Navigating climate challenges: UVA engineers and environmental scientists aid Virginia’s eastern shore
2023-12-15
Because of warming waters and melting glaciers, the sea level at Virginia’s Eastern Shore has risen almost 3 inches since 2016, and the projected trajectory looks ominous. The region, sandwiched between the Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic Ocean, has one of the highest rates of relative sea-level rise on the Atlantic coast. The Virginia Institute of Marine Science’s Center for Coastal Resource Management projects a relative sea-level rise between 4.5 to 7 feet by 2100, which is three to four times the global average.
Hampton, Virginia — its neighbor across the bay — ranks second only to New Orleans as the largest population center ...
Using AI to pinpoint hidden sources of clean energy underground
2023-12-15
SAN FRANCISCO – As efforts to transition away from fossil fuels strengthen the hunt for new sources of low-carbon energy, scientists have developed a deep learning model to scan the Earth for surface expressions of subsurface reservoirs of naturally occurring free hydrogen.
Researchers used the algorithm to help narrow down the potential whereabouts of ovoids or semicircular depressions (SCDs) in the ground that form near areas associated with natural or “gold hydrogen” deposits. Though these circular ...
A study from IMDEA Software researchers reveals hidden fortunes and surprising overestimations in cybercrime revenue
2023-12-15
To what extent methodological limitations and incomplete data impact the revenue estimations of cybercriminal groups using the Bitcoin blockchain was largely unknown. A new study, conducted by IMDEA Software Institute researchers Gibran Gomez, Kevin van Liebergen, and Juan Caballero challenges existing figures regarding cybercriminals' Bitcoin earnings to date. The study, entitled "Cybercrime Bitcoin Revenue Estimations: Quantifying the Impact of Methodology and Coverage", recently presented at the ...
Department of Defense grant boosts study of pressure, humidity on thermal energy storage
2023-12-15
Under the Defense University Research Instrumentation Program, Dr. Patrick Shamberger and a research team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering received a grant from the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) to acquire instrumentation for thermal energy storage research.
The grant, administered through the Office of Naval Research, will support the acquisition of a high-sensitivity multi-modal calorimeter for advanced research and education on tunable energy storage materials. This equipment will allow cutting-edge research to study the capability of pressure and humidity to control how well these materials can store ...
IU researchers fill the final gaps in the Arabidopsis genome sequence and gain insights into gene regulatory mechanisms relevant to humans
2023-12-15
Arabidopsis thaliana is a species grown worldwide for genetic research and was the first plant to have its complete set of chromosomes (its genome) sequenced. The initial genome sequence, released in the year 2000, had numerous gaps, but technological improvements in the years since closed the gaps, one by one, until only two remained: large undefined regions on chromosomes 2 and 4 where genes encoding ribosomal RNAs are repeated in hundreds of copies. These ribosomal RNA gene clusters, known as nucleolus organizer regions (NORs), are not just difficult to define in Arabidopsis; gaps remain at ...
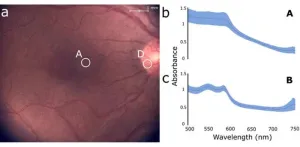
Toward more precise and flexible targeted spectroscopy measurements in the retina
2023-12-15
Many ocular diseases involve changes in the structure and function of different regions of the back of the eye, also known as the “eye fundus.” For example, fluorescent pigments and tiny yellowish deposits called drusen accumulate under the retina in age-related macular degeneration, and the degeneration of neurons called ganglion cells is a defining characteristic of glaucoma. Interestingly, changes in the eye fundus are not restricted to vision-related diseases only. Certain neurological diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s can cause changes in retinal nerves and ...
UVA biomedical engineer unveils the dynamics of maternal immune responses
2023-12-15
Sepideh Dolatshahi, an assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Virginia, is spearheading an exploration of systems immunology in its crucial development phase — during pregnancy.
Systems immunology is about unraveling concealed patterns within the human immune system, said Dolatshahi, whose approaches to her research span computational modeling, systems serology and cutting-edge spatial analysis techniques to investigate immune interactions between mother and fetus during pregnancy that could later support early childhood immunity.
Designing Tailored and Effective Vaccine Plans
Babies are immunocompromised ...
Novel therapeutic target overcomes resistance to radiation therapy
2023-12-15
A new study finds that radiation therapy (RT) suppresses a key protein called bone morphogenetic protein and activin membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI) and activates immune suppressive cells. These effects dampen the capacity of cancer-fighting immune cells and decrease the effectiveness of radiation, inducing therapy resistance in cancer patients, according to a paper published December 15, 2023 in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Radiation therapy is a common cancer treatment that kills cancer cells and activates immune cells to fight cancer. Yet this process also ...
Understanding atmospheric flash droughts in the Caribbean
2023-12-15
The word “drought” typically conjures images of parched soil, dust-swept prairies, depleted reservoirs, and dry creek beds, all the result of weeks or seasons of persistently dry atmospheric conditions.
In the sun-soaked islands in the Caribbean, however, drought conditions can occur much more rapidly, with warning signs appearing too late for mediation strategies to limit agriculture losses or prevent stresses on infrastructure systems that provide clean water to communities.
Such occurrences – known as flash droughts – are the focus of a new paper authored by Assistant Professor Craig Ramseyer of the College of Natural Resources ...
Pesticides and adjuvants disrupt honey bee’s sense of smell
2023-12-15
It has long been known that exposure to pesticide sprays is harmful to honey bees. In a new study, researchers have uncovered the effect of such sprays on the sense of smell in bees, which could disrupt their social signals.
Honey bees live in dynamic communities and constantly communicate with each other using chemicals that serve as social cues. For example, nurse bees—that are responsible for taking care of larvae that ultimately become queens and worker bees—constantly monitor the ...
Immune cells shape lung before birth and provide new avenues for treating respiratory diseases
2023-12-15
Immune cells play an active and intimate role in directing the growth of human lung tissue during development, researchers find, revolutionising our understanding of early lung development and the role of immune cells outside of immunity.
The research offers new insights for understanding and treating respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Respiratory conditions account for almost 20 per cent of all deaths in children under five years worldwide1.
The work reveals a surprising coordination between the immune and respiratory systems, much earlier in development than previously thought. This discovery raises questions about the ...
Rembrandt broke new ground with lead-based impregnation of canvas for The Night Watch
2023-12-15
New research has revealed that Rembrandt impregnated the canvas for his famous 1642 militia painting ‘The Night Watch’ with a lead-containing substance even before applying the first ground layer. Such lead-based impregnation has never before been observed with Rembrandt or his contemporaries. The discovery, published today in Science Advances, underlines Rembrandt's inventive way of working, in which he did not shy away from using new techniques.
The surprising observation is yet another result from Operation Night Watch, the largest and most wide-ranging research and conservation project in the history ...
SFU and UBC researchers receive $1.25 million to study cumulative effects on B.C. salmon
2023-12-15
Salmon researchers from British Columbia are embarking on a three-year study to understand and help mitigate the cumulative threats affecting the vulnerable species in the province’s watersheds.
The Watershed Futures Initiative, which includes researchers from Simon Fraser University, University of British Columbia and University of Montana, has received $1.25 million from the federal and provincial governments – through the joint British Columbia Salmon Restoration and Innovation Fund – to tackle the combined impacts of logging, mining, urban development, agriculture, climate change and other factors on salmon.
While ...
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in menstrual products including tampons, pads, and liners
2023-12-15
The average menstruator will use over 11,000 tampons or sanitary pads in their lifetime. Vaginal and vulvar tissue that touch pads and tampons is highly permeable. Through this permeable tissue chemicals are absorbed without being metabolized, which makes endocrine-disrupting chemicals potentially dangerous when found in menstrual products. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals can interfere with human hormones and cause medical issues, including gynecological conditions such as endometriosis and uterine fibroids.
Joanna Marroquin, a Mason PhD in Public Health student, and Associate ...
Five researchers named Argonne Distinguished Fellows for 2023
2023-12-15
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has named five highly accomplished scientists as Argonne Distinguished Fellows in 2023. They are Glenn Decker, Paul Fenter, Robert Fischetti, Sven Leyffer and Valentine Novosad.
The honor recognizes scientists who have not only achieved international esteem but who have also demonstrated exceptional achievements in science or engineering relevant to Argonne’s core missions. They are leaders of major, complex, high-priority projects or programs that have an impact on the future of the Laboratory. Only a small ...
Study shows exposure to household chemicals can lower odds of getting pregnant
2023-12-15
Exposure to phthalates, a group of plasticizing and solvent chemicals found in many household products, was linked to a lower probability of getting pregnant, but not to pregnancy loss, according to research by a University of Massachusetts Amherst environmental and reproductive epidemiologist.
The study, published this week in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, also noted an association between preconception exposure to phthalates and changes in women’s reproductive hormones, as well as increased inflammation and oxidative stress.
“Phthalates ...
NRL’s Debra Rolison elected 2023 National Academy of Inventors Fellow
2023-12-15
WASHINGTON – Debra Rolison, Ph.D., of the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) has been named Fellow of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI), for having demonstrated a highly prolific spirit of innovation in creating and facilitating outstanding inventions that have made a tangible impact on the quality of life, economic development, and welfare of society.
Rolison has been at the lab for over 43 years and heads the Advanced Electrochemical Materials section. The recognition by the NAI is attributed to the efforts made by her team’s inventions related to a new form factor for zinc anodes in rechargeable ...
North America’s first people may have arrived by sea ice highway
2023-12-15
SAN FRANCISCO — One of the hottest debates in archeology is how and when humans first arrived in North America. Archaeologists have traditionally argued that people walked through an ice-free corridor that briefly opened between ice sheets an estimated 13,000 years ago.
But a growing number of archeological and genetic finds — including human footprints in New Mexico dated to around 23,000 years old — suggests that people made their way onto the continent much earlier. These early Americans likely traveled along the Pacific coastline from Beringia, the land bridge between Asia and North America ...
Xinfeng Gao named 2024 AIAA Associate Fellow
2023-12-15
We are pleased to announce that the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), a preeminent aerospace professional society, has selected professor Xinfeng Gao to be a member of the class of 2024 AIAA associate fellows. Only one member of the Institute for every 150 members is selected as an associate fellow each year by the review committee.
“This recognition illustrates the impact of our outstanding faculty. Aerospace engineering at UVA continues on a great trajectory and professor Gao is a big part of that,” said Richard W. Kent, professor and chair of the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering.
Pioneering ...
Substance-abuse stigma impedes treatment in various ways, scientists say
2023-12-15
Addiction is one of society’s most misunderstood and rebuked health conditions. That stigma discourages many people from seeking treatment for substance dependence, according to a new report published in Psychological Science in the Public Interest, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Research on stigma toward people with substance use disorder (SUD) is relatively sparse, the report adds.
“Characterizing the nature and etiology of SUD stigma is critical for developing tailored and effective interventions ...
Ultrafast lasers map electrons 'going ballistic' in graphene, with implications for next-gen electronic devices
2023-12-15
LAWRENCE — Research appearing in ACS Nano, a premier journal on nanoscience and nanotechnology, reveals the ballistic movement of electrons in graphene in real time.
The observations, made at the University of Kansas’ Ultrafast Laser Lab, could lead to breakthroughs in governing electrons in semiconductors, fundamental components in most information and energy technology.
“Generally, electron movement is interrupted by collisions with other particles in solids,” said lead author Ryan Scott, ...
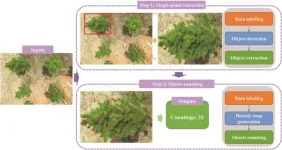
Revolutionizing forestry: 'CountShoots' unveils advanced UAV and AI techniques for precise slash pine shoot counting
2023-12-15
In southern China, the genetically improved slash pine (Pinus elliottii) plays a crucial role in timber and resin production, with new shoot density being a key growth trait. Current manual counting methods are inefficient and inaccurate. Emerging technologies such as UAV-based RGB imaging and deep learning (DL) offer promising solutions. However, DL methods face challenges in global feature capture, necessitating additional mechanisms. Innovations like the Vision Transformer and its derivatives (e.g., TransCrowd, CCTrans) show potential in plant trait counting, offering simplified and more effective approaches for large-scale and accurate ...
UMSOM researchers discover first ever link between hemoglobin-like protein and normal heart development
2023-12-15
BALTIMORE, December 14, 2023– In a landmark study led by the University of Maryland School of Medicine, researchers discovered for the first time that a certain kind of protein similar to hemoglobin, called cytoglobin, plays an important role in the development of the heart. Specifically, it affects the correct left-right pattern of the heart and other asymmetric organs. The findings, published today in the journal Nature Communications, could eventually lead to the development of new therapeutic interventions to alter the processes that lead ...
Facility fees charged by hospitals for colonoscopy procedures are about 55 percent higher than those charged by surgical centers
2023-12-15
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL FRIDAY DECEMBER 15 AT 11 A.M. EST.
U.S. hospitals charge facility fees for colonoscopy procedures covered by private health insurance that are on average approximately 55 percent higher than facility fees billed by smaller clinics known as ambulatory surgical centers, according to a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The findings appear in a peer-reviewed research letter to be published online December 15 in JAMA Health Forum.
Colonoscopies ...
Racial equity in living donor kidney transplant centers
2023-12-15
About The Study: The results of this study of data on 57,000 adults who received living donor kidney transplants indicate that additional work is necessary to identify transplant program and center-level strategies to improve racial equity in access to living donor kidney transplant.
Authors: Lisa M. McElroy, M.D., M.S., of the Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.47826)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
[1] ... [1490]
[1491]
[1492]
[1493]
[1494]
[1495]
[1496]
[1497]
1498
[1499]
[1500]
[1501]
[1502]
[1503]
[1504]
[1505]
[1506]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.