Researchers discover key to epithelial cell growth
2023-12-21
RESEARCHERS DISCOVER KEY TO EPITHELIAL CELL GROWTH
Australian researchers have discovered a new way that epithelial cells, which form layers in organs like the skin and stomach, attach to one another, and how they perceive growth signals at these attachments, helping them form tissues of the right size and shape.
Epithelial cells cover the surfaces of most organs in the body and must adhere to each other to form both a protective and permeable barrier. They are exquisitely designed to both be tightly sealed against pathogens like bacteria, and to also allow the transport of salts, fluids, and nutrients.
Researchers, led by Professor Kieran Harvey and Dr Benjamin Kroeger, at the ...
Race and ethnicity of infants enrolled in neonatal clinical trials
2023-12-21
About The Study: This systematic review of 120 studies with 14,000 participants found that Asian, Black, Hispanic, and Indigenous (e.g., Alaska Native, American Indian, and Native Hawaiian) participants were underrepresented in neonatal clinical trials, while white participants were overrepresented. There was wide variation in the terms used to report race and ethnicity data, and geographic representation was unevenly distributed, with some central and western U.S. regions underrepresented.
Authors: Elliott M. Weiss, M.D., M.S.M.E., of the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Wearable biosensing to predict imminent aggressive behavior in psychiatric inpatient youths with autism
2023-12-21
About The Study: The results of this study involving 70 youths with autism across four psychiatric inpatient hospitals suggest that wearable biosensing and machine learning may hold promise for identifying objective indicators of impending aggressive behaviors in youths with autism who are psychiatric inpatients. The findings may lay the groundwork for developing just-in-time adaptive intervention mobile health systems that may enable new opportunities for preemptive intervention.
Authors: Matthew S. Goodwin, Ph.D., of Northeastern University in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Back to the future: Weizmann Institute scientists develop the first method to measure cellular changes in the body over time
2023-12-21
While physicists continue to argue about whether time is indeed an illusion, as Albert Einstein claimed, biologists have no doubt about its significance for understanding life as a dynamic system. In recent years, they have been gaining an increasingly deeper understanding of complex biological systems using tools enabling the simultaneous analysis of vast amounts of cellular and molecular data and the probing of cellular circuitry that drives disease. However, these in-depth investigations of how cells behave and interact have provided only separate snapshots of what happens inside complex organisms, without accounting ...
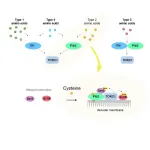
The key mechanism to cell growth has been elucidated
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Amino acids are the building blocks of life. We obtain them from the food we eat, and the body uses them to make proteins, which in turn are used for growth, development, and a multitude of other functions. However, before the body can build with these blocks, it must first be able to sense their presence.
When amino acids are available, a master regulator protein called TORC1 is switched on, causing proteins to be manufactured and cells to grow. If no amino acids are available, TORC1 is switched off, and cells start to recycle themselves in a process known as autophagy. Until now, it was unclear exactly how amino acids triggered the TORC1 switch in yeast.
Now, in a study ...
One of the keys to healthy sleep and blood sugar has been found
2023-12-21
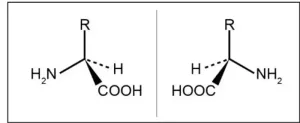
Osaka, Japan – Only recently was it discovered that amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, exist in two different forms: L- and D-forms. While all natural proteins consist exclusively of L-amino acids, the function of D-amino acids remained poorly understood, despite being present in the food we eat every day.
Now, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University has revealed a function of one D-form amino acid: D-alanine. So, what does it do, and how did they uncover its function? To understand, we need a little background information.
The circadian clock, a natural ...
Artery calcification more common in night owls
2023-12-21
Artery calcification is almost twice as common in night owls compared to early birds, according to a study from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden. Circadian function appears to be particularly important during the early stages of cardiovascular disease.
Atherosclerosis involves fatty deposits accumulating on the inside of the arteries, making it harder for blood to pass through. The disease develops over a very long period of time and is not noticed until it leads to blood clots causing angina, heart attack, or stroke. Previous research has shown that people with late-night habits have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, but this is the first study to show how circadian rhythms ...
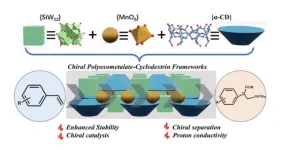
Scientists create chiral POM-based frameworks with enhanced stability and catalytic activity
2023-12-21
A team of scientists has created a chiral assembly by blending inorganic polyoxometalates and organic cyclodextrin molecules. Polyoxometalates are a class of nanomaterials with many useful applications. But the use of polyoxometalates as building blocks to construct chiral POM-based frameworks has been a long-stranding challenge for researchers. In this research, the team produced a 3D framework, constructed by coordination assembly. The resulting framework features an interlaced organic-inorganic hybrid layer.
The team has published their work in the journal, Polyoxometalates, ...
Smithsonian-led study reveals five new species of soft-furred hedgehogs from Southeast Asia
2023-12-21
A new study led by scientists at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History identifies five new species of soft-furred hedgehogs from Southeast Asia.
The study, published in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, used DNA analysis and physical characteristics to describe two entirely new species of soft-furred hedgehogs and elevate three subspecies to the level of species.
The two new species, named Hylomys vorax and H. macarong, are endemic to the endangered Leuser ecosystem, a tropical rainforest in North Sumatra and Southern Vietnam, respectively. The museum specimens that were vital to describing these two new species came from the natural history collections ...
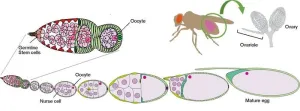
Bugs that help bugs: How environmental microbes boost fruit fly reproduction
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – For many of us, when we think of microbiomes, our first thoughts are probably about the beneficial microorganisms that live in our guts. But now, researchers from Japan and US have discovered how the microbes living in fruit flies can enhance their reproduction.
In a recently published study in Communications Biology, the research group has revealed that microbes in the fruit fly microbiome are involved in controlling the germline stem cells that form eggs, as well as subsequent egg maturation, in female fruit ...
Sleep deprivation makes us less happy, more anxious
2023-12-21
Sleep loss does more than just make us tired. It can undermine our emotional functioning, decrease positive moods and put us at higher risk for anxiety symptoms, according to a study published by the American Psychological Association that synthesized more than 50 years of research on sleep deprivation and mood.
“In our largely sleep-deprived society, quantifying the effects of sleep loss on emotion is critical for promoting psychological health,” said study lead author Cara Palmer, PhD, of Montana State University. “This study represents ...
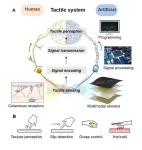
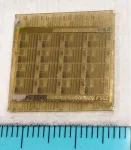
KIMM develops real-time multimodal tactile detection system applicable to robots and wearable devices
2023-12-21
A tactile perception system capable of providing human-like multimodal tactile information to objects like robots and wearable devices that require tactile data in real time has been developed.
The research team led by Research Director Hyuneui Lim of the Nano-Convergence Manufacturing Systems Research Division and Principle Researcher Youngdo Jung of the Department of Nature-Inspired System and Application of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (Chairman Seog-hyeon Ryu, hereinafter referred to as the “KIMM”), an institute under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Science and ICT, developed a real-time and ...
New 1.5-billion-pixel ESO image shows Running Chicken Nebula in unprecedented detail
2023-12-21
While many holiday traditions involve feasts of turkey, soba noodles, latkes or Pan de Pascua, this year, the European Southern Observatory (ESO) is bringing you a holiday chicken. The so-called Running Chicken Nebula, home to young stars in the making, is revealed in spectacular detail in this 1.5-billion-pixel image captured by the VLT Survey Telescope (VST), hosted at ESO’s Paranal site in Chile.
This vast stellar nursery is located in the constellation Centaurus (the Centaur), at about 6500 light-years from Earth. Young stars within this nebula emit intense radiation that makes the surrounding hydrogen gas glow in shades ...
Light exercise could be the key to reversing childhood obesity linked to sedentariness
2023-12-21
Increased sedentary time as a child through adolescence is directly linked to childhood obesity, but new research has found light physical activity may completely reverse the adverse process.
The study - conducted in collaboration with between University of Exeter, University of Eastern Finland, University of Bristol, and University of Colorado and published in Nature Communications – is the largest and longest follow-up to objectively measure physical activity and fat mass, using the University of Bristol’s Children of the 90s data (also known as the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children). ...
Are diamonds GaN’s best friend? Revolutionizing transistor technology
2023-12-21
Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University are proving that diamonds are so much more than just a girl’s best friend. Their groundbreaking research focuses on gallium nitride (GaN) transistors, which are high-power, high-frequency semiconductor devices used in mobile data and satellite communication systems. With the increasing miniaturization of semiconductor devices, problems arise such as increases in power density and heat generation that can affect the performance, reliability, and lifetime of these devices. Therefore, effective thermal management is crucial. Diamond, ...
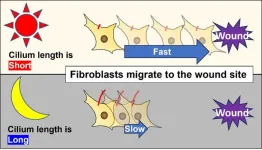
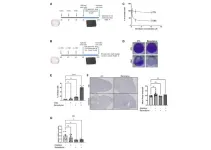
New study examines the relationship between the rate of wound healing, the circadian rhythm, and ‘hair’ on cells
2023-12-21
Nearly every organism on Earth follows a natural circadian rhythm that is coded by your cell’s clock genes, which do exactly as you suspect from the name: regulate your body’s rhythm on a 24-hour basis. Most cells in mammalian bodies have cilia of some sort, which are hair-like structures that perform a variety of functions such as movement for motile cilia and aiding in structure in function for non-motile, or primary, cilia. The primary cilia also act as a sensory organ for the cell, a function which has illuminated ...
Great British Bake Off Christmas desserts not as naughty as you may think
2023-12-21
Christmas desserts from The Great British Bake Off are more likely to use ingredients that are associated with reductions, rather than increases, in the risk of death or disease, suggests research published in the Christmas issue of The BMJ.
As the holiday season approaches, the age-old debate resurfaces: can we indulge in Christmas desserts without feeling the pang of guilt? Can we look past the negative headlines of what butter and sugar do to our bodies, and enjoy a piece of Christmas cake in heavenly peace?
To answer this Christmas conundrum, researchers set out to determine ...
Spike in morning after pill sales in the U.S. after New Year celebrations
2023-12-21
Sales of emergency contraception are estimated to rise by around 10% in the US in the week after the New Year holiday, suggesting that this period is associated with increased risks of unprotected sex compared with other holidays, finds a study published in the Christmas issue of The BMJ.
Other holidays such as Valentine’s Day and Independence Day were also associated with an increase in sales, but to a lesser extent.
Although this annual spike in sales might seem humorous, the researchers point out that as many US states have increased restrictions on abortion ...
The evolutionary timeline of diminished boric acid and urea transportation in aquaporin 10
2023-12-21
Aquaporin (Aqp) 10 water channels in humans allow the free passage of water, glycerol, urea, and boric acid across cells. However, Aqp10.2b in pufferfishes allows only the passage of water and glycerol and not urea and boric acid. Researchers from the Tokyo Institute of Technology sought to understand the evolutionary timeline that resulted in the variable substrate selection mechanisms among Aqp10s. Their results indicate that Aqp10.2 in ray-finned fishes may have reduced or lost urea and boric acid permeabilities through evolution.
Aquaporins ...
Wildflowers increasingly doing without insect pollinators
2023-12-21
Scientists at the CNRS and the University of Montpellier1 have discovered that flowering plants growing in farmland are increasingly doing without insect pollinators. As reproduction becomes more difficult for them in an environment depleted in pollinating insects, the plants are evolving towards self-fertilisation. These findings are published in a paper in the journal New Phytologist dated December 20, 2023.
By comparing field pansies growing in the Paris region today with pansies from the same localities resurrected in the laboratory from seeds collected2 between 1992 and 2001, the research team found that today's flowers are 10% smaller, produce 20% less nectar, and are less ...
Blue PHOLEDs: Final color of efficient OLEDs finally viable in lighting
2023-12-21
Dec. 20, 2023
Contact: Derek Smith, 734-546-3632, smitdere@umich.edu; Nicole Casal Moore, 734-709-1651, ncmoore@umich.edu
ANN ARBOR—Lights could soon use the full color suite of perfectly efficient organic light-emitting diodes, or OLEDs, that last tens of thousands of hours, thanks to an innovation from physicists and engineers at the University of Michigan.
The U-M team's new phosphorescent OLEDs, commonly referred to as PHOLEDs, can maintain 90% of the blue light intensity for 10-14 times longer than other designs that emit similar deep blue colors. That kind ...
Multitasking microbes: UW–Madison scientists engineer bacteria to make two valuable products from plant fiber
2023-12-20
We often look to the smallest lifeforms for help solving the biggest problems: Microbes help make foods and beverages, cure diseases, treat waste and even clean up pollution. Yeast and bacteria can also convert plant sugars into biofuels and chemicals traditionally derived from fossil fuels — a key component of most plans to slow climate change.
Now University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers have engineered bacteria that can produce two chemical products at the same time from underutilized plant fiber. And unlike humans, these ...
And now, your community health forecast…
2023-12-20
In the not-so-distant future, people might be able to tune in to their favorite news source for an update on their community health status, just as they check on the local weather forecast.
The community health status is similar to the color-coded Doppler weather data that provides meteorologists with information about rain, snow or hail, its motion and intensity, which they can use to determine specific areas where dangerous weather conditions exist. Having this information has proven to be a valuable tool to protect life and property.
“The new community ...
A framework in your brain for organising the order of things
2023-12-20
Scientists at NTNU’s Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience in Norway have discovered a pattern of activity in the brain that can serve as a template for building sequential experiences.
“I believe we have found one of the brain’s prototypes for building sequences” says Professor Edvard Moser.He describes the activity pattern as “a fundamental algorithm that is intrinsic to the brain and independent of experience.”
The breakthrough discovery was published in Nature 20. December 2023.
The ability to organise elements into sequences ...
Benidipine calcium channel blocker improves cigarette smoke-induced lung emphysema
2023-12-20
A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Benidipine calcium channel blocker promotes the death of cigarette smoke-induced senescent cells and improves lung emphysema.”
Smoking is the main risk factor for many lung diseases including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cigarette smoke (CS) contains carcinogenic and reactive oxygen species that favor DNA mutations and perturb the homeostasis and environment of cells. CS induces lung cell senescence resulting in a stable proliferation arrest and a senescence-associated ...
[1] ... [1480]
[1481]
[1482]
[1483]
[1484]
[1485]
[1486]
[1487]
1488
[1489]
[1490]
[1491]
[1492]
[1493]
[1494]
[1495]
[1496]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.