Mindfulness could help women with opioid use disorder better control drug urges
2023-12-09
Mindfulness-Oriented Recovery Enhancement (MORE) — a behavioral intervention that integrates training in mindfulness, emotion regulation strategies and savoring of natural rewards — could hold the key to mitigating relapse in women undergoing medically assisted opioid use disorder treatment, a Rutgers study found.
The pilot study published in the journal Explore, is the first to evaluate the potential neural changes that underlie women’s emotion regulation and craving after an eight-week MORE intervention.
Previous studies have shown that women report higher opioid craving and show a greater inability to ...
TTUHSC’s ARPA-H membership will spur innovation, improve access for West Texas patients
2023-12-09
Imagine if scientists developed a customizable cancer vaccine that was available — and affordable — for everyone. What if a patient scheduled for surgery also had the option of taking a pill whose composition includes nanorobotics capable of performing the procedure?
These and other medical scenarios may seem far-fetched and better suited to a science fiction thriller. However, the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) is seeking to take such ideas from the drawing board to ...
Global annual finance flows of $7 trillion fueling climate, biodiversity, and land degradation crises
2023-12-09
Almost US$7 trillion per year in government subsidies and private investment - around 7 per cent of global GDP - has a direct negative impact on nature.
Nature-based solutions remain dramatically underfunded. Current public and private finance flows are only US$200 billion per year. To meet climate, biodiversity, and restoration targets, this needs to triple by 2030 and quadruple by 2050.
Realignment of public and private nature-negative finance flows is urgently needed
Dubai, 9 December 2022 – Close to $7 trillion is invested globally each year in activities that have a direct negative impact on nature from both public and private sector sources - equivalent to ...
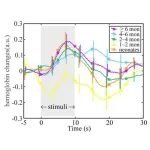
Tracing how the infant brain responds to touch with near-infrared spectroscopy
2023-12-09
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have measured how oxygenated hemoglobin levels in the blood change in infants’ brains in response to touch. Using spectroscopy methods with external sensors placed on the scalp of sleeping infants, they found that the time at which levels peak doesn’t change with infant age, but the amount by which it varies over time does. Insights like this shed light on how the physiology of infants develop.
The first phase of a newborn’s life is a dazzling array of rapid developmental ...
These are the world's most effective charities
2023-12-09
Which charities will be most effective in ensuring your donation is put to good use? For the first time in the Netherlands, researchers applied scientific methods to pinpoint which charities achieve the most with the donations they receive. The University of Amsterdam and Stichting Doneer Effectief (Donate Effectively Foundation) unveiled the list on Friday, 8 December, during a sold out evening in Rotterdam. ‘We are talking about the Champions League of good causes,’ says professor of Philanthropy & Sustainable Investment Paul Smeets of the University of Amsterdam. The ranking ...
When is an aurora not an aurora?
2023-12-08
The shimmering green, red and purple curtains of the northern and southern lights — the auroras — may be the best-known phenomena lighting up the nighttime sky, but the most mysterious are the mauve and white streaks called Steve and their frequent companion, a glowing green "picket fence."
First recognized in 2018 as distinct from the common auroras, Steve — a tongue-in-cheek reference to the benign name given a scary hedge in a 2006 children's movie — and its associated picket fence were nevertheless thought to be caused by the same physical processes. But scientists were left scratching their heads about how these glowing emissions ...
Advisory panel issues field-defining recommendations for US government investments in particle physics research
2023-12-08
The High Energy Physics Advisory Panel (HEPAP) to the High Energy Physics program of the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation’s Division of Physics has released a new Particle Physics Project Prioritization Panel (P5) report, which outlines particle physicists’ recommendations for research priorities in a field whose projects — such as building new accelerator facilities — can take years or decades, contributions from thousands of scientists, and billions of dollars.
The 2023 P5 report represents the major activity in the field of particle physics that ...
Doctors discover many patients at UNC’s Inflammatory Bowel Disease Clinic screen positive for malnutrition
2023-12-08
CHAPEL HILL, NC — Eating food and absorbing its nutrients is an everyday occurrence, but this normal activity can look different for someone who suffers from inflammatory bowel disease. IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, can cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract – which for many reasons can lead to malnutrition. This malnourished state is associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality, and new findings show that many patients in IBD clinic screen positive for malnutrition, leading to the critical need for same-day ...
BNL: Advisory panel issues field-defining recommendations for U.S. government investments in particle physics research
2023-12-08
The following news release on the 2023 Particle Physics Project Prioritization Panel (P5) report is based on one issued today by the American Physical Society (APS) with added content specific to the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory. For more information about Brookhaven Lab’s research in particle physics, contact: Karen McNulty Walsh, kmcnulty@bnl.gov, (631) 344-8350. For APS media inquiries, contact Anna Torres, torres@aps.org, (301) 209-3605.
WASHINGTON, ...
International collaboration uses faculty member’s research on ancient Roman migration, seeks to understand Balkan genomic history
2023-12-08
STARKVILLE, Miss.––A Mississippi State University anthropologist’s bioarchaeological analysis and bone samples from ancient Roman burial sites were crucial in the development of new research regarding Roman and Balkan migration featured this week in Cell, a prestigious peer-reviewed journal.
Anna Osterholtz, an associate professor in the Department of Anthropology and Middle Eastern Cultures, provided her research on the “lived experiences” of the Romans in Croatia. She currently works closely with museum ...
USF Health Heart Institute doctors are upbeat about cardiac regeneration
2023-12-08
But when those batteries – heart muscle cells called cardiomyocytes − short circuit and die, the damage can be devastating. The damage to the heart muscle is usually permanent, leaving the heart unable to pump the way it should.
That’s the subject of a new study by a team that includes two USF Health doctors who reported their findings in Circulation, the flagship journal of the American Heart Association.
“An injury like a heart attack creates a massive loss of cardiomyocytes, and you can’t renew them,’’ said Da-Zhi Wang, PhD, director of the Center for Regenerative Medicine in the USF Health Heart Institute and Morsani College ...
AI-driven breakthroughs in cells study: SFU-UBC collaboration introduces "MCS-detect" for advancements in super-resolution microscopy
2023-12-08
In 2014, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry celebrated the breakthroughs in super-resolution microscopy, a technology that allows us to capture highly detailed images of small parts of cells using fluorescent microscopy. Despite its success, the resolution of super-resolution microscopy still can’t show tiny distances between organelles in cells. This gap is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Biomedical Computer Vision intersect, as researchers from SFU Computing Science and UBC School of Biomedical Engineering and Life Sciences Institute reveal how AI enhances super-resolution microscopy ...
Advisory panel issues field-defining recommendations for investments in particle physics research
2023-12-08
Contributions from Argonne will drive innovation in particle physics and shed light on outstanding mysteries in the field.
Yesterday marked the release of a highly anticipated report from the Particle Physics Project Prioritization Panel (P5), unveiling an exciting new roadmap for unlocking the secrets of the cosmos through particle physics.
The report was released by the High Energy Physics Advisory Panel to the High Energy Physics program of the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and ...
$3.8 million NIH grant to fund Southwest Center on Resilience for Climate Change and Health
2023-12-08
A $3.8 million grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, a division of the National Institutes of Health, will fund planning for the Southwest Center on Resilience for Climate Change and Health, or SCORCH, at the University of Arizona fund planning for the Southwest Center on Resilience for Climate Change and Health, or SCORCH, at the University of Arizona Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health. The center will focus on research and programs to help communities in Arizona and other hot, dry geographic regions adapt to climate-driven health ...
What happens when the brain loses a hub?
2023-12-08
A University of Iowa-led team of international neuroscientists have obtained the first direct recordings of the human brain in the minutes before and after a brain hub crucial for language meaning was surgically disconnected. The results reveal the importance of brain hubs in neural networks and the remarkable way in which the human brain attempts to compensate when a hub is lost, with immediacy not previously observed.
Hubs are critical for connectivity
Hubs are everywhere. The hub of a bicycle wheel, with spokes shooting ...
Study reveals Zika’s shape-shifting machinery—and a possible vulnerability
2023-12-08
Viruses have limited genetic material—and few proteins—so all the pieces must work extra hard. Zika is a great example; the virus only produces 10 proteins. Now, in a study published in the journal PLOS Pathogens, researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys have shown how the virus does so much with so little and may have identified a therapeutic vulnerability.
In the study, the research team showed that Zika’s enzyme—NS2B-NS3—is a multipurpose tool with two essential functions: breaking up proteins (a protease) and dividing its own double-stranded RNA into single strands (a helicase).
“We found that Zika’s ...
RIT leading STEM co-mentoring network
2023-12-08
Two Rochester Institute of Technology professors are leading a National Science Foundation-funded project to support minoritized women students in STEM through a co-mentoring network called WiSEN (Women in STEM Network).
Betsy Dell, professor in the College of Engineering Technology, and Makini Beck, assistant professor in the College of Liberal Arts and the School of Individualized Study, have teamed up with Washington State University, Gonzaga University, and the University of Montana to use nearly $600,000 awarded by the NSF to create a network model to connect women STEM students. Sarah Bark was recently hired to be the project manager. She will support the daily operations and ensure ...
Genetic mutations that promote reproduction tend to shorten human lifespan, study shows
2023-12-08
A University of Michigan-led study based on a review of genetic and health information from more than 276,000 people finds strong support for a decades-old evolutionary theory that sought to explain aging and senescence.
In 1957, evolutionary biologist George Williams proposed that genetic mutations that contribute to aging could be favored by natural selection if they are advantageous early in life in promoting earlier reproduction or the production of more offspring. Williams was an assistant professor at Michigan State University at ...
CAMH develops potential new drug treatment for multiple sclerosis
2023-12-08
December 8, 2023 (Toronto) – CAMH-led pre-clinical studies using a small molecule drug have shown promise as a potential new treatment for multiple sclerosis (MS). The results have been published today in the journal Science Advances.
Expanding on Dr. Fang Liu’s earlier work that identified a novel drug target for the treatment of MS, she and her team have now created a small molecule compound that is effective in two different animal models of MS. This represents a key advancement that brings this MS research closer to the clinic to impact patient care.
MS is a progressive neurological ...
Polyethylene waste could be a thing of the past
2023-12-08
An international team of experts undertaking fundamental research has developed a way of using polyethylene waste (PE) as a feedstock and converted it into valuable chemicals, via light-driven photocatalysis.
The University of Adelaide’s Professor Shizhang Qiao, Chair of Nanotechnology, and Director, Centre for Materials in Energy and Catalysis, at the School of Chemical Engineering, led the team which published their findings in the journal Science Advances.
“We have upcycled polyethylene plastic waste into ethylene and propionic acid with high selectivity using atomically dispersed metal catalysts,” said Professor Qiao.
“An oxidation-coupled ...
A dynamic picture of how we respond to high or low oxygen levels
2023-12-08
SAN FRANCISCO—December 8, 2023—It only takes holding your breath for slightly too long to understand that too little oxygen is bad for you. But can you also have too much? Indeed, breathing air with a higher oxygen level than your body needs can cause health problems or even death.
But with scant research on the topic, scientists have known little about how the body senses too much oxygen. Now, a new study from Gladstone Institutes has greatly expanded the scientific body of knowledge about the mechanisms at play, and why it matters for health.
Their findings, reported in the journal Science Advances, explain how breathing air with different levels of ...
University of Toronto researchers discover new lipid nanoparticle that shows muscle-specific mRNA delivery, reduces off-target effects.
2023-12-08
TORONTO – A team of researchers based at the University of Toronto’s (U of T) Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy has discovered a novel ionizable lipid nanoparticle that enables muscle-focused mRNA delivery while minimizing off-target delivery to other tissues. The team also showed that mRNA delivered by the lipid nanoparticles investigated in their study triggered potent cellular-level immune responses as a proof-of-concept melanoma cancer vaccine.
The study, led by Bowen Li, assistant professor, Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy, U ...
Evolving insights in blood-based liquid biopsies for prostate cancer interrogation
2023-12-08
“In the United States, 288,300 new cases of prostate cancer are estimated for 2023 [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- December 8, 2023 – A new research perspective was published in Oncoscience (Volume 10) on November 30, 2023, entitled, “Evolving insights in blood-based liquid biopsies for prostate cancer interrogation.”
During the last decade, blood sampling of cancer patients aimed at analyzing the presence of cells, membrane-bound vesicles, or molecules released by primary tumors or metastatic growths emerged as an alternative to traditional tissue biopsies. The advent of this minimally invasive approach, known as blood-based liquid biopsy, ...
Finding the most heat-resistant substances ever made
2023-12-08
The most durable, heat-resistant materials ever made could be hiding in plain sight.
The U.S. Department of Defense wants to know if minerals and rocks found on Earth and in space hold the secrets of next-generation high-temperature materials. To find out, the DOD awarded $6.25 million through its Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative, or MURI, to a team from the University of Virginia and Arizona State University. The group is led by UVA’s Elizabeth J. Opila, the Rolls-Royce Commonwealth Professor and chair of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
The ...
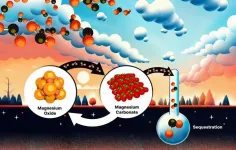
Time-tested magnesium oxide: Unveiling CO2 absorption dynamics
2023-12-08
Magnesium oxide is a promising material for capturing carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere and injecting it deep underground to limit the effects of climate change. But making the method economical will require discovering the speed at which carbon dioxide is absorbed and how environmental conditions affect the chemical reactions involved.
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory analyzed a set of magnesium oxide crystal samples exposed to the atmosphere for decades, and another for days to months, to gauge the reaction rates. They found that carbon ...
[1] ... [1506]
[1507]
[1508]
[1509]
[1510]
[1511]
[1512]
[1513]
1514
[1515]
[1516]
[1517]
[1518]
[1519]
[1520]
[1521]
[1522]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.