New gene therapy could significantly reduce seizures in severe childhood epilepsy
2023-12-15
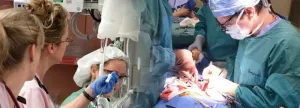
UCL researchers have developed a new gene therapy to cure a devastating form of childhood epilepsy, which a new study shows can significantly reduce seizures in mice.
The study, published in Brain, sought to find an alternative to surgery for children with focal cortical dysplasia.
Focal cortical dysplasia is caused by areas of the brain that have developed abnormally and is among the most common causes of drug-resistant epilepsy in children. It frequently occurs in the frontal lobes, which are important for planning and decision-making. Epilepsy in focal cortical dysplasia is associated with comorbidities, including learning disabilities.
Although surgery to remove the affected brain malformation ...
Mount Sinai receives $1.3 million from the National Institutes of Health to support program that introduces high school students to virus surveillance
2023-12-15
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has received more than $1.3 million from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to expand the New York City Virus Hunters program. The program engages high school students from communities historically underrepresented in science in the first large-scale citizen science effort to catalog and map circulating avian influenza and avian paramyxoviruses in New York City’s wild birds. The goal is to track emerging viruses and to prevent future outbreaks.
Wild birds can disseminate infectious ...
UM School of Medicine awarded up to $7.3M from DARPA to drive innovation in trauma triage technology, improve mass casualty response efforts
2023-12-15
In an effort to better optimize the triage of patients during mass casualty events, University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers are receiving up to $7.3 million in funding from the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for vital new research. The funding will be used to support a study that will collect data over the next 3.5 years on trauma patients with the aim of identifying and implementing lifesaving advancements in medical triage for large-scale mass casualty incidents.
“The importance of early interventions in trauma is described as the concept of the ‘golden ...
Transportation planning goes virtual
2023-12-15
Freight transportation is a backbone of the US economy — and a significant contributor to US greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, freight accounts for nearly 10% of annual U.S. emissions,ISE Dan Doulet Faculty Fellow and Professor Xueping Li points out. Li and an interdisciplinary, multi-institutional team have been awarded funding from the US Department of Energy to launch a first-of-its-kind, national-scale undertaking to address freight’s impact on climate change — and climate change’s impact on this vital sector.
Funding from DOE’s Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) is highly competitive. “Any ...
Zhou’s new tech has low-income housing covered
2023-12-15
When looking for ways to reduce their carbon footprint, most people think of first of their car, not their house. Surprisingly, however, buildings make up one of the largest energy-consuming sectors of the US economy, accounting for 39 percent of the country’s total energy use.
“Heating and cooling are among the most energy-intensive parts of building operations,” said Associate Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering Nick Zhou, who leads UT’s Sustainable and Adaptive Built Environment Group in ...
New framework to identify genetic risk of disease could lead to targeted therapeutics
2023-12-15
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) on patient blood samples are useful for identifying the genetic basis of blood cell traits and their links to common diseases. While previous experiments have focused on characterizing clinical parameters such as cell count, few have evaluated the dynamic effects of factors—such as inflammation, microbiome or medications—on blood cell contributions to disease development and progression. This lack of insight into underlying biological mechanisms behind such chronic progressive conditions has hindered ...
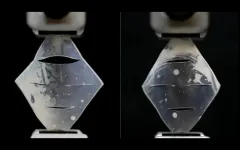
Newly developed material gulps down hydrogen, spits it out, protects fusion reactor walls
2023-12-14
MADISON – University of Wisconsin–Madison engineers have used a spray coating technology to produce a new workhorse material that can withstand the harsh conditions inside a fusion reactor.
The advance, detailed in a paper published recently in the journal Physica Scripta, could enable more efficient compact fusion reactors that are easier to repair and maintain.
“The fusion community is urgently looking for new manufacturing approaches to economically produce large plasma-facing components in fusion reactors,” says Mykola Ialovega, a postdoctoral researcher in nuclear engineering and engineering physics at ...
Tufts University announces Second Annual Cellular Agriculture Innovation Day
2023-12-14
Tufts University, home to the world’s largest concentration of academic researchers working on cultivated meat, will be hosting its second annual Cellular Agriculture Innovation Day on January 11, 2024. The day-long event will be held at Tufts’ Joyce Cummings Center in Medford, following a year of major developments in the industry — including regulatory approval of cultivated meat in the United States. Bringing together researchers, entrepreneurs, policymakers, and investors, Cellular Agriculture Innovation Day is an opportunity for candid ...
DOE’s Office of Science releases vision outlining the path to advancing fusion energy science and technology
2023-12-14
Washington, D.C. – The Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES), at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science, announced the release of its vision, Building Bridges: A Vision for the Office of Fusion Energy Sciences, during the Fusion Energy Sciences Advisory Committee hearing on December 13, 2023. This FES vision enables DOE to establish the steps needed to help advance fusion energy, including addressing key science and technology gaps in the supply chain and industry, bringing the United States one step closer to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
Fusion, the process that powers ...
Rubber that doesn’t grow cracks when stretched many times
2023-12-14
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have increased the fatigue threshold of particle-reinforced rubber, developing a new, multiscale approach that allows the material to bear high loads and resist crack growth over repeated use. This approach could not only increase the longevity of rubber products such as tires but also reduce the amount of pollution from rubber particles shed during use.
The research is published in Nature.
Naturally occurring rubber latex is soft and stretchy. For a range of applications, including tires, hoses, and dampeners, rubbers are reinforced by ...
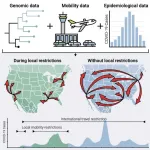
Social distancing was more effective at preventing local COVID-19 transmission than international border closures
2023-12-14
LA JOLLA, CA—Elucidating human contact networks could help predict and prevent the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and future pandemic threats. A new study from Scripps Research scientists and collaborators points to which public health protocols worked to mitigate the spread of COVID-19—and which ones didn’t.
In the study, published online in Cell on December 14, 2023, the Scripps Research-led team of scientists investigated the efficacy of different mandates—including stay-at-home measures, social distancing and travel restrictions—at preventing local and regional transmission during different phases of the COVID-19 pandemic. They found ...
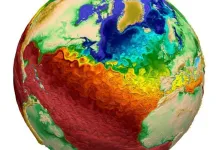
Custom software speeds up, stabilizes high-profile ocean model
2023-12-14
On the beach, ocean waves provide soothing white noise. But in scientific laboratories, they play a key role in weather forecasting and climate research. Along with the atmosphere, the ocean is typically one of the largest and most computationally demanding components of Earth system models like the Department of Energy’s Energy Exascale Earth System Model, or E3SM.
Most modern ocean models focus on two categories of waves: a barotropic system, which has a fast wave propagation speed, and a baroclinic system, which ...
Can you change a chicken into a frog, a fish or a chameleon?
2023-12-14
Gastrulation is one of the most important phases in early embryonic development. Before gastrulation, vertebrate embryos are simple two-dimensional sheets of cells. By the end of gastrulation, an embryo will have begun to differentiate distinct cell types, set up the basic axes of the body and internalize some of the precursors for organs in a three-dimensional structure. Amniotes, like chickens and humans, will have developed a primitive streak, the precursor to the brain and skin, while fish and amphibians will have developed a spherical-shaped ...
How the immune system fights to keep herpes at bay
2023-12-14
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is extremely common, affecting nearly two-thirds of the world’s population, according to the World Health Organization.
Once inside the body, HSV establishes a latent infection that periodically awakens, causing painful blisters on the skin, typically around the nose and mouth. While a mere nuisance for most people, HSV can also lead to dangerous eye infections and brain inflammation in some people and cause life-threatening infections in newborns.
Researchers have long known ...
Drones capture new clues about how water shapes mountain ranges over time
2023-12-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Drones flying along miles of rivers in the steep, mountainous terrain of central Taiwan and mapping the rock properties have revealed new clues about how water helps shape mountains over geological time, according to a team led by Penn State scientists.
The researchers found a link between the size of boulders in the rivers and the steepness of the rivers. The link shows how rock properties can influence the relationship between tectonic processes happening deep underground and how mountainous landscapes ...
NIH research identifies opportunities to improve future HIV vaccine candidates
2023-12-14
WHAT:
An effective HIV vaccine may need to prompt strong responses from immune cells called CD8+ T cells to protect people from acquiring HIV, according to a new study from researchers at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and colleagues. The study findings, appearing in Science, draw comparisons between the immune system activity of past HIV vaccine study participants and people with HIV who naturally keep the virus from replicating even in the absence of antiretroviral ...
Can an app improve your romantic relationship?
2023-12-14
Half of all marriages in the United States are likely to fail by the time the spouses reach their 50s. Understandably, many couples are looking for ways to avoid becoming part of that statistic, well aware of a divorce’s possible wide-reaching detrimental effects on families, children, personal finances, individual well-being—and direct and indirect costs to society.
Ronald Rogge, an associate professor of psychology at the University of Rochester, has been researching the complex dynamics ...
Climate-smart ocean planning in Antarctica awarded with 1.5M€ ERC starting grant
2023-12-14
Catarina Frazão Santos, researcher at the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Portugal) (Ciências ULisboa), has been awarded by the European Research Council (ERC) with a Starting Grant of approximately 1.5 million euros to study the benefits and challenges of developing sustainable, equitable and climate-smart marine spatial planning processes in Antarctica and beyond.
“We need to raise awareness and foster a ‘paradigm shift’ on how to plan for sustainability and equity in a changing ocean,” says Catarina ...
Researchers, Coast Salish people analyze 160-year-old indigenous dog pelt in the Smithsonian’s collection
2023-12-14
Researchers from the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History led a new analysis that sheds light on the ancestry and genetics of woolly dogs, a now extinct breed of dog that was a fixture of Indigenous Coast Salish communities in the Pacific Northwest for millennia. Anthropologist Logan Kistler and evolutionary molecular biologist Audrey Lin analyzed genetic clues preserved in the pelt of “Mutton,” the only known woolly dog fleece in the world, to pinpoint the genes responsible for their ...
Diverse gut bacteria communities protect against harmful pathogens by nutrient blocking
2023-12-14
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 19:00 GMT / 14:00 ET THURSDAY 14 DECEMBER 2023
Diverse gut bacteria communities protect against harmful pathogens by nutrient blocking
New study demonstrates that diverse communities of resident bacteria can protect the human gut from disease-causing microorganisms.
However, this protective effect is lost when only single species of gut bacteria are present.
The researchers found that protective communities block the growth of harmful pathogens by consuming nutrients that the pathogen needs.
The findings, published today in the journal Science, could help to develop new strategies to optimise gut health.
The ...
Astronomers discover first population of binary stripped stars
2023-12-14
Astronomers at the University of Toronto have discovered a population of massive stars that have been stripped of their hydrogen envelopes by their companions in binary systems. The findings, published today in Science, shed light on the hot helium stars that are believed to be the origins of hydrogen-poor core-collapse supernovae and neutron star mergers.
For over a decade, scientists have theorized that approximately one in three massive stars are stripped of their hydrogen envelope in binary systems. Yet, until now, only one possible candidate had been identified.
“This was such a big, glaring hole,” says co-lead author ...
Ancient genomics and Indigenous Knowledge reveal history of Coast Salish “woolly dogs”
2023-12-14
DNA analysis of a 19th-century dog, paired with traditional knowledge acquired through interviews, have together provided new insights into the decline of Coast Salish “woolly dogs” – an extinct Indigenous dog once bred for its unique woolly coat. Dogs were introduced to the Americas at least 15,000 years ago and have been ubiquitous in Indigenous societies across the continents for thousands of years. Coast Salish peoples – a group of Indigenous societies that lived in the Salish Sea region of the Pacific Northwest (PNW) – kept several different types of dogs, including a special lineage of “woolly ...
Science’s 2023 Breakthrough of the Year: GLP-1 agonists show promise for obesity-associated health problems
2023-12-14
Science has named the development of glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists and this year’s discovery that these drugs can blunt obesity-associated health problems as its 2023 Breakthrough of The Year. Although obesity’s causes span genetic, physiological, environmental, and social factors, as a medical problem, obesity’s risks can be life-threatening – including heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, liver disease, and certain cancers. Drug treatments for obesity have had “a sorry past, one often intertwined with social pressure to lose weight and the widespread belief that excess weight reflects weak will­power,” writes ...
Using genomics to map illegal pangolin poaching from Africa to Asia
2023-12-14
Genomic analyses reveal illegal pangolin trafficking routes from origins in Africa to markets in Asia, researchers report. The approach offers new opportunities to monitor pangolin poaching in near real-time, allowing for targeted and more effective anti-trafficking measures. The illegal wildlife trade is a significant driver of global biodiversity loss. Of all the species poached and traded, the white-bellied pangolin (Phataginus tricuspis) is the world’s most trafficked mammal and is at risk of extinction. Pangolins are in high demand in Asia because their scales are believed, without scientific support, ...
Solar-powered clothes provide personal heating and cooling
2023-12-14
Combining a flexible solar cell with an electrocaloric device, researchers have created solar-powered clothing that allows the body to adapt dynamically to changes in ambient temperature, according to a new study. The new device could help guarantee the safety and comfort of the human body amid fluctuating environmental temperatures and even extend survivability in extreme environments, like those in outer space or other planets. Clothing is the most common way humans regulate their body temperature relative to the environment. However, it is normally focused on keeping an individual either warm or cool. The ability of clothing to ...
[1] ... [1475]
[1476]
[1477]
[1478]
[1479]
[1480]
[1481]
[1482]
1483
[1484]
[1485]
[1486]
[1487]
[1488]
[1489]
[1490]
[1491]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.