(Press-News.org) About The Study: The findings of this study of 2,165 adolescents from the Netherlands general population suggest that global brain volumetric measures did not differ between adolescents who reported gender diversity and those who did not. However, these findings further suggest that gender diversity in the general population correlates with specific brain morphologic features in the inferior temporal gyrus among youths who are assigned male at birth. Replication of these findings is necessary to elucidate the potential neurobiological basis of gender diversity in the general population.
Authors: Akhgar Ghassabian, M.D., Ph.D., of the New York University Grossman School of Medicine in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13139)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13139?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=051223
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Gender diversity and brain morphology among adolescents
JAMA Network Open
2023-05-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Association of hospital adoption of probiotics with outcomes among neonates with very low birth weight
2023-05-12
About The Study: In this study of 307,000 neonates with very low birth weight, adoption of routine use of probiotics in neonatal intensive care units increased slowly from 2012 to 2019 and was associated with lower necrotizing enterocolitis risk but not with sepsis or mortality rates.
Authors: Leila Agha, Ph.D., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.0960)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
A look inside stem cells helps create personalized regenerative medicine
2023-05-12
Organelles – the bits and pieces of RNA and protein within a cell – play important roles in human health and disease, such as maintaining homeostasis, regulating growth and aging, and generating energy. Organelle diversity in cells not only exists between cell types but also individual cells. Studying these differences helps researchers better understand cell function, leading to improved therapeutics to treat various diseases.
In two papers out of the lab of Ahmet F. Coskun, a Bernie Marcus Early Career professor in the Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University, researchers examined a specific ...
The beginning is the end
2023-05-12
All cells in an organism contain identical DNA sequence. What determines the identity and function of individual cells and tissues, is the set of genes that will be active in a given place, at a given time. These active genes are transcribed from the DNA template into distinct messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and will encode the proteins the cell needs to function.
At specific places called promoters, a complex molecular machinery starts transcribing DNA sequences into mRNA. Interestingly, most genes contain multiple possible sites where transcription ...
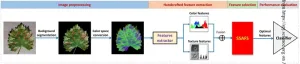
New artificial intelligence algorithm for more accurate plant disease detection
2023-05-12
Every year, plant diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi contribute to major economic losses. The prompt detection of these diseases is necessary to curb their spread and mitigate agricultural damage, but represents a major challenge, especially in areas of high-scale production. Smart agriculture systems use camera surveillance equipped with artificial intelligence (AI) models to detect features of plant diseases, which often manifest as changes in leaf morphology and appearance.
However, conventional methods ...
Visualizing PET's degradation by bacterial enzymes
2023-05-12
The rigidity, transparency and hardness of PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) make it one of the most valuable plastics for the manufacture of plastic bottles, packaging and other single-use products. However, these characteristics make it highly persistent in the environment, to the point that a plastic PET bottle may take several hundred years to degrade in the ocean.
At the molecular level, PET, and all plastics, have a polymeric structure made up of tens of thousands of repetitions of small subunits called monomers. In the last decades, the degradation ...
Study highlights best practices in buffelgrass control
2023-05-12
WESTMINSTER, Colorado – 9 May, 2023 – Buffelgrass is a highly invasive perennial found in arid regions around the globe. It is known to reduce the biodiversity of native ecosystems and to increase the frequency and intensity of wildfires.
A team of researchers recently took a close look at efforts to control buffelgrass in Arizona’s Saguaro National Park, located in the Sonoran Desert. An article featured in volume 16, issue 1 of the journal Invasive Plant Science and Management describes what that investigation can tell us about effective control strategies. ...
Scientists discover a deadly brain cancer’s hidden weakness
2023-05-12
The difficult-to-treat brain cancer glioblastoma steals a person’s mental faculties as it spreads, yet the tumor’s insidious ability to infiltrate neighboring networks in the brain could also prove its undoing.
Scientists at UC San Francisco have discovered that neural activity in these deadly tumors can restructure connections in surrounding brain tissue, causing the cognitive decline associated with the disease, and that the drug gabapentin, commonly used to prevent seizures, could block this growth-causing ...
Researchers discover a way to improve nonviral gene editing as well as a new type of DNA repair
2023-05-12
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Gene editing is a powerful method for both research and therapy. Since the advent of the Nobel Prize-winning CRISPR/Cas9 technology, a quick and accurate tool for genome editing discovered in 2012, scientists have been working to explore its capabilities and boost its performance.
Researchers in UC Santa Barbara biologist Chris Richardson’s lab have added to that growing toolbox, with a method that increases the efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9 editing without the use of viral material to deliver the genetic template used to edit the target genetic sequence. According to their new paper ...
Vast majority of tweets about obesity are negative, study finds
2023-05-12
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO, Dublin, 17-20 May). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
New research to be presented at next week’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Dublin, Ireland (17-20 May), has found that tweets about obesity are predominantly negative.
The analysis, by researchers in Switzerland and the UK, also found that Twitter activity spiked around the time of significant political events.
These included comments about Donald Trump’s weight when he was US president and ...
USC research identifies biomarker that may predict treatment response to chemoimmunotherapy
2023-05-12
Cutting-edge cancer treatments like immunotherapy are offering new hope for patients, often in combination with more common approaches such as chemotherapy. But determining the best treatment combination isn't always straightforward. Many patients spend valuable time on expensive therapies with serious side effects that aren’t effective against their cancer.
Now, a new discovery is poised to help. Researchers from USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center have identified a biomarker that indicates which patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) will respond well to chemoimmunotherapy. The biomarker, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Gender diversity and brain morphology among adolescentsJAMA Network Open