Finding that statins could slow dementia stimulates further research
2023-12-20
Blood fat-lowering statins could slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease, at least for some patients. This is the result of a new study led by Karolinska Institutet published in Alzheimer Research and Therapy. But the researchers are cautious in their interpretations and see the results as a first step in a research journey that may eventually provide the answer.
A new study shows that people with Alzheimer's dementia deteriorated more slowly in their cognitive functions if they were also treated with a lipid-lowering ...
Potentially harmful ‘trip-killers’ to cut short ‘bad’ drug trips, emerging concern, warn doctors
2023-12-20
The use of potentially harmful ‘trip-killers’ to cut short ‘bad drug trips’ after taking psychedelics, such as LSD or magic mushrooms, is an emerging concern, warn doctors in a research letter, published online in Emergency Medicine Journal.
Their analysis of relevant threads on the social media platform Reddit, shows that drugs such as benzodiazepines (sedatives) and antipsychotics are the options most frequently recommended, but warnings about their potential side effects are rarely included, they highlight.
The intensity of a psychedelic drug trip can cause distress, agitation, ...
3 potentially unique acoustic features of healing music that transcend genre identified
2023-12-20
There are three potentially unique acoustic features of healing music that transcend musical genres, suggests research published in the open access journal General Psychiatry.
The findings might help to personalise playlists for patients, using artificial intelligence to analyse individual physiological and psychological responses, and help to evaluate the effectiveness of existing music therapies, suggest the researchers.
Despite evidence of the therapeutic effects of music for mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and post traumatic stress disorder, there’s no consensus on what defines healing ...
Diabetes drug may significantly lower women’s risk of substantial weight gain after giving up smoking
2023-12-20
The diabetes drug dulaglutide (Trulicity) may significantly lower a woman’s risk of substantial weight gain after she has given up smoking, finds a secondary analysis of clinical trial data, published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health.
Women seem to be 5 times as likely as men to put on a lot of weight after they’ve stubbed out what they intend to be their last cigarette, the analysis suggests.
Women seem to have higher smoking relapse rates than men. And it’s been suggested that one of the possible explanations for this is that they may be more concerned about ...
Antimicrobial resistance leads to more deaths and illnesses in the WHO African region than anywhere else
2023-12-20
SEATTLE, Wash., Dec. 19, 2023 ‑‑­­ Over 1.05 million deaths were associated with antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and 250,000 deaths were attributable to AMR in the WHO African region, posing an unprecedented health threat. That’s according to a new study published in The Lancet Global Health today.
The number of deaths linked to AMR in the WHO African region is higher than those caused by both HIV/AIDS (639,554) and malaria (594,348), marking a pivotal shift in the health challenges facing the region. Despite the relatively low prevalence of resistance, the WHO African region had the highest burden of AMR mortality, which ...
Groundbreaking discovery at Museums Victoria Research Institute rewrites our understanding of whale evolution
2023-12-20
Groundbreaking new research from the Museums Victoria Research Institute has turned upside down our previous understanding of the evolution of the largest animals ever––baleen whales.
Palaeontologists Dr James Rule (Monash University and Natural History Museum, London) and Dr Erich Fitzgerald (Museums Victoria Research Institute) have co-authored the open access paper ‘Giant baleen whales emerged from a cold southern cradle’, published today in the prestigious journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Until now, it was believed that the beginning of the Ice Age in the ...
Scientists provide recipe to halve pollution from food production
2023-12-20
A major report for the United Nations has put forward solutions to halve nitrogen pollution from agriculture and the food system in Europe, including reducing meat and dairy consumption, fertiliser use and food waste.
Nitrogen, which is vital for plant growth, is present in animal excreta and synthetic fertilisers that are applied to land to boost crop production. But excessive and inefficient use of this nutrient means up to 80% of it leaks into the environment, mostly in various polluting forms of nitrogen: ammonia and nitrogen oxides, which are harmful air pollutants; ...
Huntsman Cancer Institute investigator receives award for metastatic breast cancer research
2023-12-20
Alana Welm, Ph.D., senior director of basic science at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor of oncological sciences at the University of Utah (the U), received the 2023 American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Outstanding Investigator Award for Breast Cancer Research.
“Dr. Welm is an exceptionally talented and internationally-recognized scientist, applying her discoveries to the development of improved breast cancer therapies,” says Neli Ulrich, Ph.D., MS, chief scientific officer and executive director of the comprehensive cancer center at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor of population health sciences at the U. “She has a highly productive research ...
Endometrial cancer: New insights into a deadly disparity
2023-12-20
The numbers are stark and deeply troubling.
Endometrial cancer — which develops in the lining of the uterus (womb) and is sometimes called uterine cancer — is on the rise in the U.S. In 1987, there were 35,000 cases annually. That number has nearly doubled in 2023 to more than 66,000 cases.
Deaths from the disease have also grown alarmingly in the same period, from less than 3,000 to more than 13,000 in the U.S. every year. And the trend line is not getting better.
“Endometrial cancer has been increasing at unprecedented levels over the past five years,” ...
Sanford Burnham Prebys continues unprecedented recruitment of early-career scientists
2023-12-20
Continuing its rapid and dramatic recruitment of emerging, top-tier researchers, Sanford Burnham Prebys has hired two more highly regarded early-career scientists: Angela Liou, M.D., a specialist in pediatric oncology and hematology; and Xueqin Sherine Sun, Ph.D., a cancer biologist and genome engineer.
“With Drs. Liou and Sun, we have now hired eight superb young scientists and physicians in less than a year, an achievement that reflects the extraordinary challenges in biomedical research today and our ambitious plans ...
Research offers a reason why diversity in plant species causes higher farming yield, solving 'a bit of a mystery'
2023-12-20
LAWRENCE — A study appearing in Nature Communications based on field and greenhouse experiments at the University of Kansas shows how a boost in agricultural yield comes from planting diverse crops rather than just one plant species: Soil pathogens harmful to plants have a harder time thriving.
“It’s commonly observed that diverse plant communities can be more productive and stable over time,” said corresponding author James Bever, senior scientist with the Kansas Biological Survey & Center for Ecological Research and Foundation Distinguished Professor of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology at KU. ...
UM School of Medicine review highlights rise in psychiatric disorders linked to increased cannabis use
2023-12-20
The widespread use of cannabis (marijuana) and its increased potency are associated with a rise in cannabis-related psychiatric conditions, according to a new University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) review article that was recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine. It highlights the urgent need for doctors to screen for and treat patients who are experiencing symptoms of cannabis use disorder, which means they are experiencing significant problems from their use of the drug.
Nearly one in five Americans ages 12 and older used cannabis in 2021, according to the article, and more than 16 million met the criteria for ...
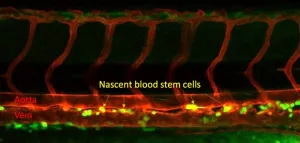
Immune system plays crucial step in creating blood stem cells
2023-12-20
AMES, Iowa – A microbial sensor that helps identify and fight bacterial infections also plays a key role in the development of blood stem cells, valuable new insight in the effort to create patient-derived blood stem cells that could eliminate the need for bone marrow transplants.
The discovery by a research team led by Raquel Espin Palazon, an assistant professor of genetics, development and cell biology at Iowa State University, was published last month in Nature Communications. It builds on prior ...
New grant gives South Carolina life sciences companies a chance to accelerate
2023-12-19
The Medical University of South Carolina is one of nine leading research universities across six states partnering with Innosphere Ventures on its Regional Life Sciences Incubator. Innosphere Ventures is a Colorado-based life sciences incubator with proven methods for propelling startups to successful market entry. Funding from a $2 million three-year Build to Scale Venture Challenge grant from the U.S. Department of Commerce will create a regional incubator that will offer its partnering institutions and selected startups ...
Predicting prenatal care to improve pregnancy outcomes
2023-12-19
Socioeconomic factors, like education and location, can affect access to life-saving prenatal care services. Researchers at Boston Children’s Hospital are taking steps towards implementing strategies that improve access to prenatal care: estimating how many pregnant people attend the recommended number of visits and identifying pregnant people who are at high risk of failing to attend. This could help policymakers allocate resources to populations not getting enough prenatal care and could, in turn, improve health outcomes for mothers and babies.
Led by Grace Chan, M.D., Ph.D., Attending Physician in the Intermediate Care Program at Boston ...
JMIR Medical Education accepted for MEDLINE indexing
2023-12-19
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Medical Education has passed the Scientific Quality Review for MEDLINE and has been accepted for inclusion in MEDLINE, which is the U.S. National Library of Medicine's premier bibliographic database.
JMIR Medical Education was already indexed in PubMed. MEDLINE is a more selective subset of PubMed, consisting of the top 5,200 biomedical journals, and indexing in MEDLINE also means that articles are now also indexed with NLM Medical Subject Headings (MeSH terms) and other metadata.
Selection for MEDLINE is a result of a thorough review ...
Fish display distinct individual behaviours when swimming to find food
2023-12-19
Fish from the same species can evolve their sense of smell and display individual foraging ‘personalities’ to successfully find food in different habitats, according to new research.
In the study, published today as a Reviewed Preprint in eLife, researchers developed a high-throughput behavioural assay to test spontaneous swimming and differences in the sense of smell of individual Mexican cavefish larvae. eLife editors described the work as important, presenting compelling evidence that the surface and cave morphs of the fish show different olfactory preferences and odour sensitivities, and that individual fish show substantial variability in their spontaneous ...
Protein allows poison dart frogs to accumulate toxins safely
2023-12-19
Scientists have identified the protein that helps poison dart frogs safely accumulate their namesake toxins, according to a study published today in eLife.
The findings solve a long-standing scientific mystery and may suggest potential therapeutic strategies for treating humans poisoned with similar molecules.
Alkaloid compounds, such as caffeine, make coffee, tea and chocolate delicious and pleasant to consume, but can be harmful in large amounts. In humans, the liver can safely metabolise modest ...
Toxic chemicals found in oil spills and wildfire smoke detected in killer whales
2023-12-19
Toxic chemicals produced from oil emissions and wildfire smoke have been found in muscle and liver samples from Southern Resident killer whales and Bigg’s killer whales.
A study published today in Scientific Reports is the first to find polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in orcas off the coast of B.C., as well as in utero transfer of the chemicals from mother to fetus.
“Killer whales are iconic in the Pacific Northwest—important culturally, economically, ecologically and more. Because they are able to metabolically process PAHs, these are most likely recent exposures. Orcas are our canary in the coal ...
Schar school researchers to receive funding for nonprofit employment data project
2023-12-19
Schar School Researchers To Receive Funding For Nonprofit Employment Data Project
Alan Abramson, Professor, Government and Politics; Mirae Kim, Associate Professor, Nonprofit Studies; and Stefan Toepler, Professor, Nonprofit Studies, are set to receive funding for: "Nonprofit Employment Data Project."
The researchers will produce a comprehensive report on nonprofit employment in the United States, based on new data that is expected to be released by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) early in 2024. The researchers will also arrange for the transfer of the Nonprofit Works interactive database application, which is currently hosted by Johns ...
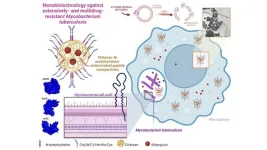
Nanoparticles with antibacterial action shorten duration of tuberculosis treatment
2023-12-19
A low-cost technology involving nanoparticles loaded with antibiotics and other antimicrobial compounds that can be used in multiple attacks on infections by the bacterium responsible for most cases of tuberculosis has been developed by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil and is reported in an article published in the journal Carbohydrate Polymers. Results of in vitro tests suggest it could be the basis for a treatment strategy to combat multidrug bacterial resistance.
According ...
Marzougui & Kan developing crashworthy tangent end treatment for low-speed & curbed roadways
2023-12-19
Marzougui & Kan Developing Crashworthy Tangent End Treatment For Low-Speed & Curbed Roadways
Dhafer Marzougui, Associate Professor, Physics and Astronomy, and Cing-Dao Kan, Professor/Director, Center for Collision Safety and Analysis, received $749,954 from the National Cooperative Highway Research Program for: "Development of a Crashworthy Tangent End Treatment for Low-Speed and Curbed Roadways."
This funding began in Nov. 2023 and will end in Nov. 2026.
###
About George Mason University
George Mason University is Virginia's largest public research university. ...
A malaria drug treatment could save babies’ lives
2023-12-19
Wars, drought, displacement, and instability are causing a dramatic increase in the number of pregnant and breastfeeding women around the world who suffer from malnutrition. Without access to sufficient nutrients in the womb, babies born to these women are more likely to die due to complications like pre-term birth, low birth weight, and susceptibility to diseases like malaria. To try to reduce the risk of malarial infection, the WHO recommends that pregnant women in low-income countries be treated with a combination of the antimalarial drugs sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine ...
Engineered human heart tissue shows Stanford Medicine researchers the mechanics of tachycardia
2023-12-19
Heart rates are easier to monitor today than ever before. Thanks to smartwatches that can sense a pulse, all it takes is a quick flip of the wrist to check your heart. But monitoring the cells responsible for heart rate is much more challenging — and it’s encouraged researchers to invent new ways to analyze them.
Joseph Wu, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Stanford Cardiovascular Institute and professor of medicine and of radiology, has devised a new stem cell-derived model of heart tissue ...
Molecular jackhammers’ ‘good vibrations’ eradicate cancer cells
2023-12-19
The Beach Boys’ iconic hit single “Good Vibrations” takes on a whole new layer of meaning thanks to a recent discovery by Rice University scientists and collaborators, who have uncovered a way to destroy cancer cells by using the ability of some molecules to vibrate strongly when stimulated by light.
The researchers found that the atoms of a small dye molecule used for medical imaging can vibrate in unison ⎯ forming what is known as a plasmon ⎯ when stimulated by near-infrared light, causing the cell membrane of cancerous cells to rupture. ...
[1] ... [1471]
[1472]
[1473]
[1474]
[1475]
[1476]
[1477]
[1478]
1479
[1480]
[1481]
[1482]
[1483]
[1484]
[1485]
[1486]
[1487]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.