Unleashing canine travel: Hospitality and tourism sector urged to adapt to dog-friendly travel demands
2023-12-18
Estimated to be worth USD 50.1 billion by 2030, a Surrey team of researchers has uncovered the potential of the growing dog-friendly travel market. The Covid-19 pandemic drove an increase in UK household dog ownership, creating a need for tourism providers to adapt to accommodate these four-legged family members.
The Surrey team set out to understand why people travel with their dogs, how they feel about it, and what challenges they face doing so.
Lori Hoy, PhD Researcher and lead author of the study at the University of Surrey, said:
"Some reports suggest that the UK dog population stands at 11 million, with 29% of UK adults having a dog in their ...
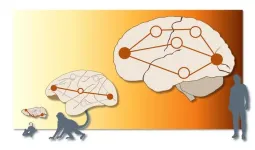
More parallel ‘traffic' observed in human brains than in animals
2023-12-18
In a study comparing human brain communication networks with those of macaques and mice, EPFL researchers found that only the human brains transmitted information via multiple parallel pathways, yielding new insights into mammalian evolution.
When describing brain communication networks, EPFL senior postdoctoral researcher Alessandra Griffa likes to use travel metaphors. Brain signals are sent from a source to a target, establishing a polysynaptic pathway that intersects multiple brain regions “like a road with many stops along the way.”
She explains that structural brain ...
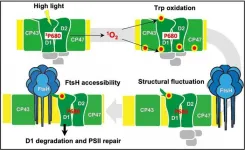
The role of oxidized tryptophan residues in repairing damaged photosystem II protein
2023-12-18
Photosynthesis refers to the fundamental biological process of the conversion of light energy into chemical energy by chlorophyll (a green pigment) containing plants. This seemingly routine process in plants sustains all the biological life and activities on Earth. First reaction of photosynthesis occurs at a site called photosystem II (PSII), present on the thylakoid membrane in the chloroplast where light energy is transferred to chlorophyll molecules. PSII is made up of a complex group of proteins, including the D1 and D2 reaction center proteins.
Light ...
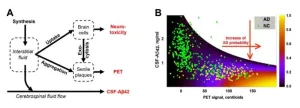
Breaking the mold: Zarbio and Georgia State scientists unveil game-changing theory on Alzheimer's disease
2023-12-18
Despite affecting millions worldwide, Alzheimer's disease (AD) has long lacked effective treatments due to a fundamental inadequacy of our understanding of its etiology and pathogenesis. The absence of an integrative theory connecting the molecular origins of AD with disturbances at the organelle and cell levels, changes in relevant biomarkers, and population-level prevalence has hindered progress. Even though most scientists only hope that an integrative theory of AD will emerge soon, scientists from Zarbio and Georgia State University discovered sufficient data to formulate a framework for such a theory.
The molecular and cellular ...
Scientists collect aardvark poop to understand how the species is impacted by climate in Africa
2023-12-18
CORVALLIS, Ore. – In a first-of-its-kind study of aardvarks, Oregon State University researchers spent months in sub-Saharan Africa collecting poop from the animal and concluded that aridification of the landscape is isolating them, which they say could have implications for their long-term survival.
“Everyone had heard of aardvarks and they are considered very ecologically important but there has been little study of them,” said Clint Epps, a wildlife biologist at Oregon State. “We wanted to see if we could collect enough data to begin to understand them.”
In ...
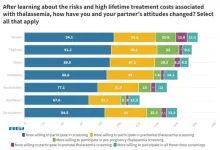
Thalassemia screening in Thailand: Medical Sciences Dean advocates for elevated trust
2023-12-18
- Insights from Professor Sakorn Pornprasert, Dean, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences at Chiang Mai University, on raising thalassemia awareness in Thailand.
Thalassemia, a genetic disorder affecting hemoglobin production, poses a significant public health challenge in Thailand, with a high prevalence and substantial healthcare costs. According to Thailand's Ministry of Public Health, approximately 18-24 million or 30-40 percent of the Thai population carries the thalassemia gene.
Professor Sakorn Pornprasert, Dean, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University, shared his views on BGI Genomics Global 2023 State of Thalassemia Awareness ...
Lung nodule program provides benefits patients ineligible for lung cancer screening
2023-12-18
(Denver—December 18, 2023) – Adopting a lung nodule program (LNP) may increase the detection of early lung cancer for patients who are not eligible for lung cancer screening under existing age eligibility criteria, according to a study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
LNPs are established to follow up on lung nodules that are frequently identified during routine imaging for reasons other than suspected lung cancer or lung cancer screening.
The research was conducted by a team led by Dr. Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist ...
Multi-site study reveals addressable socioeconomic barriers to prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart defects
2023-12-18
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart defects – the most common birth defects in the United States – is associated with improved outcomes. Despite its importance, however, overall prevalence of prenatal diagnosis is low (12-50 percent). A recent multi-center study surveyed caretakers of infants who received congenital heart surgery in the Chicago area and found that social determinants or influencers of health constitute significant barriers to prenatal diagnosis from the patients’ perspective.
In ...
Wildfires increasing across eastern U.S., new study reveals
2023-12-18
In a new analysis of data spanning more than three decades in the eastern United States, a team of scientists found a concerning trend – an increasing number of wildfires across a large swath of America.
“It’s a serious issue that people aren’t paying enough attention to: We have a rising incidence of wildfires across several regions of the U.S., not only in the West,” said Victoria Donovan, lead author of the study and an assistant professor of forest management at the UF/IFAS ...
Nurse aide turnover linked to scheduling decisions
2023-12-18
Long-term care facilities that scheduled part-time Certified Nursing Assistants (CNAs) with more hours and more consistently with the same co-workers had reduced turnover, according to research led by Washington State University. The findings could help address staffing challenges that affect millions of patients at long-term care facilities nationwide.
Using a model based on real scheduling data of thousands of nurse aides, the researchers estimated that a one-hour increase in CNAs’ weekly hours worked could reduce turnover by 1.9%. Also, the analysis found that by scheduling ...
TAMEST names Nidhi Sahni, Ph.D., as the Recipient of the 2024 Mary Beth Maddox Award & Lectureship
2023-12-18
AUSTIN/HOUSTON – TAMEST (Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology) has announced Nidhi Sahni, Ph.D., The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, as the recipient of the 2024 Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship in cancer research. She was chosen for her role in identifying novel biomarkers and drug targets, which are expected to have a significant impact on cancer by translating into more effective prognosis and therapy for the disease.
The Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship recognizes women scientists in Texas bringing new ideas and innovations to the fight ...
Do genes that code athletic heart enlargement carry a risk of future heart problems?
2023-12-18
A new landmark study involving 281 elite athletes from Australia and Belgium has revealed one in six have measures that would normally suggest reduced heart function.
Genetic analysis published in Circulation conducted by scientists in Australia and Belgium revealed those athletes also had an enrichment of genes associated with heart muscle disease.
Thus, a genetic predisposition may be ‘stressed’ by exercise to cause profound heart changes. The international collaboration will continue to monitor the athletes over the long-term to determine the consequences on their heart health.
Associate Professor Andre la Gerche, who heads the HEART Laboratory that is jointly ...
ASU research reveals regions in U.S. where heat adaptation and mitigation efforts can most benefit future populations
2023-12-18
Tempe, Ariz., December 18, 2023 – Extreme heat waves, once considered rare, are now frequent and severe in cities due to climate change. Phoenix faced such a brutal heat wave in July of 2023 when it endured 31 consecutive days of high temperatures of at least 110 F. The severity of the heat wave triggered a state of emergency. In June of 2021, the town of Lytton, B.C., Canada, hit a blistering 121 F, leading to a fire that burnt most of the village. This pattern repeated in Europe in 2022, where heat caused fatal illnesses, wildfires and damaged infrastructure, highlighting ...
Global inventory of sound production brings us one step closer to understanding aquatic ecosystems
2023-12-18
Scientists looking to uncover the mysteries of the underwater world have more valuable information at their fingertips thanks to an international team that has produced an inventory of species confirmed or expected to produce sound underwater.
Led by Audrey Looby from the University of Florida Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, the Global Library of Underwater Biological Sounds working group collaborated with the World Register of Marine Species to document 729 aquatic mammals, other tetrapods, fishes, and invertebrates that produce active or passive sounds. In addition, the inventory includes another 21,911 species that ...
Early-life diseases linked to lifelong childlessness
2023-12-18
Led by Aoxing Liu and senior authors Melinda Mills, Andrea Ganna and an international team, the study examined the link between 414 early-life diseases and lifetime childlessness in over 2.5 million individuals born in Finland and Sweden.
In many Western European and East Asian countries, up to 15-20% of individuals born around 1970 are now childless. Although multiple social, economic and individual preferences have been studied, there has been limited research examining the contribution of different diseases to being childless over a lifetime, particularly those diseases with onset prior to the peak reproductive age.
Dr Aoxing Liu, lead author ...
Some coral species might be more resilient to climate change than previously thought
2023-12-18
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Some coral species can be resilient to marine heat waves by “remembering” how they lived through previous ones, research by Oregon State University scientists suggests.
The study, funded by the National Science Foundation, also contains evidence that the ecological memory response is likely linked to the microbial communities that dwell among the corals.
The findings, published today in Global Change Biology, are important because coral reefs, crucial to the functioning ...
Big Science in the 21st Century – a new ebook published by IOP Publishing
2023-12-18
IOP Publishing is proud to announce the release of ‘Big Science in the 21st Century’, a comprehensive exploration of the impact of Big Science on our society and the new perspectives it opens on evaluating its societal benefits.
Authored by a diverse group of contributors, the book offers a multifaceted view of the challenges, merits, and transformations of Big Science across different disciplines and geographical boundaries. It delves into the transformative role of Big Science in shaping the world we live in, from its historical roots in the aftermath of the Second World War to its contemporary ...
Researchers invent "methane cleaner": Could become a permanent fixture in cattle and pig barns
2023-12-18
In a spectacular new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen have used light and chlorine to eradicate low-concentration methane from air. The result gets us closer to being able to remove greenhouse gases from livestock housing, biogas production plants and wastewater treatment plants to benefit the climate. The research has just been published in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has determined that reducing methane gas emissions will immediately reduce the rise in global temperatures. The gas is up to 85 times more potent ...
Algae as a surprising meat alternative and source of environmentally friendly protein
2023-12-18
With more of us looking for alternatives to eating animals, new research has found a surprising environmentally friendly source of protein – algae.
The University of Exeter study has been published in The Journal of Nutrition and is the first of its kind to demonstrate that the ingestion of two of the most commercially available algal species are rich in protein which supports muscle remodeling in young healthy adults. Their findings suggest that algae may be an interesting and sustainable alternative to animal-derived protein with respect to maintaining and building muscle.
Researcher Ino Van Der Heijden ...
Unconventional cancer research consortium created with $3.2M grant from US Department of Defense
2023-12-18
Funding an unconventional approach to fighting cancer that emphasizes the integration of diverse scientific disciplines, the U.S. Department of Defense has awarded $3.2 million to establish the Convergent Science Cancer Consortium (CSCC), led by Dean’s Professor of Biological Sciences Peter Kuhn at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences.
The consortium, which includes Stanford University, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and Children’s Hospital Los Angeles as inaugural members, unites experts from fields such as biology, engineering, mathematics and computer science, to discover more effective treatment strategies ...
Psychedelic psilocybin-assisted therapy reduces depressive symptoms in adults with cancer and depression
2023-12-18
Results from a phase II clinical trial indicate that psilocybin, a hallucinogenic chemical found in certain mushrooms of the genus Psiloybe, may benefit individuals with cancer and major depression. Trial participants treated with psilocybin not only experienced a lessening of depressive symptoms but also spoke highly of the therapy when interviewed at the end of the trial. The findings are published by Wiley in two articles appearing online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
By binding to a specific subtype of serotonin receptor in the brain, psilocybin can cause alterations to mood, ...
Parents’ top resolutions: More patience, less time on phones
2023-12-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Among many parents’ top resolutions for the New Year: More patience, less time on phones, better consistency with discipline and healthier family habits.
Their tweens and teens are setting goals too – including achievements related to grades and school, success in an activity, exercise and nutrition and earning money, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
Nearly three in four parents polled report making ...
Few patients receive opioid agonist therapy after opioid overdose, despite benefits
2023-12-18
In the week following any hospital visit for an overdose, only 1 in 18 people with opioid use disorder begin a treatment known to be highly effective in reducing illness and deaths, according to new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231014.
“These results highlight critical missed opportunities to prevent future mortality and morbidity related to opioid use, despite connection to health care for many patients in the days after a toxicity event,” writes Dr. Tara Gomes, a researcher at ...
Time to move on from ‘doctor knows best’, say experts, as study finds clinicians rank patient views as least important in diagnosis
2023-12-18
Experts today call for more value to be given to patients’ ‘lived experiences’ as a study of over 1,000 patients and clinicians found multiple examples of patient reports being under-valued.
The research, led by a team at the University of Cambridge and Kings’ College London, found that clinicians ranked patient self-assessments as least important in diagnostic decisions, and said that patients both over- and under-played their symptoms more often than patients reported doing so.
One patient shared the common feeling of being disbelieved ...
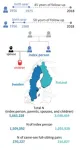
Stalled progress toward eliminating child marriage in India
2023-12-16
Embargoed for release: Friday, December 15, 6:30 PM ET
Key points:
Using national data between 1993 and 2021, researchers observed that India’s national prevalence of child marriage—defined by the study as marriage before age 18—declined throughout the study period.
The decade between 2006 and 2016 saw the largest magnitude of reduction in child marriage, while the years between 2016 and 2021 saw the smallest. During these latter years, six Indian states/union territories saw increases in the prevalence of girl child marriage and eight saw increases in boy child marriage.
The study is among the first to examine how the prevalence of child marriage ...
[1] ... [1476]
[1477]
[1478]
[1479]
[1480]
[1481]
[1482]
[1483]
1484
[1485]
[1486]
[1487]
[1488]
[1489]
[1490]
[1491]
[1492]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.