PNNL creates Center for Artificial Intelligence
2023-12-14
RICHLAND, Wash.—The Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has created the Center for AI @PNNL to coordinate the pioneering research of hundreds of scientists working on a range of projects focused on science, security and energy resilience.
Researchers at PNNL were among the first to dive into artificial intelligence decades ago. But AI has surged in the past year with the ready availability of generative AI, which allows almost anyone to produce sophisticated—though sometimes errant—text and images with just a small amount of data. At the same time, AI is a vital tool for ...
Photonics research reveals potential for next-gen AR/VR and IoT
2023-12-14
USD$200,000 awarded to tackle today’s pressing consumer technology demands
Utilizing smart optical sensors for IoT
Providing more realistic virtual and augmented realities
WASHINGTON – The Optica Foundation today released more detailed information on information technology research funded by the 2023 Optica Foundation Challenge. Researchers Zaijun Chen, University of Southern California, USA, and Alejandro Velez-Zea, Universidad de Antioquia, Colombia, both proposed novel approaches to addressing the flow of data and information in consumer-centric technologies.
“The ...
Jurors recommend death penalty based on looks, but new training can correct the bias
2023-12-14
Certain facial features—like downturned lips and a heavy brow—are known to make someone appear untrustworthy to others, even though these do not indicate a person’s actual character. Such facial biases influence our everyday social interactions as well as high-stakes decisions, including who we hire, or elect to political office.
But a new study by Columbia researchers shows that the effects of these judgments can be mitigated. The study outlines the results of four experiments that the authors conducted with 1,400 volunteers. Through those experiments, the researchers found that when real-world defendants have facial features that appear untrustworthy, they are more likely ...
Closing the design-to-manufacturing gap for optical devices
2023-12-14
Photolithography involves manipulating light to precisely etch features onto a surface, and is commonly used to fabricate computer chips and optical devices like lenses. But tiny deviations during the manufacturing process often cause these devices to fall short of their designers’ intentions.
To help close this design-to-manufacturing gap, researchers from MIT and the Chinese University of Hong Kong used machine learning to build a digital simulator that mimics a specific photolithography manufacturing process. Their technique utilizes real data gathered from the photolithography system, so it can more ...
Seals stay warm and hydrated in the arctic with larger, more convoluted nasal passages
2023-12-14
Arctic seals have evolved many adaptations to cope with their frosty environment—one that you might not immediately think of is the bones in their nasal cavity. Arctic seals have more convoluted nasal passages than seal species that live in milder environments, and researchers report December 14 in the Biophysical Journal that these structures help the seals more efficiently retain heat and moisture as they breathe in and out.
“Thanks to this elaborate structure in their nasal cavities, Arctic seals lose less heat through nasal heat exchange than subtropical seals when both are exposed to the same ...
D-mannose reduces age-triggered changes in urinary tract that increase susceptibility to UTIs
2023-12-14
Aging poses a number of challenges to the body’s well-being, one of the most important being an increased susceptibility to multiple diseases, including urinary tract infections (UTIs). The connection between aging and more prevalent UTIs is not well understood, but now researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have found an explanation.
The researchers show in the journal Developmental Cell that, compared to the younger counterpart, the aging urinary tract in animal models changes how it functions at the cellular level in ways that seem to favor the establishment ...
Where patients live impacts whether they pick up their heart-failure medications
2023-12-14
People who live in neighborhoods with higher levels of poverty and unemployment are less likely to fill their heart-failure drug prescriptions than those living in wealthier areas, a new study shows. The findings not only add to understanding geographic and economic disparities in heart disease care, but also point to new ways to address barriers for patients taking these lifesaving drugs.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study explored prescription pickup patterns among patients with systolic heart failure, a chronic, life-threatening ...
Animal behavior: Cats like to fetch when they’re feline playful
2023-12-14
Cats tend to dictate games of fetch with their owners and most cats who play fetch learned to do so without explicit training, according to a survey of 924 cat owners published in Scientific Reports. The findings also highlight the variety of objects that cats prefer to fetch, including hair ties and bottle parts.
Jemma Forman, Elizabeth Renner and David Leavens surveyed cat owners who reported fetching behaviours in 1,154 cats that they currently or previously owned. Owners reported how fetching first occurred, how often it occurs ...
New understanding of ancient genetic parasite may spur medical breakthroughs
2023-12-14
A multidisciplinary study published in Nature has elucidated the structure of the machinery responsible for writing much of our “dark genome” — the 98 percent of our DNA that has largely unknown biological function. These results may spur entirely novel treatments for autoimmune diseases, cancer and neurodegeneration.
An international team of scientists from Rutgers and more than a dozen other institutions, including both academia and industry, have published the first high-resolution images and structural details of avirus-like element known as LINE-1. They describe it as “an ancient genetic parasite” that is one of the most common parts of human DNA (video ...
Neighborhood-level socioeconomic status and prescription fill patterns among patients with heart failure
2023-12-14
About The Study: In this study of 6,247 patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, patients living in neighborhoods with lower neighborhood-level socioeconomic status had significantly higher odds of nonadherence to guideline-directed medical therapy. These findings highlight the importance of considering neighborhood-level disparities when developing approaches to improve medication adherence.
Authors: Amrita Mukhopadhyay, M.D., of the NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York, is the corresponding ...
Sleep disturbances and emotional and behavioral difficulties among preschool-aged children
2023-12-14
About The Study: The natural history of sleep disturbances was associated with both resolved and incident emotional and behavioral difficulties in this study of 17,000 preschool-aged children. Routine screening and precise intervention for sleep disturbances may benefit the psychosocial well-being of this population.
Authors: Fan Jiang, M.D., Ph.D., and Guanghai Wang, Ph.D., of Shanghai Jiao Tong University in Shanghai, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Clinical trial shows efficacy for atezolizumab combined with carboplatin
2023-12-14
Immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy has become an important therapeutic treatment option in some patients with metastatic breast cancer. Which patients will benefit the most, however, remains unclear; current biomarkers such as PD-L1 that are used to predict response are mediocre at best. Vanderbilt researchers led a clinical trial combining atezolizumab, an immunotherapy, in combination with chemotherapy in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer to both evaluate the efficacy of the treatment combination and to understand biomarkers of response ...
Egocentric coding unveiled: researchers unlock brain's spatial perception mechanisms
2023-12-14
Researchers from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and their collaborators have uncovered the coding principle underlying self-centered (egocentric) representation in spatial perception. The study was published in Neuron on Dec. 14.
Our understanding of the intricate spatial perception mechanisms in the human brain has recently advanced with the discovery that self-centered perception of external items is closely integrated with our world-centered understanding of the world, which is the brain's internal "GPS" system. Given ...
AI study reveals individuality of tongue’s surface
2023-12-14
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and 3D images of the human tongue have revealed that the surface of our tongues are unique to each of us, new findings suggest.
The results offer an unprecedented insight into the biological make-up of our tongue’s surface and how our sense of taste and touch differ from person to person.
The research has huge potential for discovering individual food preferences, developing healthy food alternatives and early diagnosis of oral cancers in the future, experts say.
The human tongue is a highly sophisticated and ...
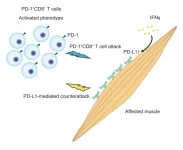
Finding the source of debilitating, body-wide muscular pain and weakness
2023-12-14
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify the T cells that, when activated, are pathogenic in a subset of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
Tokyo, Japan – Inflammation is an important part of the body’s defenses, eliminating threats and repairing damage. When the immune system is overactivated, though, it can turn from friend to foe. Now, researchers from Japan have identified the culprit responsible for one type of harmful inflammation that occurs in certain muscular disorders.
In a study published last month in the Journal of Autoimmunity, ...
Jacob Tsimerman receives Ostrowski Prize in Higher Mathematics
2023-12-14
The Canadian mathematician Jacob Tsimerman has been awarded the International Ostrowski Prize in Higher Mathematics 2023. The Ostrowski Prize is worth 100,000 Swiss Francs and named after Alexander M. Ostrowski, a professor of mathematics who taught at the University of Basel.
Jacob Tsimerman, a professor of mathematics at the University of Toronto (Canada), received the Ostrowski Prize 2023 in recognition of his work at the interface of transcendence theory, analytic number theory and arithmetic geometry, including recent breakthroughs on the André-Oort and Griffiths conjectures.
Shimura varieties are algebraic varieties of great ...
This next generation blue light could potentially promote or hinder sleep on command
2023-12-14
Blue light from LED lamps and consumer electronics can mess with your sleep because it disrupts production of the natural sleep hormone melatonin. Tinted glasses or displays in night mode can mask, but don’t remove, a portion of the disruptive wavelengths. But now, researchers report in ACS Omega that they have designed more “human-centric” LEDs that could potentially enhance drowsiness or alertness on command.
Humans have evolved over millennia to be active during the day and to rest at night; we’ve depended on the sun to regulate our sleep/wake cycle. But many people ...
New app to bridge information gap between hospitals and nursing homes; better care for patients
2023-12-14
INDIANAPOLIS – Approximately one in five older adults in the U.S. is transferred to a nursing home following a hospital stay. For many of these patients, an accessible medical record does not accompany them, often negatively affecting the care they receive at the nursing home. This poor information sharing is a significant problem contributing to the adverse events within 45 days of hospital discharge experienced by nearly 40 percent of nursing home residents.
Regenstrief Institute research scientists Kathleen Unroe, M.D., MHA, and Joshua Vest, PhD, ...
Timothy Rhoads of the University of Wisconsin Madison receives the AFAR 2023 Sagol Network GerOmic Award for Junior Faculty
2023-12-14
NEW YORK — The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) is pleased to announce recipient of the 2023 Sagol Network GerOmic Award for Junior Faculty: Timothy Rhoads, PhD, Assistant Professor, University of Wisconsin-Madison. Established in 2020, the Sagol Network GerOmic Award for Junior Faculty is a one- to two-year award given to junior faculty (MDs and PhDs) to conduct aging-related Omics (GerOmics) research.
Omics is a rapidly evolving, multi-disciplinary, and emerging field that encompasses genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. Each of these fields offers ...
American Meteorological Society Announces David J. Stensrud as New President-Elect
2023-12-14
[Boston, MA—December 13, 2023] Members of the American Meteorological Society (AMS)—composed of weather, water, and climate professionals—have voted to elect David J. Stensrud to the position of President-Elect for 2024. He will be inducted to the post Sunday, 28 January, 2024, during the 104th AMS Annual Meeting in Baltimore, Maryland.
The AMS will also induct five new Councilors at the 2024 Annual Meeting. Cynthia Atherton, Gina Eosco, Andrew Humphrey, Ying-Hwa (Bill) Kuo, and Clifford Mass have been selected to serve three-year ...
Being overweight costs society far more than obesity
2023-12-14
“We often hear that obesity represents a high cost for both individuals and society because it increases the risk of health problems. All in all, however, the costs associated with being overweight are much higher,” says Christina Hansen Edwards, a researcher at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
Since the 1980s, Norwegians have become increasingly heavier. Over the past 40 years, the percentage of people with obesity, i.e. a body mass index (BMI) of over 30, has increased significantly. It is currently estimated that almost one in four Norwegians is obese, ...
People, not the climate, caused the decline of the giant mammals
2023-12-14
About 100,000 years ago, the first modern humans migrated out of Africa in large numbers. They were eminent at adapting to new habitats, and they settled in virtually every kind of landscape - from deserts to jungles to the icy taiga in the far north.
Part of the success was human's ability to hunt large animals. With clever hunting techniques and specially built weapons, they perfected the art of killing even the most dangerous mammals.
But unfortunately, the great success of our ancestors came at the expense of the other large mammals.
It is well-known that numerous large species went extinct ...
Children who are sedentary may have a higher risk of heart attack or stroke later in life
2023-12-14
WASHINGTON—Children who are physically inactive may have high cholesterol in early adulthood and subsequent heart health issues in their mid-forties, according to new research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
High cholesterol during childhood has been associated with early signs of heart disease when individuals reach their mid-twenties and an increased risk of premature cardiovascular death in their mid-forties. Several clinical trials aimed at lowering cholesterol levels in the youth population have had minimal ...
Cockroaches can transmit antimicrobial resistance genes between groups
2023-12-14
Washington, D.C.—A new paper describes a study of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) transmission among cockroaches, with implications for AMR transmission in humans. The study was published in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
AMR represents a serious threat to the health of humans and other animals. With fewer and fewer drugs being effective against some microbial pathogens, infections have become increasingly difficult to treat. Theoretical modeling has been used to explore the spread of AMR through the microbiome of the symbiotic, or nonpathogenic, gut of animals. The present study ...
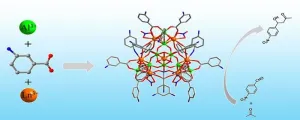
Three novel inorganic clusters accelerate ‘one of the most important’ chemical reactions
2023-12-14
Perfume, rubbing alcohol, a cholesterol medication and even biological processes all depend on a chemical process called the aldol reaction. The reaction primarily combines compounds to form carbon-carbon bonds, which are incredibly strong and provide a molecule with stability. Catalyst clusters made of aluminum and oxygen typically help accelerate this reaction, but clusters that also include rare earth elements could offer more desirable and synergistic properties, according to a team of researchers based in China.
The team developed three such clusters, ...
[1] ... [1494]
[1495]
[1496]
[1497]
[1498]
[1499]
[1500]
[1501]
1502
[1503]
[1504]
[1505]
[1506]
[1507]
[1508]
[1509]
[1510]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.