Copy and paste: New AI tool helps computers interpret the world
2023-12-13
Copy and paste.
It’s a simple concept.
You define some text or image on your computer, copy it, and paste it where you want it.
Now, think of that new leather sofa you crave.
Popular augmented reality (AR) apps allow you to cut and paste an image of the sofa into a photo of your living room to see if you like it before buying.
A team of researchers at USC Viterbi’s Thomas Lord Department of Computer Science has now developed a similar technique to copy virtual 3D objects and paste them into real indoor scenes. This creates an overall ...
Consumers grapple with confusion over food-date labels
2023-12-13
Consumers grapple with confusion over food-date labels
The use of food-date labels such as “use-by” and “best if used by” causes consumer confusion that results in many Americans discarding food that is safe to eat or donate, according to the November 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural ...
This adaptive roof tile can cut both heating and cooling costs
2023-12-13
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — About half of an average American building’s energy consumption is spent on heating and cooling. That’s a lot of money spent, fossil fuel burned and strain on an aging energy infrastructure during times of severe temperatures.
It’s also a problem UC Santa Barbara researchers Charlie Xiao, Elliot Hawkes and Bolin Liao are hoping to make a dent in. In a paper in the journal Device, the trio present an adaptive tile, which when deployed in arrays on roofs, can lower heating ...
WFIRM and partnering institutions awarded five-year, $6 million grant on kidney, urology, and hematology research
2023-12-13
WINSTON-SALEM, NC, December 13, 2023 - The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) has received a $6 million grant from the National Institute for Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. Alongside five other North Carolina institutions, the collaborative effort aims to address critical issues and advance research in the fields of kidney, urology and hematology. Dr. Anthony Atala, the W. Boyce professor and chair of urology at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and director of WFIRM, Dr. Ronald Falk, Nan and Hugh Cullman Eminent professor of medicine at UNC, and Dr. Thomas Ortel, professor of medicine ...
Beef farming that keeps cattle on lifelong grass diets may have higher carbon footprint
2023-12-13
Beef operations that keep cattle on lifelong grass-based diets may have an overall higher carbon footprint than those that switch cattle to grain-based diets partway through their lives. Daniel Blaustein-Rejto of the Breakthrough Institute, USA, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on December 13.
Cattle on lifelong grass diets are known as “pasture finished,” while those that switch from grass to grain before slaughter are “grain finished.” Prior research has suggested that ...
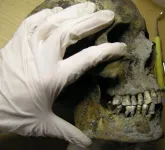
Vikings in Sweden suffered from tooth decay
2023-12-13
Vikings in Sweden suffered from painful dental issues and occasionally tried to treat them, according to a study published December 13, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Carolina Bertilsson of the University of Gothenburg, Sweden and colleagues.
In 2005, excavations in Varnhem, Sweden uncovered the remains of a Christian church, nearby which was a cemetery containing thousands of Viking graves dating to the 10th-12th century AD. In this study, Bertilsson and colleagues performed clinical and radiographical examination of the dentition of individuals from this site. In total, the team analyzed over 2300 teeth ...
The methane and nitrous oxide we exhale might contribute - in a very small way - to greenhouse gas emissions, with breath analysis indicating this may comprise up to 0.1% of UK emissions of the gases
2023-12-13
The methane and nitrous oxide we exhale might contribute - in a very small way - to greenhouse gas emissions, with breath analysis indicating this may comprise up to 0.1% of UK emissions of the gases
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295157
Article Title: Measurements of methane and nitrous oxide in human breath and the development of UK scale emissions
Author Countries: UK
Funding: The analysis was funded by the UK NERC grant E/S003614/2 ‘Detection and Attribution of Regional greenhouse gas Emissions in the UK (DAREUK)’. ...
Moms who participate in baby massage report reduced postnatal depression symptoms and better interactions with their child, per systematic review
2023-12-13
Moms who participate in baby massage report reduced postnatal depression symptoms and better interactions with their child, per systematic review
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0294156
Article Title: The effectiveness of mother-led infant massage on symptoms of maternal postnatal depression: A systematic review
Author Countries: Ireland
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Yoga nidra might be a path to better sleep and improved memory
2023-12-13
Practicing yoga nidra—a kind of mindfulness training— might improve sleep, cognition, learning, and memory, even in novices, according to a pilot study publishing in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on December 13 by Karuna Datta of the Armed Forces Medical College in India, and colleagues. After a two-week intervention with a cohort of novice practitioners, the researchers found that the percentage of delta-waves in deep sleep increased and that all tested cognitive abilities improved.
Unlike more active forms of yoga, which focus on physical postures, breathing, and muscle control, yoga nidra guides people into a state of conscious relaxation ...
Cognitive strategies for augmenting the body with a wearable, robotic arm
2023-12-13
Neuroengineer Silvestro Micera develops advanced technological solutions to help people regain sensory and motor functions that have been lost due to traumatic events or neurological disorders. Until now, he had never before worked on enhancing the human body and cognition with the help of technology.
Now in a study published in Science Robotics, Micera and his team report on how diaphragm movement can be monitored for successful control of an extra arm, essentially augmenting a healthy individual with a third – robotic – arm.
“This study opens up new and exciting opportunities, ...
Earliest evidence for domestic yak found using both archaeology, ancient DNA
2023-12-13
The high-altitude hero of the Himalayas, yak are among the few large animals that can survive the extremely cold, harsh and oxygen-poor conditions of the Tibetan Plateau. In the mountainous regions of Asia, yak and yak-cattle hybrids serve as vital sources of meat, milk, transportation and fuel. However, little is known about their history: when or where yak were domesticated.
In a study published Dec. 13 in Science Advances, an international team of researchers that includes archaeologists at Washington University in St. Louis report archaeologically and genetically confirmed evidence for domestic yak, dating back 2,500 years, by far the oldest record.
The researchers ...
Deep neural networks show promise as models of human hearing
2023-12-13
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Computational models that mimic the structure and function of the human auditory system could help researchers design better hearing aids, cochlear implants, and brain-machine interfaces. A new study from MIT has found that modern computational models derived from machine learning are moving closer to this goal.
In the largest study yet of deep neural networks that have been trained to perform auditory tasks, the MIT team showed that most of these models generate internal representations ...
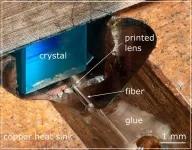
Researchers create stable hybrid laser by 3D printing micro-optics onto fibers
2023-12-13
WASHINGTON — For the first time, researchers have shown that 3D-printed polymer-based micro-optics can withstand the heat and power levels that occur inside a laser. The advance enables inexpensive compact and stable laser sources that would be useful in a variety of applications, including the lidar systems used for autonomous vehicles.
“We significantly reduced the size of a laser by using 3D printing to fabricate high-quality micro-optics directly on glass fibers used inside of lasers,” said research team leader Simon Angstenberger from the 4th Physics Institute at University of Stuttgart ...
Wistar scientists enhance cell-based therapy to destroy solid tumors
2023-12-13
PHILADELPHIA—(Dec. 13, 2023)—Wistar researchers successfully tested a simple intervention that could unlock greater anti-tumor power in therapies that use T cells — an approach known as “cell-based therapy,” which uses specially designed T cells to fight cancer. Led by Dr. Hildegund C.J. Ertl — a professor in The Wistar Institute’s Vaccine & Immunotherapy Center — the team has proven an exciting concept: that the common cholesterol drug fenofibrate can boost T cells’ ability to destroy human tumors, as described in their new paper, “Treatment ...
Trees are in trouble
2023-12-13
This holiday season brings surprising news about your Christmas tree. Scientists just discovered that globally, trees growing in wetter regions are more sensitive to drought. That means if your tree hails from a more humid clime, it’s likely been spoiled for generations.
Scientists have long debated whether arid conditions make trees more or less resilient to drought. It seems intuitive that trees living at their biological limits will be most vulnerable to climate change, since even just a little extra stress could tip them past the brink. On the other hand, these populations have adapted to a harsher setting, so they might be more capable of withstanding a drought.
According ...
New genetic vulnerability to herbicide found in nearly 50 sweet and field corn lines
2023-12-13
URBANA, Ill. — When a sweet corn breeder reached out in 2021 to report severe injury from the herbicide tolpyralate, Marty Williams hoped it was a fluke isolated to a single inbred line. But two years later, after methodical field, greenhouse, and genetic testing, his new Pest Management Science study not only confirms sensitivity to tolpyralate in 49 sweet corn and field corn lines, but also reveals a new genetic vulnerability that may affect corn more generally.
Tolpyralate is a relatively new ...
Charles Lee inducted as a fellow of The Korean Academy of Science and Technology
2023-12-13
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST), the highest institution of its kind in South Korea, announced Charles Lee, Ph.D., FACMG, as a newly inducted fellow of the Academy. This recognition is given to scientists and engineers who have been active in their field for more than 20 years and made significant contributions during that time.
Lee is the scientific director and professor at The Jackson Laboratory for Genomic Medicine, and is the Robert Alvine Family Endowed Chair. He was awarded the KAST honor in recognition of his extensive global contributions to human genomics research. Dr. Lee is one of 33 newly appointed fellows to the academy ...
Women may pay a "MOM PENALTY" when AI is used in hiring, new research from NYU Tandon School of Engineering suggests
2023-12-13
Maternity-related employment gaps may cause job candidates to be unfairly screened out of positions for which they are otherwise qualified, according to new research from NYU Tandon School of Engineering.
A research team led by Siddharth Garg, Institute Associate Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, examined bias in Large Language Models (LLMs) – advanced AI systems trained to understand and generate human language – when used in hiring processes.
The team will present its findings in a paper presented at NeurIPS ...
Study presents new pathway for electrochemically controlling ion selectivity
2023-12-13
A new study by researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign advances fundamental knowledge about the role of solvation in ion binding and presents a new pathway for electrochemically controlling ion selectivity. The study was published in JACS Au.
The team, led by Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering professor Xiao Su and recently graduated Ph.D. student Raylin Chen, is building on their prior work exploring electrochemical separations of ions, which has revealed that a critical mechanism for binding ions is solvation.
Here, the researchers set out to control solvation of a polymer and use that to bind different ...
Poor diet quality during adolescence is linked to serious health risks
2023-12-13
Philadelphia, December 13, 2023 – Diet quality among adolescents in the United States is among the worst across all age groups, putting young people at risk for heart attack, stroke, and diabetes, among other cardiometabolic diseases later in life. The research brief shared in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, used the Healthy Eating Index-2015 and medical testing to assess a group of youth aged 10-16 years.
This study examined data from the Translational Investigation of Growth and Everyday Routine in Kids cohort. This study measured physical activity, sleep, and overall dietary guidelines for youth living in metropolitan areas ...
Stuart Parkin to receive American Physical Society’s highest award for contributions to spintronics and data storage
2023-12-13
The American Physical Society (APS) has awarded Stuart Parkin of the Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics the 2024 APS Medal for Exceptional Achievement in Research. Parkin will be recognized “for major discoveries in spintronics leading to a revolution in data storage and memory” at a ceremony during the APS Annual Leadership Meeting in January 2024.
“Stuart Parkin is a luminary whose incisive experiments and major discoveries in spintronics led to a revolution in data storage and memory,” said APS President-Elect Young-Kee Kim, who chaired the medal’s selection committee. “His indomitable ...
New research shows that US renters are hit the hardest when a hurricane strikes
2023-12-13
WASHINGTON, DC, December 13, 2023 –With a severe shortage of affordable housing in the United States, renters living along the East and Gulf coasts are uniquely vulnerable to hurricane disasters. Two new studies based on data from 2009 to 2018 show that renters living along the East and Gulf coasts of the United States face rent increases, higher eviction rates, and a lack of affordable housing in the aftermath of a hurricane. The research will be presented in December at the annual meeting of the 2023 Society for Risk Analysis Annual Conference ...
Early research shows Gen Z perceives more dangers in life than previous generations
2023-12-13
There appears to be a common understanding that there is a mental health crisis among young people, but has society understood why?
As presented at the 2023 Society for Risk Analysis Annual Conference, Gabriel Rubin from Montclair State University conducted 40 interviews with members of Gen Z (as of publication) in an ongoing study about risk factors that have led to the current mental health crisis in young people. So far, this study has identified risk factors such as mass shootings, school lockdown drills, parental pressure, social media and the climate crisis.
Despite risk analysis research demonstrating that we ...
Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology examines effects of climate change on allergic conditions
2023-12-13
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (December 13, 2023) – As we head into the new year, some issues may be coming into sharper focus for those involved in allergy-immunology issues. The current issue of Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, the scientific journal of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, focuses its attention on a key problem affecting those with allergic conditions and the world today: climate change.
“We recognize that climate change affects the global population, and that many people feel they as individuals don’t have much control,” says allergist Donald Leung, MD, PhD, Senior Executive Editor of Annals. “But ...
Unique cell-based approach for pulmonary arterial hypertension shown to be safe
2023-12-13
Infusions of potentially therapeutic cells derived from the heart are safe for people with pulmonary arterial hypertension, a form of high blood pressure that occurs in the blood vessels of the lungs and typically affects middle-aged women, according to a study led by Cedars-Sinai investigators.
The Phase I clinical trial results are published in the peer-reviewed journal eBioMedicine, a Lancet journal.
“Although several drugs are approved for pulmonary arterial hypertension, mortality remains high,” said Eduardo Marbán, MD, PhD, executive director of the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai, the Mark S. Siegel Family Foundation ...
[1] ... [1485]
[1486]
[1487]
[1488]
[1489]
[1490]
[1491]
[1492]
1493
[1494]
[1495]
[1496]
[1497]
[1498]
[1499]
[1500]
[1501]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.