs itself after traumatic brain injury. Findings could lead to drug treatments that improve the brain’s ability to recover after concussions and prevent long-term brain disease.
“Brain recovery mechanisms are very, very powerful,” said Albayram. “We don’t always have to develop new treatment approaches. We can also just give the brain a chance to heal itself properly.”
Repetitive mild ...
Climate polices to reduce motor vehicle emissions can improve children’s health, save money
2024-03-12
A new study finds that policies to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from motor vehicles combined with investments in electric vehicles and public transportation would reduce air pollution and bring large benefits to children’s health. They would also save money.
The findings by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health with collaborators at the University of California, Los Angeles, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and the Boston University School of Public Health appear in the journal Environmental Research ...
Research finds a college degree remains a sound investment despite rising tuition
2024-03-12
A new analysis of 5.8 million Americans finds that earning a college degree is still a sound investment, although the rate of economic return varies across college majors and student demographics. The findings come as skepticism continues to grow over the value of a degree in the face of rising college costs, a decline in college enrollment, and a transforming economy.
The study was published today in American Educational Research Journal, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association. It was conducted by Liang Zhang from New York University, Xiangmin Liu from Rutgers University, and Yitong Hu from New York University.
The study estimated ...
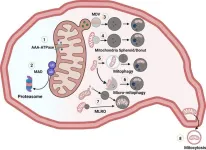
Understanding chronic liver disease through the powerhouse of the cells
2024-03-12
Scientists have identified a new organelle in liver cells called the mitochondria-lysosome-related organelle (MLRO). This discovery could improve our understanding of chronic liver diseases like alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD).
Mitochondria are essential components of cells, often called the "powerhouses" because they generate energy. They also play a crucial role in metabolism, calcium signalling, and cell survival. When mitochondria malfunction, it's linked to various liver diseases.
Cells have intricate mechanisms to maintain healthy mitochondria. One way is to ...
Outstanding achievements of UNIST students at the 30th Samsung Humantech Paper Award ceremony!
2024-03-12
Four exceptional UNIST students were honored for their outstanding academic and research achievements at the prestigious 30th Annual Samsung Humantech Paper Award ceremony.
Among the many eminent individuals, JungSoo Lee (Advisor: Professor Han Gi Chae) from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering notched the highest score and won the Gold Prize within the category of Energy & Environment. His groundbreaking research on enhancing the efficiency of thermoelectric power generation through the development of a new power generation device structure technology earned him this accolade. By focusing on optimizing the structure ...
Increasing disability employment could boost national economy by billions
2024-03-12
-- There is a widening employment gap between people with and without disability --
-- In 2022, only 53.1 per cent of people with work-limiting disability were employed, compared to 81.8 per cent of people without disability --
-- People with disability are 25-30 percentage points less likely to be employed --
-- Over a quarter of people with disability cite transport as a barrier to finding work --
A new report by the Bankwest Curtin Economics Centre at Curtin University reveals that there has been no improvement in employment rates for people with disability ...
Novel risk score for cardiovascular complications after bone marrow transplant
2024-03-12
For thousands of Americans each year, a bone marrow transplant has the potential to cure diseases such as leukemias, lymphomas and immune deficiency disorders. While lifesaving, bone marrow transplants are taxing procedures that can affect various organs, including the cardiovascular system.
With advances in medical science and improvement in protocols, more bone marrow transplants, also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, are being offered to older patients, a population at greater risk of cardiovascular disease.
Researchers led by ...
[1] ... [1315]
[1316]
[1317]
[1318]
[1319]
[1320]
[1321]
[1322]
1323
[1324]
[1325]
[1326]
[1327]
[1328]
[1329]
[1330]
[1331]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.