Free electric vehicle charging at work? It’s possible with optimum solar
2023-12-13
The global surge in electric vehicle sales has prompted an Australian university to explore how it could offer free or nominal EV charging facilities to staff and students by optimising its solar PV system and minimising workplace electricity costs.
Engineering researchers based at the University of South Australia (UniSA) Mawson Lakes campus say that using renewable energy to power EV day charging is the key, lowering electricity grid demand in the evening and helping to support Australia’s net zero emission targets by 2050.
The campus currently has rooftop solar panels on 18 buildings, supplemented by ground-mounted solar panels. The 2019 installation ...
Size of attainment gap between UK White and minority ethnic medical students varies by ethnicity and medical school
2023-12-13
The size of the gap in academic achievement between White and minority ethnic medical students in the UK varies considerably, depending on their individual ethnicity and which medical school they attended, finds the largest study of its kind, published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Their findings prompt the researchers to call for urgent remedial action to close the gap and reverse the career-long disadvantage faced by future minority ethnic doctors in the UK.
Despite a growing body of research on differences in outcomes within UK medical education, no large studies drawing on national data and universally applicable outcome measures have been done, so hampering ...
US female gun violence victims less likely to die than male victims despite same injury severity
2023-12-13
Female victims of gun violence in the US are less likely to die than their male counterparts, despite having similar injury severity, finds a 7-year analysis of a US national injury database, published in the open access journal Trauma Surgery & Acute Care Open.
They are also likely to have better outcomes, with fewer complications after hospital admission, the analysis shows.
The US has the highest number of firearm deaths of all developed countries, and firearms injuries and deaths have been rising year on year, point out the researchers.
And women are 21 times more likely to die from firearm injuries than their peers in any other developed nation. But it’s not ...
Grade difficulty of skatepark features like ski runs to curb fall risk, say researchers
2023-12-13
To curb the risk of falls, it may be worth grading skateboard parks like ski runs according to the popularity of the metal and concrete features they contain and the level of expertise required, conclude researchers in the journal Injury Prevention.
Their analysis of the moves performed by more than 500 young skateboarders reveals that flips, jumps, and turns on flat ground and quarterpipe (a curved concave ramp) and ramp tricks seem to pose the greatest risk, and are universally popular.
A grind box, ...
Patients can interrupt treatment of immune-supressing medicines for two weeks in order to boost immunity provided by COVID-19 booster vaccine, finds major study
2023-12-13
A major clinical trial, led by experts at the University of Nottingham, has shown that people with inflammatory conditions are able to improve the antibody response from a COVID-19 booster vaccination by interrupting their treatment for two weeks immediately after having the vaccine.
The antibody response to the jab was doubled at four weeks, and one and a half times greater at 26 weeks, when compared to those who continued with their treatment as usual. The improved antibody response lasted for six months. Patients who interrupted treatment reported experiencing more flare-ups of their inflammatory conditions in the next few weeks, but most flares ...
Mental health care gaps for women veterans - report
2023-12-13
Issues of identity, male-dominated branding and apprehension that their needs will go unmet are among the reasons women are not accessing veterans’ mental health support, according to new research being discussed today (Wednesday, 13 December) at a conference in Cambridge.
The report, I don’t feel like that’s for me: Overcoming barriers to mental healthcare for women veterans, was carried out by the Centre for Military Women’s Research (CMWR) at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), to investigate the low numbers of ex-servicewomen engaging with veteran-specific mental health services.
The ...
National policy aimed at reducing U.S. greenhouse gases also would improve water quality
2023-12-13
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — A climate policy that raises the price of carbon-intensive products across the entire U.S. economy would yield a side benefit of reducing nitrate groundwater contamination throughout the Mississippi River Basin.
The Gulf of Mexico, an important U.S. fishery, also would see modest benefits from the nitrate reductions. These were among the conclusions of a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The study, led by four early career researchers, three of them from ...
Twenty-year study confirms California forests are healthier when burned — or thinned
2023-12-13
Berkeley — A 20-year experiment in the Sierra Nevada confirms that different forest management techniques — prescribed burning, restoration thinning or a combination of both — are effective at reducing the risk of catastrophic wildfire in California.
These treatments also improve forest health, making trees more resilient to stressors like drought and bark beetles, and they do not negatively impact plant or wildlife biodiversity within individual tree stands, the research found. The findings of the experiment, called the Fire Surrogate Study, were published today in the journal Ecological Applications.
“The research ...
Caregiving can be stressful, but it could also lower risk of depression
2023-12-12
Becoming a caregiver to an aging parent or spouse can be stressful, but a new study from a researcher at The University of Texas at Austin is questioning the idea that family caregiving is also a risk factor for depression.
The study, published in the journal Advances in Life Course Research, found that depression in adult caregivers is mostly driven by having a loved one experiencing serious health problems, while becoming a caregiver is associated with fewer symptoms of depression.
“Decades of research on this topic indicate that there are positive and negative aspects to being a caregiver,” said Sae Hwang Han, ...
UCF researcher discovers new technique for photon detection
2023-12-12
University of Central Florida researcher Debashis Chanda, a professor at the NanoScience Technology Center, has developed a new technique to detect photons — elementary particles that span from visible light to radio frequencies and are instrumental in carrying cellular communication.
The advancement could lead to more precise and efficient technologies in various fields, from improving medical imaging and communication systems to enhancing scientific research and even potentially bolstering security measures.
Photon detection has typically relied on change/modulation of voltage or ...
Fat flies live longer on a diet at any age
2023-12-12
Old, obese flies get healthier and live longer if put on a diet, University of Connecticut researchers report on Dec. 8 in PNAS. If the effect holds true for humans, it would mean it’s never too late for obese people to improve their health with diet.
For way too many of us, eating too much goes along with getting old and a tendency to be obese. Different health organizations define obesity differently, but all agree it means having too much body fat, and is associated with a host of diseases related to metabolism including heart disease and diabetes. Many animal studies have shown that eating less—meaning sharply ...
European Policy Lab gathers stakeholders to map forest policy opportunities and barriers
2023-12-12
ForestPaths’ first Policy Lab convened stakeholders in Helsinki, Finland, on 27-29 September 2023. Nineteen carefully selected participants with diverse expertise – including research, policy, governance, civil society, value chain professionals, and forestry practitioners – engaged in discussions on forest-based policymaking and modelling related to climate change and biodiversity.
Tasked with considering policy actions given different timescales, governance paradigms, enablers, and barriers, participants contributed ...
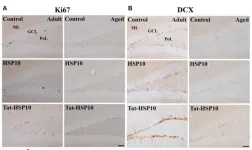
Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes in the hippocampus
2023-12-12
“Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major cellular change observed in the hippocampus during aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 22, entitled, “Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes by facilitating neuronal plasticity and reducing age-related genes in the hippocampus.”
In this new study, researchers Hyo Young Jung, Hyun Jung Kwon, Kyu ...
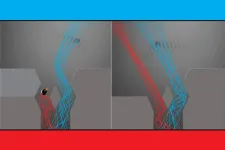
MIT researchers observe a hallmark quantum behavior in bouncing droplets
2023-12-12
In our everyday classical world, what you see is what you get. A ball is just a ball, and when lobbed through the air, its trajectory is straightforward and clear. But if that ball were shrunk to the size of an atom or smaller, its behavior would shift into a quantum, fuzzy reality. The ball would exist as not just a physical particle but also a wave of possible particle states. And this wave-particle duality can give rise to some weird and sneaky phenomena.
One of the stranger prospects comes from a thought experiment known as the “quantum bomb tester.” The experiment proposes that a quantum particle, such ...
Smoking causes brain shrinkage
2023-12-12
Smoking shrinks the brain, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The good news is that quitting smoking prevents further loss of brain tissue — but still, stopping smoking doesn’t restore the brain to its original size. Since people’s brains naturally lose volume with age, smoking effectively causes the brain to age prematurely, the researchers said.
The findings, published in Biological Psychiatry: Global Open Science, help explain why smokers are at high risk of age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
“Up until recently, scientists have overlooked ...
Mammogram rates increase when patients schedule themselves
2023-12-12
PHILADELPHIA— Having the ability to self-schedule mammograms was associated with a 15 percentage point increase following through with getting the screening, according to research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The paper was published today in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
“Self-scheduling helps make the path to mammogram completion a little smoother, where you don’t have to find the time to call a scheduling line, wait on hold, or go back and forth trying to find an appointment that works for your schedule,” said the study’s lead author, Kimberly Waddell, ...
Protein study could one day advance Parkinson’s, breast cancer care
2023-12-12
PORTLAND, Oregon -- New research from Oregon Health & Science University could one day lead to therapies that prevent or treat diseases and infections tied to a protein that’s found in all human cells.
A study published today in the journal Molecular Cell describes how the protein ubiquitin is modified during a bacterial infection. The study details the steps taken to create a form of the protein known as lysine 6 polyubiquitin, where a long chain of ubiquitin molecules are linked through ...
Study exposes opportunities for strengthening cancer drugs trials in China
2023-12-12
More than one-eighth of the randomized trials of cancer drugs seeking regulatory approval in China in recent years used inappropriate controls to test the effectiveness and safety of the drugs, according to a new study published December 12th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Professor Xiaodong Guan of Peking University, China, and colleagues.
In randomized trials, patients are assigned to either a control arm, in which they receive the current optimal treatment, or an experimental arm, in which they receive the new drug being tested. However, studies have previously ...
Zapping manure with special electrode promises an efficient method to produce fertilizers, other chemicals
2023-12-12
MADISON – An interdisciplinary team led by University of Wisconsin–Madison scientists has developed a new technique that could help farmers extract useful nutrients such as ammonia and potassium from livestock manure to efficiently make fertilizer and other useful chemical products. While the strategy still needs to be scaled up beyond a proof-of-concept stage, the group's preliminary analyses show it could offer considerable benefits by cutting water and air pollution while simultaneously creating products that farmers could use or sell.
Manure stinks in part because it contains ammonia, one of the more ...
Novel early-detection method aims to stem disease spread in animal trade
2023-12-12
DENVER/Dec. 12, 2023 – A new article published in the journal Methods in Ecology and Evolution by Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers describes a simplified method to detect a deadly fungus killing European salamanders. The ability to rapidly find the fungus is significant as the disease, although not detected in the U.S., could impact the millions of amphibians and salamanders annually imported.
The fungal pathogen Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans, or Bsal, threatens salamander diversity. Initially identified in northern Europe, evidence suggests it was introduced from Southeast Asia via the pet trade.
“The impacts of Bsal ...
EMBO launches new award for sustainability in the lab
2023-12-12
EMBO launches a new award for laboratory sustainability: The EMBO Lab Sustainability Award will recognize new and significant contributions to the development of sustainable wet and dry labs with a focus on their environmental impact. The award will be presented to an individual representing the initiative or project. Applications can be submitted between 15 January and 15 March 2024.
The award winner will have the opportunity to present their initiative or project at scientific events and publish a commentary in EMBO Reports. In addition, the winning project will be supported with a grant of 10,000 euros. The award is one of ...
Clinical trial finds cell therapy improves quality of life in advanced heart failure
2023-12-12
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Stem cell-based therapy improved quality of life for patients with advanced heart failure, Mayo Clinic researchers and international collaborators discovered in a late-stage multinational clinical trial. In one of the largest studies of cell intervention after a heart attack, patients reported their daily hardship lessened when stem cells optimized for heart repair supplemented standard of care. This clinical study further documented lower death and hospitalization rates among those treated with cell therapy. This research ...
ASH: Mantle cell lymphoma patients see improved outcomes with oral combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax
2023-12-12
ABSTRACT: LBA-2
SAN DIEGO ― The targeted therapy combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) and achieved an overall remission rate in 82% of patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Results from the Phase III SYMPATICO trial were presented at the 2023 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting.
At a median follow-up of 51.2 months, median PFS was 31.9 months with the combination compared to 22.1 months with ibrutinib plus placebo. PFS benefits were consistent across patient subgroups, including those with blastoid-variant ...
New test predicts risk of cognitive dysfunction in older surgery patients
2023-12-12
DURHAM, N.C. – Identifying an older patient who is at risk for post-operative cognitive dysfunction might be done in the blink of an eye – literally.
Researchers at Duke Health found that a simple EEG measurement detects a signal of cognitive vulnerability when patients are asked to close, then open their eyes. Conducted prior to surgery, the non-invasive readout of brain waves helps predict which patients are at risk of post-operative confusion and attention problems.
“Roughly half of seemingly normal older adults experience problems with thinking, memory or attention after surgery,” said Leah Acker, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor in ...
Archaeologists unearth one of earliest known frame saddles
2023-12-12
In April 2015, looters sacked an ancient cave burial at a site called Urd Ulaan Uneet high within the Altai Mountains of western Mongolia. When police apprehended the criminals, they uncovered, among other artifacts, an elegantly carved saddle made from several pieces of birch wood.
Now, in a new study, researchers from Mongolia collaborating with University of Colorado Boulder archaeologist William Taylor have described the find. The team’s radiocarbon dating pins the artifact to roughly the 4th Century ...
[1] ... [1500]
[1501]
[1502]
[1503]
[1504]
[1505]
[1506]
[1507]
1508
[1509]
[1510]
[1511]
[1512]
[1513]
[1514]
[1515]
[1516]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.