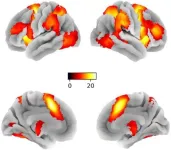
Protein found in brain linked to frontotemporal dementia
2023-12-07
INDIANAPOLIS—An international team of researchers including experts at the Indiana University School of Medicine has identified a protein found in the brains of people with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), discovering a new target for potential treatments for the disease.
According to the National Institutes of Health, FTD results from damage to neurons in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. People with this type of dementia typically present symptoms, including unusual behaviors, emotional problems, trouble communicating, difficulty with work or in some cases difficulty with walking, ...
CU's CellSight contributes light-sensitive retinal organoids and RPE cells to new AMD study
2023-12-07
A partnership between ophthalmology researchers at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and Johns Hopkins University expands the understanding of how oxidative stress contributes to the development of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) in patients with age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
To study the roles oxidative stress, a condition in which the body lacks antioxidants, and hypoxia play in the progression of AMD, Johns Hopkins University researchers turned to CellSight, the ocular stem cell and regeneration research program in the CU Department of Ophthalmology, for tools that allow researchers to explore specific conditions ...
Novel stem cell therapy using technology from mRNA COVID-19 vaccines may stimulate natural repair in treatment of chronic and acute liver disease
2023-12-07
BOSTON – Mortality related to end stage liver disease is ranked as the 12th most common cause of death in the U.S. Liver transplantation remains the only treatment for end stage liver disease, but there is a critical shortage of organ donors, necessitating a dire need for new forms of treatment.
New research from Boston Medical Center and Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine’s Center for Regenerative Medicine (CReM) found evidence that a novel stem cell treatment, using mRNA technology encapsulated into nanoparticles (LNP) that was ...
Unlocking brain secrets: New insights into how our minds control impulses
2023-12-07
Published in the 2023 Volume 3 issue of Psychoradiology a team of dedicated researchers from The University of Hong Kong and The University of Electronic Science and Technology of China has conclusively identified the right inferior frontal gyrus (rIFG) as a key input and causal regulator within the subcortical response inhibition nodes. This right-lateralized inhibitory control circuit, characterized by its significant intrinsic connectivity, highlights the crucial role of the rIFG in orchestrating top-down cortical-subcortical control, underscoring the intricate dynamics of brain function in response inhibition.
In ...
How the first contact of the virus influences the immune response to new SARS-CoV-2 variants
2023-12-07
Although SARS-CoV-2 is no longer a stranger to the immune system, new virus variants still pose a challenge. The working group led by Professor Dr Florian Klein, Director of the Institute of Virology at the University Hospital Cologne and the Faculty of Medicine, has now published two studies investigating how the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 changes over time and how the immune system is preparing itself for new variants with clever strategies. The work has been published under the title ‘Enhanced ...
Sage partners with Overton on free-to-use tool that empowers researchers to uncover their policy impact
2023-12-07
Sage has launched a tool to empower researchers to discover the real-world impact of their work on policy. Sage Policy Profiles lets researchers easily see specific citations of their work in policy documents and then illustrate and share that work’s impact graphically. The tool is powered by Overton, which hosts an extensive repository of global policy documents, guidelines, think-tank publications, and working papers.
The free-of-charge, browser-based tool shows researchers where their work appears in evidence-based policies, offering insights into how policymakers make use of their research. Sage Policy Profiles presents these results ...
New open-source platform cuts costs for running AI
2023-12-07
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have released a new, open-source platform called Cascade that can run artificial intelligence models in a way that slashes expenses and energy costs while dramatically improving performance.
Cascade is designed for settings like smart traffic intersections, medical diagnostics, equipment servicing using augmented reality, digital agriculture, smart power grids and automatic product inspection during manufacturing – situations where AI models must react within a fraction of a second.
With the rise of AI, many companies are eager to leverage new capabilities but worried about the associated computing ...
NIH study suggests maternal inflammation risk factors associated with children's behavioral and emotional regulation
2023-12-07
Maternal inflammation risk factors may be associated with dysregulation in children, according to a study funded by the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program at the National Institutes of Health. “Dysregulation” in this context refers to children’s attention, anxiety and depression, and aggression being measurably different from what is typically expected at their age.
While inflammation is a normal bodily response to injury or infection, ECHO investigators wanted to learn whether factors linked ...
Cancer: Towards a new treatment for leukaemia
2023-12-07
Around 320,000 new cases of leukaemia, a type of blood cancer that can affect all population groups, are diagnosed every year in Europe. In children, cases of leukaemia make up a third of diagnosed cancers. Chemotherapy is the main treatment for leukaemia. Often, the exact cause cannot be identified and the molecular and cellular mechanisms responsible for leukaemia remain shrouded in mystery. Discovering new detection methods and new treatments to eradicate leukaemia is therefore a major challenge in oncology.
Messenger RNA has been in the news in recent months, in connection with COVID-19 vaccinations. In an article published in Molecular Cell, researchers ...
Wasps that recognize faces cooperate more, may be smarter
2023-12-07
ITHACA, N.Y. – A new study of paper wasps suggests social interactions may make animals smarter. The research offers behavioral evidence of an evolutionary link between the ability to recognize individuals and social cooperation.
Furthermore, genomic sequencing revealed that populations of wasps that recognized each other – and cooperated more – showed recent adaptations (positive selection) in areas of the brain associated with cognitive abilities such as learning, memory and vision.
The study focused on two distinct populations of paper wasps (Polistes fuscatus): A southern ...
Key to fatty liver disease and its consequences for billions of people
2023-12-07
Key to fatty liver disease and its consequences for billions of people
The global rise in obesity and diabetes is leading to an epidemic in fatty liver disease affecting 20-30 per cent of the world’s population. Almost a third of people with fatty liver disease go on to develop an advanced form of the disease, known as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that can progress to cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease, or even liver cancer, and is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Why some people remain relatively healthy with fatty liver disease and some go onto potentially life-threatening illness has been a mystery. Until now.
A study ...
It turns out, this fossil plant is really a fossil baby turtle
2023-12-07
From the 1950s to the 1970s, a Colombian priest named Padre Gustavo Huertas collected rocks and fossils near a town called Villa de Levya. Two of the specimens he found were small, round rocks patterned with lines that looked like leaves; he classified them as a type of fossil plant. But in a new study, published in the journal Palaeontologia Electronica, researchers re-examined these “plant” fossils and found that they weren’t plants at all: they were the fossilized remains of baby turtles.
“It was truly surprising to find these fossils,” says Héctor Palma-Castro, a paleobotany student at the Universidad Nacional de Colombia.
The plants in question ...
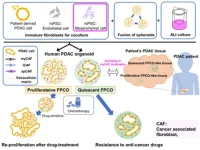
Novel and promising pancreatic cancer organoids for effective screening of anticancer drugs
2023-12-07
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), that arises from pancreatic epithelial cells, is the most common form of pancreatic cancer, with a very high mortality rate. This elevated mortality is associated with the unique tumor microenvironment (TME), known for increased resistance to chemotherapy and high metastatic potential. TME is characterized by the presence of a complex stromal structure comprising cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), tumor endothelial cells (TECs), and a variety of immune cells.
CAFs are specific cells, primarily involved in the overall aggressiveness and spread of cancer cells. These cells can further be categorized into several types based on their ...
New certification applies proven science to tobacco cessation treatment
2023-12-07
DALLAS, December 7, 2023 — The Tobacco Endgame — the path to ending tobacco use and nicotine addiction in the U.S. — is within sight, but there has been a sharp increase in electronic cigarette use among high school students, from 1.5% in 2011 to about 27.4% in 2019.[1]
The American Heart Association, the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, is collaborating with the Association for the Treatment of Tobacco Use and Dependence (ATTUD) to change that. New individual certification as a Certified Professional by the American Heart Association – Tobacco Treatment is ...
Ancient Balkan genomes trace the rise and fall of Roman Empire’s frontier, reveal Slavic migrations to southeastern Europe
2023-12-07
A multidisciplinary study led by the Institute of Evolutionary Biology in Spain (a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council and Pompeu Fabra University), the University of Belgrade in Serbia, the University of Western Ontario in Canada, and Harvard University in the USA, reconstructs the genomic history of the Balkan Peninsula during the first millennium of the common era, a time and place of profound demographic, cultural and linguistic change. The team has recovered and analyzed whole genome data from 146 ancient people excavated primarily from Serbia and Croatia—more than a third of which came from the ...
Ancient DNA analysis reveals how the rise and fall of the Roman Empire shifted populations in the Balkans
2023-12-07
Despite the Roman Empire’s extensive military and cultural influence on the nearby Balkan peninsula, a DNA analysis of individuals who lived in the region between 1 and 1000 CE found no genetic evidence of Iron Age Italian ancestry. Instead, a study published December 7 in the journal Cell revealed successive waves of migrations from Western Anatolia, central and northern Europe, and the Pontic-Kazakh Steppe during the Empire’s reign.
From the 7th century CE onwards (coincident with the fall of the Western Roman Empire), large numbers of people emigrated from Eastern Europe, likely related to the arrival of Slavic-speaking populations, which ...
Why presence of healthy cells enables cancer to resist treatment
2023-12-07
Chemotherapy becomes less effective because healthy cells push cancer cells to grow more slowly, according to two studies from researchers at UCL and Yale.
In the two studies, supported by Cancer Research UK and published in Cell, researchers used ‘mini-tumours’ and the latest single-cell analysis technologies to begin to solve the puzzle of why healthy cells in a patient’s bowel cancer tumour might lead to poor outcomes.
Bowel cancer kills over 900,000 people a year and is the second highest cause of cancer mortality worldwide. In the UK, it accounts for 10% of all cancer deaths.
In the first study, UCL researchers used the latest single-cell analysis ...
Cocoa extract supplement found to have benefits for cognition among older adults with lower diet quality
2023-12-07
WHO: Mass General Brigham researchers, Dr. Chirag Vyas and Dr. Olivia I. Okereke at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Dr. Howard Sesso and Dr. JoAnn Manson at Brigham and Women’s Hospital
WHAT: Cocoa extract has shown a potential protective effect on cognition but randomized clinical trials in older adults have had inconsistent results. A new study of cognition in a randomized trial, known as the Cocoa Supplement and Multivitamin Outcomes Study (COSMOS), suggests that taking cocoa extract supplements containing 500 mg per day of cocoa flavanols had cognitive benefits for older adults who had lower habitual ...
New Case Western Reserve University study finds diabetes drug may reduce risk for colorectal cancer
2023-12-07
CLEVELAND—A groundbreaking study by researchers at Case Western Reserve University suggests a class of medications used to treat type 2 diabetes may also reduce the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC).
The findings, published today (Dec. 7) in the journal JAMA Oncology, support the need for clinical trials to determine whether these medications could prevent one of the deadliest types of cancers. Eventually, the medications may also show promise in warding off other types of cancer associated with obesity and diabetes.
“Our results clearly demonstrate ...
Ecology: Mediterranean green turtles nesting range expands under warming climate
2023-12-07
Rising global temperatures could lead to an increase in the nesting range of green turtles in the Mediterranean Sea, according to a modelling study published in Scientific Reports. Under the worst-case climate scenario, the nesting range could increase by over 60 percentage points, spreading west from the current area to include much of the North African, Italian, and Greek coastlines.
Human-caused climate change has caused sea surface temperatures to increase globally, with severe impacts on some marine life. Sea turtles are potentially particularly susceptible, as the sex of their offspring is dependent on incubation temperature. Although previous research ...
Racial and ethnic disparities in clinical trial enrollment among women with gynecologic cancer
2023-12-07
About The Study: Clinical trial enrollment was lower among certain minoritized racial and ethnic groups in this study of 562,000 women with endometrial, ovarian, or cervical cancer. Continued efforts are needed to address disparate clinical trial enrollment among underrepresented groups.
Authors: Ashley S. Felix, Ph.D., of Ohio State University in Columbus, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.46494)
Editor’s ...
Opioid prescribing by surgeons
2023-12-07
About The Study: This study found that during 2016 to 2022, the rate and size of opioid prescriptions from U.S. surgeons declined, but these declines were slower after mid-2020 compared with before 2020. During the initial months of the COVID-19 pandemic, the opioid dispensing rate declined, potentially owing to decreased surgical volume, while opioid prescription size increased, potentially because surgeons wrote larger discharge prescriptions owing to barriers to obtaining refills. However, these changes were transient.
Authors: Kao-Ping ...
Improving prediction of advanced breast cancer among women of different races and ethnicities
2023-12-07
While regular screenings may decrease the chance of diagnosis of advanced breast cancer in some women and lead to a 20% reduction in breast cancer mortality, other women will be diagnosed with advanced breast cancer despite screening at regular intervals. The chances of being diagnosed with advanced breast cancer are higher among women who are Black or Hispanic/Latinx as well as women who are overweight and obese.
In a study publishing December 7, 2023 in JAMA Oncology, UC San Francisco researchers found that regular screening is not always sufficient to prevent an advanced breast cancer diagnosis. To reduce the number of advanced cancer diagnoses, ...
Surgery patients now less likely to get opioids – but decline has slowed
2023-12-07
Post-surgery pain relief has shifted away from opioid-containing medications over the past seven years, but the downward trend has slowed since 2020, a new study shows.
Overall, the rate of surgery-related opioid prescriptions dropped by 36% from 2016 to the end of 2022, and the average amount of opioids in those prescriptions dropped by 46%, the study of pharmacy data finds.
That combination of declines means that the total amount of opioids dispensed to surgical patients in late 2022 was 66% lower compared with early 2016, according to the findings published in JAMA Network Open by a team from the University of Michigan.
But the rate of decline was much faster before the pandemic, ...
Three-day exceptional heatwave in China linked to human-induced climate change
2023-12-07
In June, temperatures in North China hit record breaking heights, with temperatures in Beijing reaching or exceeding 40℃ for three consecutive days.
The intensity of such events has increased by at least 1.0℃ due to human-induced climate change.
Heatwaves like these will occur twice as likely even under proposed carbon neutral targets and will be 0.5℃ more intense.
Current emissions scenario will increase the probability of reoccurrence to over five times this century with a 2.9℃ rise in intensity.
A record-breaking heatwave occurred in North China in June, marking the ...
[1] ... [1510]
[1511]
[1512]
[1513]
[1514]
[1515]
[1516]
[1517]
1518
[1519]
[1520]
[1521]
[1522]
[1523]
[1524]
[1525]
[1526]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.