New conductive, cotton-based fiber developed for smart textiles
2023-12-11
PULLMAN, Wash. – A single strand of fiber developed at Washington State University has the flexibility of cotton and the electric conductivity of a polymer, called polyaniline.
The newly developed material showed good potential for wearable e-textiles. The WSU researchers tested the fibers with a system that powered an LED light and another that sensed ammonia gas, detailing their findings in the journal Carbohydrate Polymers.
“We have one fiber in two sections: one section is the conventional cotton: flexible and strong enough for everyday use, and the other side is the conductive material,” said Hang Liu, WSU textile ...
New therapeutic target for rare type of childhood epilepsy
2023-12-11
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, UCL and MSD have identified a potential treatment target for a genetic type of epilepsy.
Developmental and epileptic encephalopathies are rare types of epilepsy which start in early childhood. One of the most common types of genetic epilepsy, CDKL5 deficiency disorder (CDD), causes seizures and impaired development. Children are currently treated with generic antiepileptic drugs, as there aren’t yet any disease-targeting medications for this disorder.
CDD involves losing the function of a gene producing the CDKL5 enzyme, which phosphorylates proteins, meaning it adds an extra phosphate ...
Advanced MRI technology detects changes in the brain after COVID-19
2023-12-11
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have examined the brains of 16 patients previously hospitalised for COVID-19 with persisting symptoms. They have found differences in brain tissue structure between patients with persisting symptoms after COVID-19 and healthy people. Their findings, published in the journal Brain Communications, can bring insights into the underlying mechanisms of persisting neurological problems after COVID-19.
Several previous studies of persisting problems after COVID have involved MRI brain scanning. Although researchers have found differences compared with healthy brains, these differences are not specific ...
New study reveals latest data on global burden of cardiovascular disease
2023-12-11
A world without cardiovascular disease (CVD) is possible, yet millions of lives are lost prematurely to heart disease each year, according to the new Global Burden of Disease (GBD) special report published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. The report provides an update of health estimates for the global, regional and national burden and trends of CVD from 1990-2022 by analyzing the impact of cardiovascular conditions and risk factors across 21 global regions.
Research from this study reflects an urgent need ...
Rail industry urged to consider safety risks of space weather
2023-12-11
Train accidents could be caused by solar storms switching signalling from red to green according to new research examining the impact of space weather.
Solar storms can trigger powerful magnetic disturbances on Earth, creating geomagnetically induced currents (GICs) which could potentially interfere with electricity transmission and distribution grids.
A team led by PhD researcher Cameron Patterson and Professor Jim Wild from Lancaster University modelled how GICs flowed through the track circuits of AC electrified lines powered with overhead cables.
Using two routes - the Preston to Lancaster section of the West ...
Technology not growing fast enough to decarbonize steel and cement industries by 2050
2023-12-11
Steel and cement are two materials that no society can do without. Their production comes with a significant carbon footprint, however. To meet zero-emission targets under the Paris Agreement, countries, cities, and industries are depending on new large-scale infrastructure for CO2 transport and storage, renewable electricity and green hydrogen. A new study by researchers at the National Institute for Environmental Studies, Japan, and the University of Cambridge, United Kingdom, shows that the current rate of deployment of this infrastructure is insufficient. The study ...
Landscape for AML patients evolving rapidly as research discoveries advance new treatments
2023-12-11
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL DEC. 10, 2023, AT 7:30 P.M. ET) – The treatment landscape for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is evolving rapidly, as research discoveries at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and other academic cancer centers advance new, more effective therapies for this aggressive blood cancer.
“We’ve seen more progress during the past 10 years than the previous four decades combined,” said Justin M. Watts, M.D., Sylvester hematologist, associate professor of medicine, and Pap Corps Early Career ...
'Exceptional' results in phase III leukaemia trial
2023-12-11
University of Leeds news
Embargo: 19:30 ET on Sunday 10 December 2023 / 00.30 GMT on Monday 11 December 2023
New personalised therapy improves survival for patients with CLL leukaemia
Personalised treatment for the most common form of adult leukaemia helps patients survive for longer and stay in remission, a phase III trial has found.
The trial, by the University of Leeds, has been identified as groundbreaking research by the New England Journal of Medicine and the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition in San Diego, where ...
Cell therapy appears safe and effective for lymphoma in remission
2023-12-11
DOWNLOADABLE VIDEO HERE
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL SUNDAY, DEC. 10, 2023 AT 8:00 P.M. ET) – A study led by researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine suggests that CAR-T immunotherapy remains a viable option for patients who have lymphoma that goes into remission before the cell therapy begins.
While the study doesn’t answer the question of whether cell therapy in remission is the right choice, it does say that it’s not the wrong choice.
“I ...
ASH: Novel combination therapy significantly reduces spleen volume in patients with myelofibrosis
2023-12-10
SAN DIEGO ― Combining the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib with the BCL-xL inhibitor navitoclax was twice as effective in reducing enlarged spleens – a major indicator of clinical improvement – compared with standard-of-care ruxolitinib monotherapy for adult patients with intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis, a rare bone marrow cancer, according to results of the Phase III TRANSFORM-1 trial reported by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Data from the global, randomized, placebo-controlled ...
ASH: Novel menin inhibitors show promise for patients with advanced acute myeloid leukemias
2023-12-09
SAN DIEGO ― Two clinical trials led by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center demonstrated early positive results from novel therapies targeting menin for the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute leukemias with specific genetic alterations. Results from the studies were shared today in oral presentations at the 2023 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting. More information on all ASH Annual Meeting content from MD Anderson can be found at MDAnderson.org/ASH.
Menin inhibitor monotherapy ...
ASH: Targeted oral therapy reduced disease burden and improved symptoms for patients with rare blood disorder
2023-12-09
SAN DIEGO ― The targeted therapy bezuclastinib was safe and rapidly reduced markers of disease burden while also improving symptoms for patients with a rare blood disorder called nonadvanced system mastocytosis, according to results of the Phase II SUMMIT trial reported by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings, presented today at the 2023 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting, demonstrate that all participants treated with bezuclastinib achieved at least a 50% reduction in markers of disease burden and 63% reported their disease symptoms eased within 12 weeks. That number increased to 78% after ...
New Sylvester cancer study provides insight into underlying gene mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes
2023-12-09
EMBARGOED UNTIL DECEMBER 9, 2023, AT 12:45 P.M. ET
A new study from researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and collaborating organizations provides insight into the underlying mechanisms of gene mutations commonly seen in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and other myeloid neoplasms.
Their findings, to be presented at ASH 2023, the American Society of Hematology’s annual meeting in Santa Diego, Dec. 9-12, could lead to development of more effective drug combinations ...
First-in-human clinical trial of CAR T cell therapy with new binding mechanism shows promising early responses
2023-12-09
SAN DIEGO – Early results from a Phase I clinical trial of AT101, a new CAR T cell therapy that uses a distinct binding mechanism to target CD19, show a 100 percent complete response (CR) rate at the higher dose levels studied in the trial, according to researchers from the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine and Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center. The findings were published today in Molecular Cancer and presented at the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting ...
Long-term results show combination treatment that skips chemotherapy is effective for older patients with Ph+ ALL
2023-12-09
Older patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who were not good candidates for the standard treatment of intensive chemotherapy had a median overall survival (OS) of 6.5 years on an alternate regimen of dasatinib and blinatumomab.
These long-term results from the S1318 clinical trial will be presented at the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition in San Diego on December 9 (abstract 1499).
Anjali S. Advani, MD, a SWOG investigator at Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute, led the study, with ...
Mindfulness could help women with opioid use disorder better control drug urges
2023-12-09
Mindfulness-Oriented Recovery Enhancement (MORE) — a behavioral intervention that integrates training in mindfulness, emotion regulation strategies and savoring of natural rewards — could hold the key to mitigating relapse in women undergoing medically assisted opioid use disorder treatment, a Rutgers study found.
The pilot study published in the journal Explore, is the first to evaluate the potential neural changes that underlie women’s emotion regulation and craving after an eight-week MORE intervention.
Previous studies have shown that women report higher opioid craving and show a greater inability to ...
TTUHSC’s ARPA-H membership will spur innovation, improve access for West Texas patients
2023-12-09
Imagine if scientists developed a customizable cancer vaccine that was available — and affordable — for everyone. What if a patient scheduled for surgery also had the option of taking a pill whose composition includes nanorobotics capable of performing the procedure?
These and other medical scenarios may seem far-fetched and better suited to a science fiction thriller. However, the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) is seeking to take such ideas from the drawing board to ...
Global annual finance flows of $7 trillion fueling climate, biodiversity, and land degradation crises
2023-12-09
Almost US$7 trillion per year in government subsidies and private investment - around 7 per cent of global GDP - has a direct negative impact on nature.
Nature-based solutions remain dramatically underfunded. Current public and private finance flows are only US$200 billion per year. To meet climate, biodiversity, and restoration targets, this needs to triple by 2030 and quadruple by 2050.
Realignment of public and private nature-negative finance flows is urgently needed
Dubai, 9 December 2022 – Close to $7 trillion is invested globally each year in activities that have a direct negative impact on nature from both public and private sector sources - equivalent to ...
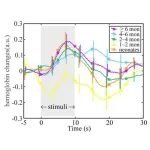
Tracing how the infant brain responds to touch with near-infrared spectroscopy
2023-12-09
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have measured how oxygenated hemoglobin levels in the blood change in infants’ brains in response to touch. Using spectroscopy methods with external sensors placed on the scalp of sleeping infants, they found that the time at which levels peak doesn’t change with infant age, but the amount by which it varies over time does. Insights like this shed light on how the physiology of infants develop.
The first phase of a newborn’s life is a dazzling array of rapid developmental ...
These are the world's most effective charities
2023-12-09
Which charities will be most effective in ensuring your donation is put to good use? For the first time in the Netherlands, researchers applied scientific methods to pinpoint which charities achieve the most with the donations they receive. The University of Amsterdam and Stichting Doneer Effectief (Donate Effectively Foundation) unveiled the list on Friday, 8 December, during a sold out evening in Rotterdam. ‘We are talking about the Champions League of good causes,’ says professor of Philanthropy & Sustainable Investment Paul Smeets of the University of Amsterdam. The ranking ...
When is an aurora not an aurora?
2023-12-08
The shimmering green, red and purple curtains of the northern and southern lights — the auroras — may be the best-known phenomena lighting up the nighttime sky, but the most mysterious are the mauve and white streaks called Steve and their frequent companion, a glowing green "picket fence."
First recognized in 2018 as distinct from the common auroras, Steve — a tongue-in-cheek reference to the benign name given a scary hedge in a 2006 children's movie — and its associated picket fence were nevertheless thought to be caused by the same physical processes. But scientists were left scratching their heads about how these glowing emissions ...
Advisory panel issues field-defining recommendations for US government investments in particle physics research
2023-12-08
The High Energy Physics Advisory Panel (HEPAP) to the High Energy Physics program of the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation’s Division of Physics has released a new Particle Physics Project Prioritization Panel (P5) report, which outlines particle physicists’ recommendations for research priorities in a field whose projects — such as building new accelerator facilities — can take years or decades, contributions from thousands of scientists, and billions of dollars.
The 2023 P5 report represents the major activity in the field of particle physics that ...
Doctors discover many patients at UNC’s Inflammatory Bowel Disease Clinic screen positive for malnutrition
2023-12-08
CHAPEL HILL, NC — Eating food and absorbing its nutrients is an everyday occurrence, but this normal activity can look different for someone who suffers from inflammatory bowel disease. IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, can cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract – which for many reasons can lead to malnutrition. This malnourished state is associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality, and new findings show that many patients in IBD clinic screen positive for malnutrition, leading to the critical need for same-day ...
BNL: Advisory panel issues field-defining recommendations for U.S. government investments in particle physics research
2023-12-08
The following news release on the 2023 Particle Physics Project Prioritization Panel (P5) report is based on one issued today by the American Physical Society (APS) with added content specific to the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory. For more information about Brookhaven Lab’s research in particle physics, contact: Karen McNulty Walsh, kmcnulty@bnl.gov, (631) 344-8350. For APS media inquiries, contact Anna Torres, torres@aps.org, (301) 209-3605.
WASHINGTON, ...
International collaboration uses faculty member’s research on ancient Roman migration, seeks to understand Balkan genomic history
2023-12-08
STARKVILLE, Miss.––A Mississippi State University anthropologist’s bioarchaeological analysis and bone samples from ancient Roman burial sites were crucial in the development of new research regarding Roman and Balkan migration featured this week in Cell, a prestigious peer-reviewed journal.
Anna Osterholtz, an associate professor in the Department of Anthropology and Middle Eastern Cultures, provided her research on the “lived experiences” of the Romans in Croatia. She currently works closely with museum ...
[1] ... [1493]
[1494]
[1495]
[1496]
[1497]
[1498]
[1499]
[1500]
1501
[1502]
[1503]
[1504]
[1505]
[1506]
[1507]
[1508]
[1509]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.