A trillion scents, one nose
2023-12-20
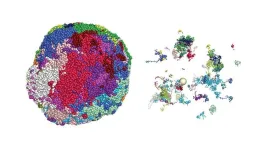
The mammalian nose is a work of evolutionary art. Its millions of nerve cells, each tailored with just one of thousands of specific odor-chemical receptors encoded in the genome, can collectively distinguish a trillion distinct scents. Those sensations, in turn, inform many behaviors, from assessing food options to discerning friends from foes to sparking memories.
Today, in the journal Nature, a research team led by scientists at Columbia’s Zuckerman Institute describes a previously undetected mechanism in mice—starring the genetic molecule RNA—that could explain how each sensory cell, or neuron, in mammalian noses becomes tailored to detect a specific ...
Innovation in development of dermatologic drugs approved by the FDA
2023-12-20
About The Study: Compared with prior decades, the number of new dermatologic drug approvals by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) increased between 2012 and 2022. Nearly half of these drugs were considered first in class or first in indication, and several were deemed clinically useful or to have high added therapeutic benefit by health technology assessment organizations in Germany, Canada, or France.
Authors: Ravi Gupta, M.D., M.S.H.P., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine ...
New brain-like transistor mimics human intelligence
2023-12-20
Taking inspiration from the human brain, researchers have developed a new synaptic transistor capable of higher-level thinking.
Designed by researchers at Northwestern University, Boston College and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the device simultaneously processes and stores information just like the human brain. In new experiments, the researchers demonstrated that the transistor goes beyond simple machine-learning tasks to categorize data and is capable of performing associative learning.
Although previous studies have leveraged similar strategies to develop brain-like computing devices, those transistors cannot function outside cryogenic temperatures. The new ...
Home-delivered meals and nursing home placement among people with self-reported dementia
2023-12-20
About The Study: This pilot pragmatic clinical trial included 243 homebound older adults with self- or proxy-reported dementia found a lower although nonsignificant likelihood of nursing home placement among those receiving daily-delivered meals compared with those receiving drop-shipped frozen meals. While this study was not powered to detect meaningful, statistically significant differences in nursing home placement, its feasibility and initial results warrant exploration in an adequately powered trial.
Authors: Kali S. Thomas, Ph.D., of the Brown University School of Public Health in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
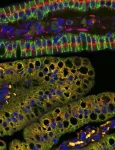
Integrating research and clinical care to uncover secrets of brain development
2023-12-20
The human brain continues to be built after we are born for far longer than previously recognized, suggests research by Shawn Sorrells, assistant professor of neuroscience in the Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences. Sorrells’s research on postnatal brain development, published today inthe journal Nature, shines light on fundamental processes that contribute to the development of important brain functions, such as learning, memory and spatial navigation.
The new research suggests that a subset of inhibitory neurons within the entorhinal cortex, or EC -- an area of the brain essential for forming memories -- continue ...
Meet 'Coscientist,' your AI lab partner
2023-12-20
In less time than it will take you to read this article, an artificial intelligence-driven system was able to autonomously learn about certain Nobel Prize-winning chemical reactions and design a successful laboratory procedure to make them. The AI did all that in just a few minutes — and nailed it on the first try.
"This is the first time that a non-organic intelligence planned, designed and executed this complex reaction that was invented by humans," says Carnegie Mellon University chemist and ...
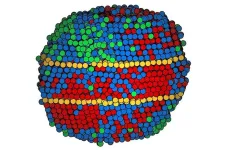
3D atomic details of next-generation alloys revealed for first time
2023-12-20
Alloys, which are materials such as steel that are made by combining two or more metallic elements, are among the underpinnings of contemporary life. They are essential for buildings, transportation, appliances and tools — including, very likely, the device you are using to read this story. In applying alloys, engineers have faced an age-old trade-off common in most materials: Alloys that are hard tend to be brittle and break under strain, while those that are flexible under strain tend to dent easily.
Possibilities for sidestepping that trade-off arose about 20 years ago, when researchers first developed medium- and high-entropy alloys, stable materials that combine ...
Catalyzing drug discovery with explainable deep learning
2023-12-20
Scientists have discovered one of the first new classes of antibiotics identified in the past 60 years, and the first discovered leveraging an AI-powered platform built around explainable deep learning.
Published in Nature today, the peer-reviewed paper, entitled “Discovery of a structural class of antibiotics with explainable deep learning,” was co-authored by a team of 21 researchers, led by Felix Wong, Ph.D., co-founder of Integrated Biosciences, and James J. Collins, Ph.D., Termeer Professor of Medical Engineering ...
Study unveils a role of mitochondria in dietary fat processing
2023-12-20
The maintenance of a balanced lipid homeostasis is critical for our health. While consumption of excessive amounts of fatty foods contributes to metabolic diseases such as obesity and atherosclerosis, fat is an indispensable component of our diet. Digested lipids supply the body with essential building blocks and facilitate the absorption of important vitamins. In a new study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers led by Professor Manolis Pasparakis and their collaborators Professor Aleksandra Trifunovic and Professor Christian Frezza at the Excellence Cluster CECAD of the University of Cologne, and Professor Jörg Heeren ...
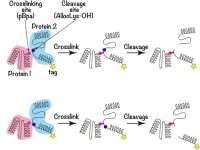
Protein secrets unveiled: Newl molecular insight of protein–protein interactions
2023-12-20
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have developed a new technique allowing the binding interfaces on two interacting proteins to be characterized, and validated it by describing the homophilic interaction between LAMP2A molecules
Tokyo, Japan – Proteins are building blocks of our bodies, but they do not work solo. They form partners to facilitate in different biological processes that keep us going. However, analyzing how proteins interact at a molecular level can be challenging. Now, a research team from Japan reveals the secrets behind these “protein partnerships”.
In a study published recently in Protein Science, researchers ...
Alzheimer’s discovery reveals dire effect of toxic tau protein on brain cells
2023-12-20
University of Virginia Alzheimer’s researchers have discovered how harmful tau proteins damage the essential operating instructions for our brain cells, a finding which could lead to new treatments.
The toxic protein, the researchers found, warps the shape of the nuclei of nerve cells, or neurons. This alters the function of genes contained inside and reprograms the cells to make more tau.
While the protein has long been a prime suspect in Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative “tauopathies,” the new research from UVA’s ...
Fraunhofer USA releases Annual Research Report, Focus 2023
2023-12-20
Fraunhofer USA, a leading nonprofit research organization dedicated to applied research and development services, is proud to announce the release of its Annual Report, Focus 2023. The report underscores Fraunhofer USA's commitment to fostering transatlantic collaboration, strengthening university-government partnerships, and driving impactful technology transfer.
Transatlantic Collaboration: A Pillar of Innovation
In the pursuit of global innovation, Fraunhofer USA continues to play a pivotal role in fostering transatlantic collaboration. The annual report highlights the organization's successful partnerships with Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft research institutes, resulting in groundbreaking ...
International collaboration to improve cancer care in Sub-Saharan Africa updates resources for sixth year
2023-12-20
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [December 20, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading academic cancer centers in the United States—is celebrating six years of working alongside the African Cancer Coalition (ACC), the American Cancer Society (ACS), and the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI), as part of Allied Against Cancer. The collaboration was formed to support and empower the Sub-Saharan African oncology community to advance health system capacity, ...
New study sheds light on the connection between the microbiome and kidney stones
2023-12-20
A new study from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University published in the journal Microbiome has found changes in the microbiome in multiple locations in the body are linked to the formation of kidney stones.
The human microbiome comprises trillions of microorganisms, including healthy bacteria. In recent years, research has begun to uncover its role in health and numerous diseases.
The research team examined the gut, urinary and salivary microbiomes in 83 patients who had kidney stones ...
TTUHSC researcher studies the ability of brine shrimp to thrive in high salinity
2023-12-20
Brine shrimp of the genus Artemia are small crustaceans that can thrive in environments where sodium concentrations are as high as 25% (more than eight times typical ocean sea water). Also known by the household pet trademark ‘sea monkeys,’ these animals are abundant in inland salt lakes where brine-fly larvae are the only other animals known to exist.
The mechanisms which permit brine shrimp to tolerate some of the harshest environments are only partially understood. Previously known adaptive features include a tight protective layer (integument) to avoid water loss and the increased extrusion of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions ...
Digital training program improves quality of life for care residents with dementia – even during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-12-20
Quality of life for people with dementia living in residential and nursing home care substantially improved after staff took part in a digital training programme that was specially adapted to Covid-19 restrictions. The training also led to a significant drop in the prescription of potentially harmful sedative medications to residents.
The iWHELD programme supported care home staff in delivering personalised care and encouraging meaningful social interactions. Through a digital platform featuring live coaching sessions led by trained coaches, the programme supported ...
Discovery: Plants use “trojan horse” to fight mold invasions
2023-12-20
UC Riverside scientists have discovered a stealth molecular weapon that plants use to attack the cells of invading gray mold.
If you’ve ever seen a fuzzy piece of fruit in your fridge, you’ve seen gray mold. It is an aggressive fungus that infects more than 1,400 different plant species: almost all fruits, vegetables, and many flowers. It is the second most damaging fungus for food crops in the world, causing billions in annual crop losses.
A new paper in the journal Cell Host & Microbe describes how plants send tiny, innocuous-seeming lipid “bubbles” filled with RNA across enemy lines, into the cells of the aggressive mold. Once ...
Could an electric nudge to the head help your doctor operate a surgical robot?
2023-12-20
People who received gentle electric currents on the back of their heads learned to maneuver a robotic surgery tool in virtual reality and then in a real setting much more easily than people who didn’t receive those nudges, a new study shows.
The findings offer the first glimpse of how stimulating a specific part of the brain called the cerebellum could help health care professionals take what they learn in virtual reality to real operating rooms, a much-needed transition in a field that increasingly relies on digital simulation training, said author and Johns Hopkins University roboticist Jeremy ...
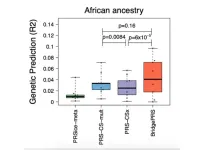
Mount Sinai researchers develop novel method to improve disease prediction across diverse ancestries
2023-12-20
A team of scientists from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has developed a groundbreaking statistical technique, “BridgePRS,” to enhance disease prediction in people of non-European ancestry, particularly those of African descent. This development represents a substantial step towards reducing health care inequities and a future of more personalized and precise medical interventions based on genetic information. Details of their work were published in Nature Genetics on Wednesday, December 20.
Current polygenic risk scores (PRS), essential tools for predicting disease risk encoded in our ...
How researchers are “CReATiNG” synthetic chromosomes faster and cheaper
2023-12-20
A groundbreaking new technique invented by researchers at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Science may revolutionize the field of synthetic biology. Known as CReATiNG (Cloning Reprogramming and Assembling Tiled Natural Genomic DNA), the method offers a simpler and more cost-effective approach to constructing synthetic chromosomes. It could significantly advance genetic engineering and enable a wide range of advances in medicine, biotechnology, biofuel production and even space exploration.
CReATiNG works by cloning and reassembling natural DNA segments from yeast, allowing scientists to create synthetic chromosomes that can replace their native counterparts in cells. ...
IOP Publishing expands open access in Asia Pacific region with its first Read and Publish agreement in Taiwan
2023-12-20
IOP Publishing (IOPP) has secured its first ‘Read and Publish’ transformative agreement in Taiwan, demonstrating its dedication to expanding open access (OA) to research in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region and at scale globally.
The three-year transformative agreement with the Physics Research Promotion Centre, which is part of the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC), will enable 20 Taiwanese universities to offer their researchers unlimited OA publishing at no cost to them. The agreement will also allow authors to retain copyright ...
Mediterranean diet ‘a straightforward approach’ among many nutritional options for improving the chance of success in IVF
2023-12-20
Adjuvant therapies to help infertile women conceive by IVF - especially those whose treatments have been unsuccessful in the past - are now a common feature both before and during the treatment cycle. Now, a new analysis of the evidence for many nutritional supplements and diets thought to improve outcome in IVF has concluded that adopting a Mediterranean diet during treatment would offer a single ‘straightforward approach’ with good evidence of benefit in contrast to that of a Western diet.
Evidence from studies of nine commonly used nutritional supplements was found to be inconsistent and not always of good quality. The analysis, by Professor Roger ...
Could gamma brain stimulation help combat Alzheimer’s disease?
2023-12-20
A review in the Journal of Internal Medicine explores the potential of non-invasive interventions such as light, sound, and magnets to stimulate gamma brain waves for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Such strategies may be beneficial because Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by reduced fast brain oscillations in the gamma range (30–100 Hz).
The authors note that recent studies reveal that it is feasible and safe to induce 40 Hz brain activity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease through a range of methods. Also, preliminary evidence suggests that such treatment can yield beneficial ...
How does the inability to burp affect daily life?
2023-12-20
The inability to burp—called retrograde cricopharyngeus dysfunction (R-CPD)—is caused by failure of the throat’s cricopharyngeal muscle to relax to allow the outward passage of gas. An interview-based study in Neurogastroenterology & Motility that included 199 adults affected by the condition reveals the impact of R-CPD on quality of life.
Most participants reported abdominal bloating, socially awkward gurgling noises, excessive flatulence, and difficulty vomiting. Only half discussed their symptoms with their primary care clinician, and 90% felt they did not receive ...
Does losing a parent during childhood contribute to separation anxiety and anxious attachment in women?
2023-12-20
Women who lost a parent early in life may be more likely to experience separation anxiety with romantic partners during adulthood, according to a study published in Stress and Health. In addition to feeling distressed when separated from their partners, these women may also experience anxious attachment, or worry that significant others will not be available at times of need.
The study included 60 women who lost one or both parents in their youth and 60 who had living parents. Based on participants’ answers to questionnaires, women who lost a parent reported higher levels of anxious attachment and adult separation anxiety ...
[1] ... [1482]
[1483]
[1484]
[1485]
[1486]
[1487]
[1488]
[1489]
1490
[1491]
[1492]
[1493]
[1494]
[1495]
[1496]
[1497]
[1498]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.