Octopus DNA reveals West Antarctic Ice Sheet collapse during Last Interglacial
2023-12-21
Genetic analyses of an Antarctic octopus show that the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) collapsed during the Last Interglacial ~129,000 to 116,000 years ago when temperatures were only about 1 degree Celsius (°C) warmer than preindustrial levels. The findings suggest that WAIS collapse and resultant sea-level rise could be caused by even the minimal temperature rises projected by the most optimistic climate change mitigation plans. Climate change is driving unprecedented change to Earth’s cryosphere. The West Antarctic Ice Sheet is considered particularly vulnerable to warming ...
Can cryptocurrencies be legal tender? A case study from El Salvador
2023-12-21
In El Salvador, preference for cash and privacy fears deterred the widespread adoption of Bitcoin as an everyday currency, researchers report. The findings suggest that policies incentivizing cryptocurrency adoption as legal tender will likely fail unless populations are financially literate and already trust digital currencies. The introduction of digital currencies is one of the most important developments in monetary economics in the last decade. Unlike traditional digital currencies, which rely on central authorities such as governments or banks governed by regulations ...
Researchers map how measles virus spreads in human brain
2023-12-21
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic researchers mapped how the measles virus mutated and spread in the brain of a person who succumbed to a rare, lethal brain disease. New cases of this disease, which is a complication of the measles virus, may occur as measles reemerges among the unvaccinated, say researchers.
Using the latest tools in genetic sequencing, researchers at Mayo Clinic reconstructed how a collective of viral genomes colonized a human brain. The virus acquired distinct mutations that drove the spread of the virus from the frontal cortex outward.
"Our study provides compelling data that ...
Organic compounds in asteroids formed in colder regions of space: study
2023-12-21
Analysis of organic compounds – called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) – extracted from the Ryugu asteroid and Murchison meteorite has found that certain PAHs likely formed in the cold areas of space between stars rather than in hot regions near stars as was previously thought. The findings open new possibilities for studying life beyond Earth and the chemistry of objects in space.
The only Australian members of an international research team, scientists from Curtin’s WA-Organic ...
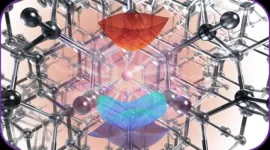
Advanced computational tool for understanding quantum materials
2023-12-21
Researchers at the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME), Argonne National Laboratory, and the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia have developed a new computational tool to describe how the atoms within quantum materials behave when they absorb and emit light. The tool will be released as part of the open-source software package WEST, developed within the Midwest Integrated Center for Computational Materials (MICCoM) by a team led by Prof. Marco ...
Role of enzyme SMYD3 clarified in prostate cancer progression
2023-12-21
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men other than skin cancer, and more than 288,000 new cases are diagnosed every year, according to the American Cancer Society. The disease’s fatality rate has decreased by more than half since the 1990s, but there is still room for progress—especially in treating or preventing advanced, metastatic disease, which is much more likely to be fatal.
A new paper published in Science Advances clarifies how an enzyme called SMYD3 may be involved in prostate ...
Professor Vladimir A. Botchkarev, Boston University School of Medicine, receives Skin Ageing & Challenges Best Scientific Award 2023
2023-12-21
The Skin Ageing & Challenges 2023 conference, held in November 2023 in Lisbon, has recognized the outstanding contributions of Prof. Vladimir A. Botchkarev, a distinguished Professor of Dermatology and Co-Director at the Boston University Center for Aging Research, with the prestigious Skin Ageing & Challenges Best Scientific Award 2023. The award acknowledges Prof. Botchkarev's exceptional research in the field of skin biology and aging.
Prof. Botchkarev's award-winning work, titled "Skin Aging in Long-Lived Naked Mole-Rats: Mechanisms and Perspectives", delves into the complicated aging process of Naked Mole Rats' skin. His comprehensive ...
Save the date for the 11th World Congress on Targeting Microbiota 2024 – Revolutionizing Future Medicine
2023-12-21
Targeting Microbiota 2024: Vision, Strategies and Perspectives
The 11th Annual Congress of the International Society of Microbiota (ISM), Targeting Microbiota 2024, is scheduled on October 17-18, at Corinthia Palace Malta. Targeting Microbiota 2024 will not only present the latest advancements but also serve as a pivotal hub for sharing visionary strategies and perspectives that will redefine the landscape of medicine. The Congress promises an immersive experience, offering a dynamic platform for the exchange of ideas, insights, and the exploration of innovative approaches that will shape the future of medicine.
Save the date and ...
Location, location, location: The hidden power of intracellular neighborhoods
2023-12-21
Highlights
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is translated into proteins in the cytoplasm of cells. But rather than being a uniform “soup,” the cytoplasm is divided into multiple distinct compartments or regions.
Each region is largely responsible for translating functionally similar types of mRNA, a new MSK study finds. And the location of translation determines the amount of protein produced by the mRNA.
The movement of mRNA to specific regions is directed by their size and shape, as well as by RNA-binding protein partners.
The findings could help develop new approaches to increase ...
Better prosthetics: $3M to develop more natural robotic leg control
2023-12-21
Dec. 21, 2023
Contact: Nicole Casal Moore, 734-709-1651, ncmoore@umich.edu
Images and videos
Better prosthetics: $3M to develop more natural robotic leg control
An effort to create a control model that moves seamlessly between different activities like standing, walking and climbing stairs is renewed by the National Institutes of Health
ANN ARBOR—A smoother experience for robotic prosthetic leg users is the aim of a University of Michigan project that has received renewed support from the National Institutes of Health. The R01 grant ...
The Council of Medical Specialty Societies awards CHEST a $100,000 grant to improve diagnostic excellence in ILD
2023-12-21
Glenview, IL – The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) was awarded a $100,000 grant from the Council of Medical Specialty Societies (CMSS) to improve diagnostic excellence in interstitial lung disease (ILD).
The funded project, called, "'How We Do It': CHEST Experts Weigh In," aims to inform future best practices in reducing the time to diagnosis for ILDs. The activities in the series will prepare the learner to:
define symptoms and patient profiles associated with ILD;
recognize health inequities that may assist in the diagnosis of ILD;
identify the appropriate tests that may help validate a suspicion of ILD; ...
Center for BrainHealth investigates the impact of auditory beat stimulation on cognition
2023-12-21
Certain Frequencies Enhance Comprehension
New research conducted by the Center for BrainHealth at The University of Texas at Dallas investigates the impact of binaural beat (BB) on language skills. BB is a sound that occurs when two slightly mismatched pure tones are heard. There is a growing interest in using BB as a non-invasive neuromodulation to enhance cognitive performance.
The study, Neural consequences of binaural beat stimulation on auditory sentence comprehension: an EEG study, was recently published in Cerebral Cortex.
Led by researchers in the Speech, Language and Music (SLAM) Lab, this EEG ...
Where you live matters: A first-of-its-kind study illustrates how racism is interrelated with poor health
2023-12-21
Where You Live Matters: A First-of-Its-Kind Study Illustrates How Racism Is Interrelated With Poor Health
Study published in JAMA Network Open points to discrete factors, like voting participation, employment, education, and housing, that may serve as promising targets for interventions
New York, NY (December 21, 2023) – A team of health equity researchers from several institutions has leveraged a complex web of data to test a hypothesis: That structural racism is associated with resources and structures at the neighborhood level that are closely associated with poor health. What they found in an analysis of highly localized, ...
New tool unifies single-cell data
2023-12-21
A new methodology that allows for the categorisation and organisation of single-cell data has been launched. It can be used to create a harmonised dataset for the study of human health and disease.
Researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Cambridge, EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), and collaborators developed the tool, known as CellHint. CellHint uses machine learning to unify data produced across the world, allowing it to be accessed by the wider research community, potentially driving new discoveries.
In a new study, ...
Pancake stack of films on a balloon most accurate gamma-ray telescope
2023-12-21
A pancake stack of radioactivity-sensitive films carried through the sky by a balloon was able to take the world's most accurate picture of a neutron star's gamma ray beam. To achieve this, Kobe University researchers combined the oldest method of capturing radioactive radiation with the newest data capturing techniques and a clever time-recording device.
The stars shine their light on us in the full range of the spectrum of light, from infra-red to gamma rays. For each of these bands, different sensing equipment is needed. The most challenging one is gamma rays, famous for being a high-energy product of nuclear fission, ...
Wireless tracking system could help improve the XR experience
2023-12-21
A new technology developed by engineers at the University of California San Diego has the potential to make the extended reality (XR) experience smoother and more seamless. The technology consists of an asset localization system that uses wireless signals to track physical objects with centimeter-level accuracy in real time, and then generates a virtual representation of these objects. Applications of this technology range from enhancing virtual gaming experiences to improving workplace safety.
The team, led by Dinesh Bharadia, a professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering, ...
Fleeing drought, vulnerable populations face flood risk in most African countries
2023-12-21
American Geophysical Union
Press Release 23-47
21 December 2023
For Immediate Release
This press release is also available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/fleeing-drought-vulnerable-populations-face-flood-risk-in-most-african-countries
AGU press contact:
Liza Lester, +1 (202) 777-7494, news@agu.org (UTC-5 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Serena Ceola, University of Bologna, serena.ceola@unibo.it (GMT+1 hours)
WASHINGTON — In 80% of African countries, moved toward rivers and into cities during or following drought, increasing the number of people living in flood-risk areas in ...
The future of canine stem cell therapy: unprecedented, painless, and feeder-free
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Dog owners may need to learn to appreciate their best friend’s urine. Scientists at Osaka Metropolitan University have devised an efficient, non-invasive, and pain-free method to reprogram canine stem cells from urine samples, bringing furry companions one step closer to veterinary regenerative treatment.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have been widely employed in studies on human generative medicine. With the growing importance of advanced medical care for dogs and cats, there is an expectation that new therapies utilizing iPSCs will ...
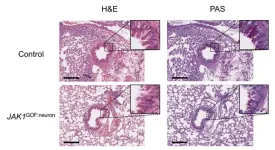
New insights revealed on tissue-dependent roles of JAK signaling in inflammation
2023-12-21
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have gained a deeper understanding of the nuanced roles of JAK inhibitors, or modulators, in inflammation across various cell types and tissues. Their findings suggest a more precise approach is required to potentially expand JAK inhibitor use to a wider range of allergy and inflammatory disorders. Details on the findings were published in the December 21, 2023, issue of the journal Cell.
JAK1 is a key protein in the body that supports cell communication and controls the immune system. It is part of ...
Researchers discover key to epithelial cell growth
2023-12-21
RESEARCHERS DISCOVER KEY TO EPITHELIAL CELL GROWTH
Australian researchers have discovered a new way that epithelial cells, which form layers in organs like the skin and stomach, attach to one another, and how they perceive growth signals at these attachments, helping them form tissues of the right size and shape.
Epithelial cells cover the surfaces of most organs in the body and must adhere to each other to form both a protective and permeable barrier. They are exquisitely designed to both be tightly sealed against pathogens like bacteria, and to also allow the transport of salts, fluids, and nutrients.
Researchers, led by Professor Kieran Harvey and Dr Benjamin Kroeger, at the ...
Race and ethnicity of infants enrolled in neonatal clinical trials
2023-12-21
About The Study: This systematic review of 120 studies with 14,000 participants found that Asian, Black, Hispanic, and Indigenous (e.g., Alaska Native, American Indian, and Native Hawaiian) participants were underrepresented in neonatal clinical trials, while white participants were overrepresented. There was wide variation in the terms used to report race and ethnicity data, and geographic representation was unevenly distributed, with some central and western U.S. regions underrepresented.
Authors: Elliott M. Weiss, M.D., M.S.M.E., of the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Wearable biosensing to predict imminent aggressive behavior in psychiatric inpatient youths with autism
2023-12-21
About The Study: The results of this study involving 70 youths with autism across four psychiatric inpatient hospitals suggest that wearable biosensing and machine learning may hold promise for identifying objective indicators of impending aggressive behaviors in youths with autism who are psychiatric inpatients. The findings may lay the groundwork for developing just-in-time adaptive intervention mobile health systems that may enable new opportunities for preemptive intervention.
Authors: Matthew S. Goodwin, Ph.D., of Northeastern University in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Back to the future: Weizmann Institute scientists develop the first method to measure cellular changes in the body over time
2023-12-21
While physicists continue to argue about whether time is indeed an illusion, as Albert Einstein claimed, biologists have no doubt about its significance for understanding life as a dynamic system. In recent years, they have been gaining an increasingly deeper understanding of complex biological systems using tools enabling the simultaneous analysis of vast amounts of cellular and molecular data and the probing of cellular circuitry that drives disease. However, these in-depth investigations of how cells behave and interact have provided only separate snapshots of what happens inside complex organisms, without accounting ...
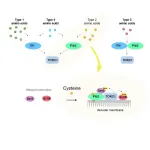
The key mechanism to cell growth has been elucidated
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Amino acids are the building blocks of life. We obtain them from the food we eat, and the body uses them to make proteins, which in turn are used for growth, development, and a multitude of other functions. However, before the body can build with these blocks, it must first be able to sense their presence.
When amino acids are available, a master regulator protein called TORC1 is switched on, causing proteins to be manufactured and cells to grow. If no amino acids are available, TORC1 is switched off, and cells start to recycle themselves in a process known as autophagy. Until now, it was unclear exactly how amino acids triggered the TORC1 switch in yeast.
Now, in a study ...
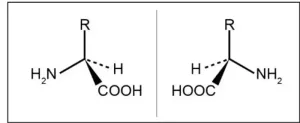
One of the keys to healthy sleep and blood sugar has been found
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Only recently was it discovered that amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, exist in two different forms: L- and D-forms. While all natural proteins consist exclusively of L-amino acids, the function of D-amino acids remained poorly understood, despite being present in the food we eat every day.
Now, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University has revealed a function of one D-form amino acid: D-alanine. So, what does it do, and how did they uncover its function? To understand, we need a little background information.
The circadian clock, a natural ...
[1] ... [1469]
[1470]
[1471]
[1472]
[1473]
[1474]
[1475]
[1476]
1477
[1478]
[1479]
[1480]
[1481]
[1482]
[1483]
[1484]
[1485]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.