Can telehealth assessments identify infants more likely to be on the autism spectrum?
2023-12-13
Is it possible to identify infants more likely to be on the autism spectrum through telehealth assessments? The UC Davis MIND Institute’s Meagan Talbott, a professional researcher in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, has received a $3.2 million grant to seek the answer to that question. The five-year grant is from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Talbott is now recruiting for a national study of 120 infants, 6-12 months of age, who are showing delays or differences in their development. Parents might have questions about autism or other conditions, but ...
Virginia Tech researcher probes the potential for preventing and reversing age-related memory loss
2023-12-13
About 40 percent of people over age 65 suffer some form of age-related memory loss, which puts them at higher risk for developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. However, there are currently no approved methods for preventing memory loss with age.
Tim Jarome, associate professor of neurobiology in the Virginia Tech College of Agriculture and Life Sciences’ School of Animal Sciences is hoping to change that, aided by a $433,000 grant from the National Institute on Aging, which is part of the National Institutes of Health.
Jarome and his research partner, Assistant Professor Sydney Trask of Purdue University’s Department ...
Mpox (monkeypox) vaccine triggers equally strong immune response in smaller than usual doses and in people with or without HIV
2023-12-13
Delivering the two-dose mpox vaccine, called JYNNEOS, in smaller than the usual FDA-approved doses, and by injection between layers of the skin rather than by the standard route under the skin, produced a detectable immune response, a new study shows. This also occurred regardless of whether people were living with or without HIV.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study showed no significant difference in the strength of the immune response (as gauged by the amount of detectable IgG antibodies, immune proteins that help kill the mpox virus) between most of those who received their vaccine injections in small doses ...
Interactive screen use reduces sleep time in kids, researchers find
2023-12-13
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — While screen time is generally known to affect sleep, new research suggests that interactive engagement, such as texting friends or playing video games, delays and reduces the time spent asleep to a greater extent than passive screen time, like watching television — especially for teens.
The research, which published today (Dec. 13) in the Journal of Adolescent Health, demonstrates that adolescents at age 15 who used screens to communicate with friends or play video games in the hour before bed took 30 minutes longer to fall asleep than if they had refrained from interactive screen time. But it wasn’t just interactive screen time ...
New study shows exercise can boost brain health
2023-12-13
Santa Monica, Calif. (Dec. 12, 2023) – A fascinating link between regular exercise and better brain health has been revealed, according to an international study that included a team of clinical researchers from Pacific Neuroscience Institute’s Brain Health Center, located at Providence Saint John’s Health Center.
The research, detailed in the paper "Exercise-Related Physical Activity Relates to Brain Volumes in 10,125 Individuals," was published this week in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease and shows being physically active is related to increased size of brain areas important ...
UNC researchers reveal prevalence of persistent symptoms in patients with microscopic colitis
2023-12-13
It’s a hidden cause of diarrhea and the development of the disease is poorly understood. Multiple factors work against the diagnosis of microscopic colitis, an inflammatory digestive disease, because the symptom distress compared to patients with other causes of chronic diarrhea remains unknown. Now, a new study published in journal Gastro Hep Advances, shows patients may be unsure of a diagnosis based on their colonoscopy results, patients may not be prescribed the proper medications, and many patients may remain symptomatic one year after colonoscopy.
The ...
Don't say vegan: Americans more likely to choose vegan food if labeled ‘healthy’ and ‘sustainable’
2023-12-13
There may be a simple way to convince meat eaters to consume vegan food, according to a new USC study: Don’t call the food “vegan.”
Americans were far less likely to choose a gourmet gift basket without meat or dairy if it was labeled “vegan” or “plant-based,” according to a nationally representative survey of more than 7,500 U.S. adults. By contrast, labeling the basket “healthy” and/or “sustainable” roughly doubled the likelihood that Americans ...
UTA’s Woods and Weidanz named to NAI
2023-12-13
The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) has elected Jon Weidanz and Robert Woods, two professors from The University of Texas at Arlington, as fellows.
Weidanz is vice president for research and innovation and holds research positions in bioengineering and kinesiology. He also is a member of the Bone and Muscle Research Center and the Multi-Professional Center for Health Informatics at UTA.
Woods is a professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering, the advisor of the Formula Society of Automotive Engineering (FSAE) student racing team and the holder of the Dr. Bob Woods Chair in Automotive Engineering Endowed by Paul Andrews ...
Breastfeeding alters infant gut in ways that boost brain development, may improve test scores
2023-12-13
Breastfeeding, even partially alongside formula feeding, changes the chemical makeup—or metabolome—of an infant’s gut in ways that positively influence brain development and may boost test scores years later, suggests new CU Boulder research.
“For those who struggle with exclusively breastfeeding, this study suggests your baby can still get significant benefits if you breastfeed as much as you can,” said senior author Tanya Alderete, an assistant professor of integrative physiology at CU Boulder.
The study, published Dec. 13 in the journal npj Metabolic Health and Disease, also identifies specific ...
Scientists identify a key cause of female infertility
2023-12-13
Infertility affects around 48 million couples worldwide and can have various causes. In mammals, including humans, eggs are produced in the ovary. When this process goes wrong, it can lead to female infertility. One example of this is premature ovarian insufficiency, which is characterised by problems with egg production before the age of 40. Up to 3.7% of females experience infertility as a result of this condition, and around 30% of cases are due to genetic variations. Professor Kehkooi Kee, from Tsinghua University, China, who helped ...
Very irregular sleep linked to higher risk of dementia
2023-12-13
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET,WEDNESDAY, DECEMBER 13, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have very irregular sleep patterns may have a higher risk of dementia than those who have more regular sleep patterns, according to new research published in the December 13, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that sleep irregularity causes dementia. It only shows an association.
Sleep regularity is how consistent you are at going to sleep and waking up at the same time each day.
“Sleep health recommendations often focus on getting the recommended ...
Rare sleep disorder more prevalent than previously thought
2023-12-13
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, DECEMBER 13, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People who are very sleepy during the day, despite a good night’s rest, may have a sleep disorder called idiopathic hypersomnia. New research has found this neurologic disorder may not be as rare as once thought. The study is published in the December 13, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Symptoms of idiopathic hypersomnia include not only being very sleepy during the day, but ...
Prediabetes treatment may reduce heart and kidney risks in childhood cancer survivors
2023-12-13
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – December 13, 2023) A study from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital sheds light on the incidence of prediabetes and diabetes in childhood cancer survivors for better prevention and treatment. At a younger age, childhood cancer survivors can experience chronic conditions such as diabetes, typically associated with older individuals. Researchers found survivors have twice the risk of developing prediabetes than the general public, which increases their risk of other life-threatening diseases. In the general population, prediabetes can be modified with lifestyle and other interventions, suggesting the potential to improve ...
Copy and paste: New AI tool helps computers interpret the world
2023-12-13
Copy and paste.
It’s a simple concept.
You define some text or image on your computer, copy it, and paste it where you want it.
Now, think of that new leather sofa you crave.
Popular augmented reality (AR) apps allow you to cut and paste an image of the sofa into a photo of your living room to see if you like it before buying.
A team of researchers at USC Viterbi’s Thomas Lord Department of Computer Science has now developed a similar technique to copy virtual 3D objects and paste them into real indoor scenes. This creates an overall ...
Consumers grapple with confusion over food-date labels
2023-12-13
Consumers grapple with confusion over food-date labels
The use of food-date labels such as “use-by” and “best if used by” causes consumer confusion that results in many Americans discarding food that is safe to eat or donate, according to the November 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural ...
This adaptive roof tile can cut both heating and cooling costs
2023-12-13
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — About half of an average American building’s energy consumption is spent on heating and cooling. That’s a lot of money spent, fossil fuel burned and strain on an aging energy infrastructure during times of severe temperatures.
It’s also a problem UC Santa Barbara researchers Charlie Xiao, Elliot Hawkes and Bolin Liao are hoping to make a dent in. In a paper in the journal Device, the trio present an adaptive tile, which when deployed in arrays on roofs, can lower heating ...
WFIRM and partnering institutions awarded five-year, $6 million grant on kidney, urology, and hematology research
2023-12-13
WINSTON-SALEM, NC, December 13, 2023 - The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) has received a $6 million grant from the National Institute for Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. Alongside five other North Carolina institutions, the collaborative effort aims to address critical issues and advance research in the fields of kidney, urology and hematology. Dr. Anthony Atala, the W. Boyce professor and chair of urology at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and director of WFIRM, Dr. Ronald Falk, Nan and Hugh Cullman Eminent professor of medicine at UNC, and Dr. Thomas Ortel, professor of medicine ...
Beef farming that keeps cattle on lifelong grass diets may have higher carbon footprint
2023-12-13
Beef operations that keep cattle on lifelong grass-based diets may have an overall higher carbon footprint than those that switch cattle to grain-based diets partway through their lives. Daniel Blaustein-Rejto of the Breakthrough Institute, USA, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on December 13.
Cattle on lifelong grass diets are known as “pasture finished,” while those that switch from grass to grain before slaughter are “grain finished.” Prior research has suggested that ...
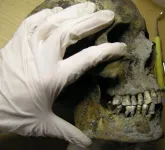
Vikings in Sweden suffered from tooth decay
2023-12-13
Vikings in Sweden suffered from painful dental issues and occasionally tried to treat them, according to a study published December 13, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Carolina Bertilsson of the University of Gothenburg, Sweden and colleagues.
In 2005, excavations in Varnhem, Sweden uncovered the remains of a Christian church, nearby which was a cemetery containing thousands of Viking graves dating to the 10th-12th century AD. In this study, Bertilsson and colleagues performed clinical and radiographical examination of the dentition of individuals from this site. In total, the team analyzed over 2300 teeth ...
The methane and nitrous oxide we exhale might contribute - in a very small way - to greenhouse gas emissions, with breath analysis indicating this may comprise up to 0.1% of UK emissions of the gases
2023-12-13
The methane and nitrous oxide we exhale might contribute - in a very small way - to greenhouse gas emissions, with breath analysis indicating this may comprise up to 0.1% of UK emissions of the gases
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295157
Article Title: Measurements of methane and nitrous oxide in human breath and the development of UK scale emissions
Author Countries: UK
Funding: The analysis was funded by the UK NERC grant E/S003614/2 ‘Detection and Attribution of Regional greenhouse gas Emissions in the UK (DAREUK)’. ...
Moms who participate in baby massage report reduced postnatal depression symptoms and better interactions with their child, per systematic review
2023-12-13
Moms who participate in baby massage report reduced postnatal depression symptoms and better interactions with their child, per systematic review
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0294156
Article Title: The effectiveness of mother-led infant massage on symptoms of maternal postnatal depression: A systematic review
Author Countries: Ireland
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Yoga nidra might be a path to better sleep and improved memory
2023-12-13
Practicing yoga nidra—a kind of mindfulness training— might improve sleep, cognition, learning, and memory, even in novices, according to a pilot study publishing in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on December 13 by Karuna Datta of the Armed Forces Medical College in India, and colleagues. After a two-week intervention with a cohort of novice practitioners, the researchers found that the percentage of delta-waves in deep sleep increased and that all tested cognitive abilities improved.
Unlike more active forms of yoga, which focus on physical postures, breathing, and muscle control, yoga nidra guides people into a state of conscious relaxation ...
Cognitive strategies for augmenting the body with a wearable, robotic arm
2023-12-13
Neuroengineer Silvestro Micera develops advanced technological solutions to help people regain sensory and motor functions that have been lost due to traumatic events or neurological disorders. Until now, he had never before worked on enhancing the human body and cognition with the help of technology.
Now in a study published in Science Robotics, Micera and his team report on how diaphragm movement can be monitored for successful control of an extra arm, essentially augmenting a healthy individual with a third – robotic – arm.
“This study opens up new and exciting opportunities, ...
Earliest evidence for domestic yak found using both archaeology, ancient DNA
2023-12-13
The high-altitude hero of the Himalayas, yak are among the few large animals that can survive the extremely cold, harsh and oxygen-poor conditions of the Tibetan Plateau. In the mountainous regions of Asia, yak and yak-cattle hybrids serve as vital sources of meat, milk, transportation and fuel. However, little is known about their history: when or where yak were domesticated.
In a study published Dec. 13 in Science Advances, an international team of researchers that includes archaeologists at Washington University in St. Louis report archaeologically and genetically confirmed evidence for domestic yak, dating back 2,500 years, by far the oldest record.
The researchers ...
Deep neural networks show promise as models of human hearing
2023-12-13
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Computational models that mimic the structure and function of the human auditory system could help researchers design better hearing aids, cochlear implants, and brain-machine interfaces. A new study from MIT has found that modern computational models derived from machine learning are moving closer to this goal.
In the largest study yet of deep neural networks that have been trained to perform auditory tasks, the MIT team showed that most of these models generate internal representations ...
[1] ... [1484]
[1485]
[1486]
[1487]
[1488]
[1489]
[1490]
[1491]
1492
[1493]
[1494]
[1495]
[1496]
[1497]
[1498]
[1499]
[1500]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.