Popularity matters more than compatibility on dating apps
2023-11-29
A new study has found that algorithms used by online dating platforms have popularity bias - meaning that they recommend more popular, attractive users over less popular, less attractive users. Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Washington published their findings in Manufacturing & Service Operations Management.
They evaluated data from over 240,000 users of a major online dating platform in Asia over three months. They found that a user's chance of being recommended by the platform's algorithm ...
Markey Cancer Center research highlights need for education to combat cancer in Appalachia
2023-11-29
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Nov. 29, 2023) — University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center research underscores the need for interventions to increase educational attainment and knowledge of cancer in Appalachian Kentucky.
Kentucky has the highest rate of cancer incidence and mortality in the country, with the Eastern Appalachian region bearing the highest burden due to health, socioeconomic and education disparities including decreased education attainment levels that cause lower health ...
Contraception: hormonal and copper coil only show minor differences
2023-11-29
In the “ThemenCheck Medizin” procedure offered by the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), interested members of the public can submit proposals for the assessment of medical procedures and technologies. On behalf of IQWiG, an interdisciplinary team of researchers led by Share to Care GmbH in Cologne investigated the advantages and disadvantages of two types of contraceptive coils (also known as intrauterine devices, IUDs) for preventing unwanted pregnancies, the copper IUD and the hormonal IUD.
Their conclusion: both types of IUDs are very safe and, compared to condoms or the pill, cost-effective contraceptive ...
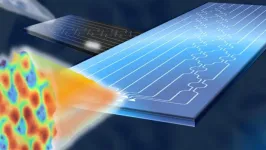
The chip that makes calculations with light
2023-11-29
Optical wireless may no longer have any obstacles. A study by Politecnico di Milano, conducted together with Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa, the University of Glasgow and Stanford University, and published in the prestigious journal Nature Photonics, has made it possible to create photonic chips that mathematically calculate the optimal shape of light to best pass through any environment, even one that is unknown or changing over time.
The problem is well known: light is sensitive to any form of obstacle, even very small ones. Think, for example, of how we see objects when looking through a frosted window ...
Severe weather disproportionately impacts Oklahoma’s native communities, study shows
2023-11-29
As the climate, demographics and land usage continue to change, tribal communities in Oklahoma are increasingly at risk of severe weather. A recent study led by Yang Hong with the University of Oklahoma examines these changes and the risks they pose.
“Indigenous communities are grappling with an imminent climate crisis compounded by systemic injustices. Recognizing their unique connections to their homelands as sovereign peoples is crucial in addressing these pressing issues,” Hong said.
Hong is the corresponding author of the paper, “Future ...
JMIR Publications announces a partnership with leading career center provider Naylor Association Solutions to power a brand-new online career development hub for digital health professionals
2023-11-29
We are thrilled to announce the official launch of the JMIR Career Center on the JMIR Publications website. This pioneering platform is set to revolutionize the way healthcare professionals access career development resources and opportunities within the digital health field.
The JMIR Career Center, in collaboration with Naylor Association Solutions, aims to bridge the gap between digital health professionals and their career advancement. As the digital health sector continues to evolve, so too does the demand for skilled and motivated professionals. By providing a dedicated hub for digital health career resources, job ...
Fighting fruit flies help researchers understand why we stay angry
2023-11-29
It’s one of those days. On the drive home from work, the car in the next lane cuts you off. You slam on the brakes, lay on the horn, and yell choice words at the offending driver. When you walk into your house half an hour later, you’re still angry, and snap at your partner when they ask about your day.
Fruit flies may not have to worry about the lingering effects of road rage, but they also experience states of persistent aggression. In the case of female fruit flies, this behavior is a survival mechanism, causing the flies to headbutt, shove, and fence other female fruit flies to guard prime egg-laying territory on a ...
Surgeon supply by county-level rurality and social vulnerability
2023-11-29
About The Study: Between 2010 and 2020, surgeon supply per 100,000 population decreased in rural counties and increased in urban counties, and decreased in socially vulnerable counties and remained unchanged in other counties. Thus, over the past decade, disparities in surgeon supply between rural and urban counties and between socially vulnerable and other counties have widened in the U.S. The largest widening was observed among general surgeons.
Authors: Vishal R. Patel, B.S., of the Dell Medical School in Austin, Texas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.5632)
Editor’s ...
Surgeon sex and health care costs for patients undergoing common surgical procedures
2023-11-29
About The Study: This analysis that included 1.1 million patients found lower 30-day, 90-day, and 1-year health care costs for patients treated by female surgeons compared with those treated by male surgeons. These data further underscore the importance of creating inclusive policies and environments supportive of women surgeons to improve recruitment and retention of a more diverse and representative workforce.
Authors: Christopher J. D. Wallis, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.6031)
Editor’s ...
Google DeepMind adds nearly 400,000 new compounds to Berkeley Lab’s Materials Project
2023-11-29
New technology often calls for new materials – and with supercomputers and simulations, researchers don’t have to wade through inefficient guesswork to invent them from scratch.
The Materials Project, an open-access database founded at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) in 2011, computes the properties of both known and predicted materials. Researchers can focus on promising materials for future technologies – think lighter alloys that improve fuel economy in cars, more ...
Tracing the evolution of the “little brain”
2023-11-29
The evolution of higher cognitive functions in human beings has so far mostly been linked to the expansion of the neocortex – a region of the brain that is responsible, inter alia, for conscious thought, movement and sensory perception. Researchers are increasingly realising, however, that the “little brain” or cerebellum also expanded during evolution and probably contributes to the capacities unique to humans, explains Prof. Dr Henrik Kaessmann from the Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University. ...
Bees are still being harmed despite tightened pesticide regulations
2023-11-29
A new study has confirmed that pesticides, commonly used in farmland, significantly harm bumblebees – one of the most important wild pollinators. In a huge study spanning 106 sites across eight European countries, researchers have shown that despite tightened pesticide regulations, far more needs to be done.
While the agricultural uses of insecticides have been in the spotlight for their negative effects on bees, it has remained unknown how the effects scale beyond single substances in focal ...
The Global Biodiversity Data Portal: enabling biodiversity research worldwide
2023-11-29
EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) has launched the Global Biodiversity Portal – an open access data portal that will consolidate genomic information from different biodiversity projects within the Earth BioGenome Project.
Sequencing and storing the genomic data of all species on Earth is vital for future conservation and biodiversity efforts. In an era where biodiversity is under threat from various environmental pressures, there is an urgent need for centralised, accessible, and actionable data. ...
Doctors call for expanded reporting of medical care given in ICE detention centers
2023-11-29
Embargoed until November 29 11 a.m. ET
A new study led by Dr. Annette Dekker, an assistant professor in the Department of Emergency Medicine at UCLA, calls for the U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) detention centers to increase health outcome reporting for detained immigrants to monitor the quality of medical care. Pulling from three different data sources, the researchers found discrepancies in care reported by emergency medical services (EMS) compared to ICE reports.
Building upon work that reviews deaths that occur at ICE detention centers, Dekker and colleagues sought to address concerns that individuals detained by ICE ...
Revisiting gene dosage
2023-11-29
Have you ever wondered why we carry two copies of each chromosome in all of our cells? During reproduction, we receive one from each of our parents. This means that we also receive two copies, or alleles, of each gene – one allele per chromosome or parent.
Both alleles are able to produce messenger RNA, which is the recipe needed to make proteins and keep cells running. Scientists hypothesize that having two alleles for each gene is the cell’s in-built redundancy system. If there is ever a mutation or drop in messenger RNA production from the allele carried on one of the chromosomes, the allele on the second chromosome will serve as a backup and ...
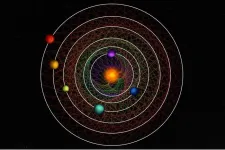
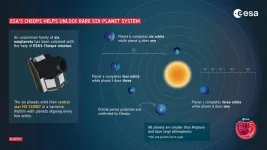
Scientists discover rare 6-planet system that moves in strange synchrony
2023-11-29
Scientists have discovered a rare sight in a nearby star system: Six planets orbiting their central star in a rhythmic beat. The planets move in an orbital waltz that repeats itself so precisely it can be readily set to music.
A rare case of an “in sync” gravitational lockstep, the system could offer deep insight into planet formation and evolution.
The analysis, led by UChicago scientist Rafael Luque, will be published Nov. 29 in Nature.
“This discovery is going to become a benchmark system to study how sub-Neptunes, the most common type of planets outside of the solar system, form, evolve, what are they made of, and if they possess the ...
Disruptive ideas rely on old fashioned meetings
2023-11-29
A marvel of modernity is the ability to collaborate with others regardless of location. Researchers can work with a colleague, maybe the only person who has a specialized skill, even if they are halfway across the globe. They can pull together a powerhouse team with a dozen of the brightest minds in the field.
Yet, according to research from the lab of Lingfei Wu, assistant professor in Pitt’s School of Computing and Information, these collaborative teams are producing fewer truly disruptive ideas or radical innovations than ...
An astronomical waltz reveals a sextuplet of planets
2023-11-29
An international collaboration between astronomers using the CHEOPS and TESS space satellites, including NCCR PlanetS members from the University of Bern and the University of Geneva, have found a key new system of six transiting planets orbiting a bright star in a harmonic rhythm. This rare property enabled the team to determine the planetary orbits which initially appeared as an unsolvable riddle.
CHEOPS is a joint mission by ESA and Switzerland, under the leadership of the University of Bern in collaboration with the University of Geneva. Thanks to a collaboration with scientists ...
Final call for Awards Nominations 2024 of the World Cultural Council
2023-11-29
The World Cultural Council (WCC) is now accepting nominations for the “Albert Einstein” World Award of Science and the “Leonardo da Vinci” World Awards of Arts.
Nominations must be submitted by 26 January, 2024. NOMINATE NOW: To nominate online or for further details of the awards visit the WCC website Nominations page.
Ideal candidates for the “Albert Einstein” World Award of Science are scientists whose achievements can serve as an inspiration for future generations. This award is granted each year. Consideration will be given to ...
BU/VA researcher awarded funding to prevent intimate partner violence
2023-11-29
(Boston)—Casey Taft, PhD, professor of psychiatry at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has been approved for a five-year, $2.8 million funding award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) for his research study “A Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate a Trauma-Informed Partner Violence Intervention Program.”
Taft, who also is a staff psychologist at the National Center for PTSD in the VA Boston Healthcare System, is conducting a randomized controlled trial of the Strength at Home program to prevent and end intimate partner violence (IPV) in Rhode Island. Strength at Home ...
The act of saying "no" under the linguistic magnifying glass
2023-11-29
FRANKFURT. Prof. Bernhard Brüne, Vice President Research, Early Career Researchers and Transfer at Goethe University Frankfurt, congratulated the researchers involved in the successful application: "Anyone who establishes a major project like a Collaborative Research Center must have both creative and viable research ideas as well as a strong network. To discover new things about language and thinking, the new CRC 1629 not only makes use of Goethe University’s structures, and the combination of philology with philosophy and didactics. It also cooperates with partner universities in Göttingen and Tübingen. Aside that, I am of course delighted that ...
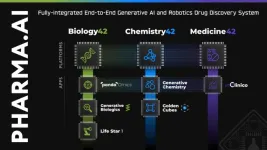
Insilico Medicine showcases latest AI drug discovery platform breakthroughs
2023-11-29
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), an artificial intelligence (AI)-driven, clinical stage biotechnology company and leader in AI drug discovery platform technology, is hosting three webinars unveiling its latest technology breakthroughs Nov. 28-30, 2023. These new features are part of the expansion of the Company’s end-to-end Pharma.AI platform and include chat functionality, off-target screening tools, enhanced knowledge graphs and more. They represent major steps forward in the advancement of AI drug discovery.
The company is an early ...
New astrophysics model sheds light on additional source of long gamma-ray bursts
2023-11-29
Cutting-edge computer simulations combined with theoretical calculations are helping astronomers better understand the origin of some of the universe’s most energetic and mysterious light shows — gamma-ray bursts, or GRBs. The new unified model confirms that some long-lasting GRBs are created in the aftermath of cosmic mergers that spawn an infant black hole surrounded by a giant disk of natal material.
Astronomers previously thought that black holes that generate long GRBs typically form when massive ...
Brain scans of former NFL athletes show a repair protein in place long after initial injury
2023-11-29
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In a new study using brain scans of former NFL athletes, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they found high levels of a repair protein present long after a traumatic brain injury such as a concussion takes place. The repair protein, known as 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO), is known to be present in the brain at high levels in the immediate aftermath of brain injury as part of the inflammatory response and to facilitate repair. The new findings, published Oct. 30 in JAMA Network Open, suggest that brain injury and repair processes persist for years after players end collision sports careers, and lead to long-term cognitive ...
Long-live quantum entanglement goes to distance
2023-11-29
Quantum technologies are currently maturing at a breath-taking pace. These technologies exploit principles of quantum mechanics in suitably engineered systems, with bright prospects such as boosting computational efficiencies or communication security well beyond what is possible with devices based on today’s 'classical' technologies. As with classical devices, however, to realise their full potential, quantum devices will need to be networked. In principle, this can be done using the fibre-optic networks employed for classical telecommunications. But practical implementation requires that the information ...
[1] ... [1515]
[1516]
[1517]
[1518]
[1519]
[1520]
[1521]
[1522]
1523
[1524]
[1525]
[1526]
[1527]
[1528]
[1529]
[1530]
[1531]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.