Reprogrammed fat cells support tumor growth
2024-01-03
Mutations of the tumor suppressor p53 not only have a growth-promoting effect on the cancer cells themselves, but also influence the cells in the tumor's microenvironment. Scientists at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the Weizmann Institute in Israel have now shown that p53-mutated mouse breast cancer cells reprogram fat cells. The manipulated fat cells create an inflammatory microenvironment, impairing the immune response against the tumor and thus promoting cancer growth.
No other gene is mutated as frequently in human tumors as the gene for the tumor suppressor p53. In around 30 percent of all cases of breast cancer, the cancer cells show mutations or losses ...
Early primates likely lived in pairs
2024-01-03
Primates – and this includes humans – are thought of as highly social animals. Many species of monkeys and apes live in groups. Lemurs and other Strepsirrhines, often colloquially referred to as “wet-nosed” primates, in contrast, have long been believed to be solitary creatures, and it has often been suggested that other forms of social organization evolved later. Previous studies have therefore attempted to explain how and when pair-living evolved in primates.
More recent research, however, indicates that many nocturnal Strepsirrhines, which are more challenging to investigate, are not in fact solitary but live in pairs of males and females. But ...
Foundation laid for improved diagnostic imaging of brain tumors
2024-01-03
Research team draws up criteria for PET-based examinations of malignant brain tumors
Diffuse gliomas are malignant brain tumors that cannot be optimally examined by means of conventional MRI imaging. So-called amino acid PET scans are better able to image the activity and spread of gliomas. An international team of researchers (RANO Working Group), led by scientists from LMU and the Medical University of Vienna, has now drawn up the first ever international criteria for the standardized imaging of gliomas using amino acid PET. It has published its results ...
Magnetic fields in the Cosmos: dark matter could help us discover their origin
2024-01-03
The mini-halos of dark matter scattered throughout the Cosmos could function as highly sensitive probes of primordial magnetic fields. This is what emerges from a theoretical study conducted by SISSA and published in Physical Review Letters. Present on immense scales, magnetic fields are found everywhere in the Universe. However, their origin are still subjects of debate among scholars. An intriguing possibility is that magnetic fields originated near the birth of the universe itself, that is they are primordial magnetic fields. In the study, researchers showed that if magnetic fields are indeed primordial then it could cause an increase in dark matter density perturbations ...
Pusan National University researchers boost signal amplification in perovskite nanosheets
2024-01-03
Perovskite materials are still attracting a lot of interest in solar cell applications. Now, the nanostructures of perovskite materials are being considered as a new laser medium. Over the years, light amplification in perovskite quantum dots has been reported, but most of the works present inadequate quantitative analysis. To assess the light amplification ability, “gain coefficient” is necessary, whereby the essential characteristic of a laser medium is revealed. An efficient laser medium is one that has a large gain.
Scientists have been exploring ways to boost this gain. Now, in a recent study, a team of researchers, led by Professor ...
PolyU researchers develop nature-inspired advanced materials to achieve 99.6% solar reflectivity
2024-01-03
Scientific researchers draw inspiration from nature’s brilliance as they seek to develop transformative solutions to unresolved challenges. Prof. WANG Zuankai, Associate Vice President (Research and Innovation) and Chair Professor of the Department of Mechanical Engineering of The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU), has meticulously explored the intricacies of nature and made remarkable findings with very significant real-world applications. His recently published research on cooling ceramic successfully translates novel discovery into sustainable applications.
Findings from his research project “Hierarchically structured passive radiative cooling ceramic with high ...
Study: Acetaminophen use during pregnancy linked to language delays in children
2024-01-03
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Acetaminophen is considered the safest over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer available during pregnancy. Studies have shown that 50%-65% of women in North America and Europe take acetaminophen during pregnancy. A new study from researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign explored the relationship between acetaminophen use during pregnancy and language outcomes in early childhood. It found that increasing acetaminophen use was associated with language delays.
The findings are reported in the journal Pediatric ...
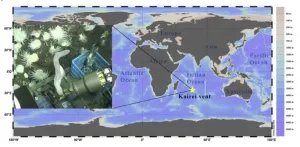
Some sea cucumbers like it hot
2024-01-03
Hydrothermal vents are an unlikely environment for animals to flourish, characterized by rapid changes in temperature and a challenging chemistry: acidic pH, rich in sulfur and methane. Not to mention the high hydrostatic pressure and the darkness of the deep sea. A team of scientists at the Sanya Institute of Deep-sea Science and Engineering (China) have now sequenced the full genome of a particularly unusual inhabitant of the hydrothermal vent environment: the sea cucumber Chiridota heheva. The research has been published in the Open Science ...
New reasons eating less fat should be one of your resolutions
2024-01-03
A UC Riverside study to motivate your new year’s resolutions: it demonstrates that high-fat diets affect genes linked not only to obesity, colon cancer and irritable bowels, but also to the immune system, brain function, and potentially COVID-19 risk.
While other studies have examined the effects of a high-fat diet, this one is unusual in its scope. UCR researchers fed mice three different diets over the course of 24 weeks where at least 40% of the calories came from fat. Then, they looked not only at the microbiome, but also at genetic changes in all four parts of the intestines.
One group of ...
Job ads with wide pay ranges can deter applicants
2024-01-03
PULLMAN, Wash. – As more states require employers to list compensation on job ads, a trending strategy to use very wide pay ranges could potentially harm recruitment, according to a Washington State University study.
The study, published in the Journal of Applied Psychology, found that participants in three different experiments were more likely to respond negatively to job ads with very wide pay ranges, viewing those employers as less trustworthy. Prior surveys have found that most people report they would trust organizations that include pay ranges in ...
What makes urine yellow? UMD scientists discover the enzyme responsible
2024-01-03
Researchers at the University of Maryland and National Institutes of Health have identified the microbial enzyme responsible for giving urine its yellow hue, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Microbiology on January 3, 2024.
The discovery of this enzyme, called bilirubin reductase, paves the way for further research into the gut microbiome’s role in ailments like jaundice and inflammatory bowel disease.
“This enzyme discovery finally unravels the mystery behind urine’s yellow color,” said the study’s lead author Brantley Hall, an assistant ...
Non-toxic quantum dots pave the way towards CMOS shortwave infrared image sensors for consumer electronics
2024-01-03
Invisible to our eyes, shortwave infrared (SWIR) light can enable unprecedented reliability, function and performance in high-volume, computer vision first applications in service robotics, automotive and consumer electronics markets. Image sensors with SWIR sensitivity can operate reliably under adverse conditions such as bright sunlight, fog, haze and smoke. Furthermore, the SWIR range provides eye-safe illumination sources and opens up the possibility of detecting material properties through molecular imaging.
Colloidal quantum ...
Complex, unfamiliar sentences make the brain’s language network work harder
2024-01-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- With help from an artificial language network, MIT neuroscientists have discovered what kind of sentences are most likely to fire up the brain’s key language processing centers.
The new study reveals that sentences that are more complex, either because of unusual grammar or unexpected meaning, generate stronger responses in these language processing centers. Sentences that are very straightforward barely engage these regions, and nonsensical sequences of words don’t do much for them either.
For ...
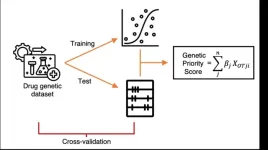
Novel genetic priority score unveiled to enhance target prioritization in drug development
2024-01-03
New York, NY [January 3, 2024]—Driven by the need for a better way to prioritize targets for drug development, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has led the development of a novel “genetic priority score” (GPS) that will integrate various types of human genetic data into a single easy-to-interpret score.
The findings were described in the January 3 online issue of Nature Genetics [DOI: 10.1038/s41588-023-01609-2].
Studies have shown that drugs have an increased likelihood of success in clinical trials when ...
Microbial awakening restructures high-latitude food webs as permafrost thaws
2024-01-03
Alaska is on the front lines of climate change, experiencing some of the fastest rates of warming of any place in the world. And when temperatures rise in the state’s interior—a vast high-latitude region spanning 113 million acres—permafrost there not only thaws, releasing significant amounts of its stored carbon back into the atmosphere where it further accelerates rising temperatures, but it decays. This decomposition has the potential to infuse above- and belowground food webs with carbon, which can affect ...
Bacteria load their syringes
2024-01-03
Disease-causing bacteria of the genus Salmonella or Yersinia can use tiny injection apparatuses to inject harmful proteins into host cells, much to the discomfort of the infected person. However, it is not only with a view to controlling disease that researchers are investigating the injection mechanism of these so-called type III secretion systems, also known as "injectisomes".
If the structure and function of the injectisome were fully understood, researchers would be able to hijack it to deliver specific drugs into cells, such as cancer cells. In fact, the structure of the injectisome has already been elucidated. ...
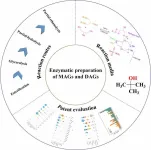
Greener and feasible production: Enzymatic methods for mono- and diacylglycerol synthesis in the food industry
2024-01-03
MAGs, predominantly in 1(3)-MAG form, and DAGs, with 1,3-DAGs as the more stable isomer, are crucial in food, cosmetic, and other industries. While MAGs are vital emulsifiers, comprising 75% of global production, DAGs are known as functional cooking oils that can reduce body fat and serum TAGs. However, their natural concentration in oils is low, prompting extensive research into their chemical and environmentally-friendly enzymatic production.
Recently, a review published in the Grain & Oil Science and Technology journal on 2 November 2023, has shed light on the advancements in enzymatic production methods with special efforts on practical and ...
Re-calibrating the sail plan for Native Hawaiians, Pacific Islanders in ocean sciences
2024-01-03
In Hawaiʻi and across much of Oceania, Pacific Islanders celebrate the connections between their islands and the ocean that surrounds them. “As descendants of the ocean, the dearth of Native Hawaiians and Pacific Islanders (NHPI) in ocean science seems inconsonant,” writes a team of authors that includes University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa faculty, students, and alumni in an article in a special issue of the journal Oceanography, “Building Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in the Ocean Sciences. The authors ask, “Where are all our island people in the ...
Monetized evaluation of landscape resources of national parks based on the willingness to pay of multiple interest groups
2024-01-03
In China, national parks represent the country’s most unique natural landscapes. Scientific evaluation of landscape resources is significant for preserving the authenticity and integrity of national parks. Taking Qianjiangyuan National Park System Pilot Zone as an example, this research investigated the willingness of internal group (residents and administrative staff) and external group (tourists) to pay for a hypothetical market project based on the pilot zone via Contingent Valuation Method to acquire the monetized value of landscape resources in the national park, and applied Logistic Regression to analyze the influencing factors. The results show ...
How big data transforms the insurance sector
2024-01-03
In 2022, the insurance industry made a whopping USD 6 trillion globally—more than the entire economy of big countries like Japan and Germany. A new study, published in The Journal of Finance and Data Science, looked at how technology, especially big data, is shaking things up in insurance. Big data means using a lot of information to make better decisions.
The study found that by using big data, insurance companies can understand risks better, offer fair prices and keep customers happier.
“What's surprising is how fast insurance companies are jumping on the big data bandwagon,” says first ...
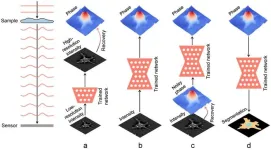
Deep learning for phase recovery
2024-01-03
Light, as an electromagnetic field, has two essential components: amplitude and phase. However, optical detectors, usually relying on photon-to-electron conversion (such as charge-coupled device sensors and the human eye), cannot capture the phase of the light field because of their limited sampling frequency. Fortunately, as the light field propagates, the phase delay also causes changes in the amplitude distribution; therefore, we can record the amplitude of the propagated light field and then calculate the corresponding phase, called phase recovery. Some common phase ...
Chicken whisperers: humans crack the clucking code
2024-01-03
A University of Queensland-led study has found humans can tell if chickens are excited or displeased, just by the sound of their clucks.
Professor Joerg Henning from UQ’s School of Veterinary Science said researchers investigated whether humans could correctly identify the context of calls or clucking sounds made by domestic chickens, the most commonly farmed species in the world.
“In this study, we used recordings of chickens vocalising in all different scenarios from a previous experiment,” ...
Newly discovered genetic mutation protects against Parkinson’s disease and offers hope for new therapies
2024-01-03
A previously unidentified genetic mutation in a small protein provides significant protection against Parkinson’s disease and offers a new direction for exploring potential treatments, according to a new USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology study.
The variant, located in a mitochondrial microprotein dubbed SHLP2, was found to be highly protective against Parkinson’s disease; individuals with this mutation are half as likely to develop the disease as those who do not carry it. The variant form of the protein is relatively rare and is found primarily in people of European descent.
The findings appear on January 3, 2024, in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
First ...
First dive survey of Lake Tahoe’s lakebed finds high amounts of plastic and other litter
2024-01-03
Plastic litter is a growing problem around the world, and new research shows that the bottom of Lake Tahoe is no exception. In one of the first studies to utilize scuba divers to collect litter from a lakebed, 673 plastic items were counted from just a small fraction of the lake.
In the study, published in the November issue of the journal Applied Spectroscopy, researchers from DRI and the UC Davis Tahoe Environmental Research Center teamed up with the nonprofit Clean Up the Lake to take a close look at the litter. First, ...
Study on extremely preterm infants provides important healthcare knowledge
2024-01-03
Infants born extremely prematurely need to get enrichment as an addition to breast milk. But does it make any difference whether the enrichment is made from breast milk or cow’s milk when it comes to the risk of severe complications in children? This has been investigated by a large clinical study led from Linköping, Sweden.
Infants born extremely prematurely, between weeks 22 and 27 of pregnancy, are among the most vulnerable patients in healthcare. The risk of serious complications is very high. Almost one in four extremely premature babies die before the age of one.
There is strong research support for giving breast ...
[1] ... [1472]
[1473]
[1474]
[1475]
[1476]
[1477]
[1478]
[1479]
1480
[1481]
[1482]
[1483]
[1484]
[1485]
[1486]
[1487]
[1488]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.