The double-edge sword of CRISPR application for in vivo studies
2023-11-28
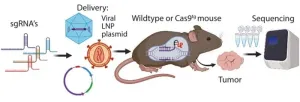
“The Achilles’ heel of CRISPR application is the delivery of sgRNA/Cas9 to the desired tissues.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 28, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on November 27, 2023, entitled, “The double-edge sword of CRISPR application for in vivo studies.”
In this new paper, researcher Martin K. Thomsen from Aarhus University begins his editorial by discussing a hallmark paper that was published a decade ago by Platt et al. on the in vivo ...
UTA research examines how to stay on task
2023-11-28
Our ability to pay attention to tasks—a key component of our everyday lives—is heavily influenced by factors like motivation, arousal and alertness. Maintaining focus can be especially challenging when the task is boring or repetitive.
“In many activities, it is difficult to maintain a high level of focus over time. Our research asks why this is the case,” said Matthew K. Robison, assistant professor of psychology at The University of Texas at Arlington.
He and colleagues at the University ...
Research spotlight: Improvements in HIV care in Black and White men who have sex with men
2023-11-28
Katherine Rich, MD MPH, resident in the MGH Department of Medicine, is the first author of a recently published paper in JAMA Network Open, “Projected Life Expectancy Gains from Improvements in HIV Care in Black and White Men Who Have Sex With Men.” Aima Ahonkhai, MD MPH and Emily Hyle, MD MSc, physician investigators in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital, are co-senior authors.
What Question Were You Investigating?
Substantial inequities persist across the HIV care continuum in the US; Black people with HIV bear a disproportionate disease burden due, ...
Sylvester study: Country of birth a key factor in assessing risk for conditions favorable to stomach cancer development
2023-11-28
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Nov. 28, 2023) – Researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have found that country of birth – not just geographic region – is a key risk factor for gastric intestinal metaplasia, a precursor lesion of stomach cancer.
Although stomach cancer, often called gastric cancer, is relatively rare in the United States, it is much more common and deadly among Hispanics, non-Hispanic Black people, Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders than among the white population.
Sylvester and the University of Miami Health System serve a widely diverse racial and ethnic population, including ...
Carnegie Mellon University's XRTC will drive research into VR, AR innovations
2023-11-28
Virtual, augmented and other extended reality technologies present the possibility to transform health care, education, entertainment, communication and more.
And that transformation is close.
Headsets and haptic gloves could connect doctors and patients thousands of miles apart in a virtual hospital. Sensors could monitor someone's health or help teachers know if their students are paying attention. Scanners could allow objects from a person's home to appear in their favorite video game. Glasses could help people with visual impairments navigate the world around them. Extended ...
UTHealth Houston School of Dentistry researcher awarded $2 million grant by NIH to study pharmacotoxicity of areca nut
2023-11-28
A five-year, $2 million grant to study the pharmacological effects of the areca nut, commonly known as the betel nut, was awarded to a UTHealth Houston researcher by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The study, led by Alan Myers, PharmD, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology with UTHealth Houston School of Dentistry, will investigate how chemicals in the areca nut are metabolized in the body’s organs, particularly in the liver, and how that process is disrupted by alcohol or menthol.
“On the global level, areca nut chewing has been around since antiquity, but still poses a major public health ...
Heart over head? Stages of the heart’s cycle affect neural responses
2023-11-28
Optimal windows exist for action and perception during the 0.8 seconds of a heartbeat, according to research published November 28th in the open access journal PLOS Biology. The sequence of contraction and relaxation is linked to changes in the motor system and its ability to respond to stimulation, and this could have implications for treatments for depression and stroke that excite nerve cells.
The ways in which we perceive and engage with the world are influenced by internal bodily processes such as heartbeats, respiration and digestion. Cardiac activity can influence auditory and ...
NASA’s Fermi Mission nets 300 gamma-ray pulsars … and counting
2023-11-28
A new catalog produced by a French-led international team of astronomers shows that NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has discovered 294 gamma-ray-emitting pulsars, while another 34 suspects await confirmation. This is 27 times the number known before the mission launched in 2008.
“Pulsars touch on a wide range of astrophysics research, from cosmic rays and stellar evolution to the search for gravitational waves and dark matter,” said study coordinator David Smith, research director at the Bordeaux Astrophysics Laboratory in Gironde, France, which is part of CNRS (the ...
Study reveals hidden immune defense against cancer
2023-11-28
FINDINGS
Researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center have found certain immune cells can still fight cancer even when the cancer cells lack an important protein that the immune system relies on to help track down cancer cells.
The team discovered the absence of the crucial protein B2M seems to activate an alternative immune response involving natural killer (NK) cells and CD4+ T cells in both animal studies and patient tumor biopsies, indicating a potential backup mechanism in the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
BACKGROUND
Immunotherapies, such as immune ...
Annals of Family Medicine: papers explore how technology is changing medical practice and how doctors are adapting
2023-11-28
Providence, R.I. – From the ability to conduct clinical visits online to utilizing artificial intelligence to effectively diagnose patients, technology has changed how all doctors practice medicine. One published paper in the November/December issue of Annals of Family Medicine explains how AI-driven technology presents new opportunities for more effective patient care while a second paper describes the interplay between fulfillment of basic psychological needs at work and technology use in maintaining clinician well-being.
In ...
Researchers advance 'placenta-on-a-chip' with sensing, imaging technology
2023-11-28
AMES, Iowa – A research poster dated Dec. 9, 2015, hangs just outside Nicole Hashemi’s Iowa State University laboratory. It introduces a major project for Hashemi and her research group. And it’s evidence that scientific persistence sometimes equals scientific advancement.
Hashemi, an associate professor of mechanical engineering, and her students have been working all these years to develop a “placenta-on-a-chip.” In this case that’s a thin, rectangular, clear, polymer block with two tiny microchannels – just millionths of ...
How neurotransmitters work together to detect and discriminate odors
2023-11-28
A longstanding hypothesis in neurobiology was that a single neuron releases a single type of neurotransmitter, a molecule used by neurons to communicate with one another. In recent decades, several neurons have been found to release more than one neurotransmitter. This phenomenon called co-transmission is increasingly gaining recognition as a powerful and versatile molecular mechanism useful for the dynamic regulation of diverse neural circuits. However, precisely how co-transmission affects the firing of ...
ChargeX Consortium recommends common EV charging station error codes
2023-11-28
New shared language will facilitate faster service, improve EV user experience
The National Charging Experience Consortium (ChargeX) has released a report that recommends 26 common electric vehicle (EV) charging error codes to enable faster error reporting, diagnostics and resolution within the EV charging industry. Ultimately, the codes would improve the U.S. charging experience.
The ChargeX Consortium is a collaboration between U.S. Department of Energy national laboratories, EV charging industry experts, consumer advocates and other stakeholders.
The Recommendations for Minimum Required Error Codes report aims to reduce confusion between charger manufacturers, EV manufacturers and ...
Ending the HIV epidemic may require addressing “everyday” discrimination
2023-11-28
Latino sexual minority men who experience racial, ethnic and sexual prejudice are more likely to delay HIV testing, complicating efforts to end the more than 40-year epidemic, according to a new Rutgers study.
“Total HIV infection rates in the United States are stabilizing, which is good news,” said Gabriel Robles, an assistant professor at the Rutgers School of Social Work and coauthor of the paper published in the journal AIDS Education and Prevention. “What’s bad is that the trend for some subgroups, including some Latino/x sexual minority men, is going in the opposite direction. Our study offers ...
Anonymous $10 million gift to Henry Ford Health establishes lung cancer tissue repository, bolsters research
2023-11-28
As Lung Cancer Awareness Month comes to a close, Henry Ford Health is proud to announce it has received an anonymous gift of $10 million, which is poised to significantly advance lung cancer research at Henry Ford Cancer.
This transformative gift has enabled Henry Ford to establish a new lung cancer tissue biorepository, which is a facility that catalogs and stores biological samples for research. These samples – in this case, lung cancer tissue – are crucial for scientists who are studying ...
RCSI researchers develop material that reduces bacterial infection and speeds up bone healing
2023-11-28
28 November 2023: Researchers at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and Advanced Materials and Bioengineering Research Centre (AMBER) have developed a new surgical implant that has the potential to transform the treatment of complex bone infections. When implanted on an injured or infected bone, the material can not only speed up bone healing, it also reduces the risk of infections without the need for traditional antibiotics.
The newly published paper in the journal Advanced Materials, tackles the complex clinical problem of bone infection, ...
Contrast sensitivity of ON and OFF human retinal pathways in myopia
2023-11-28
Across the entire animal kingdom, visual images are processed by two major neuronal pathways that extract light and dark stimuli from visual scenes – ON (light on) and OFF (light off) pathways.
Light stimuli are brighter than their background like a white cloud in a gray sky whereas dark stimuli are darker than the background like a black bird in a blue sky. The two pathways can extract stimuli with different contrasts but some pathways are more sensitive than others. In carnivores and rodents, ON pathways are more sensitive ...
DFW air quality continues to miss EPA goals for safety
2023-11-28
Air quality in the Dallas-Fort Worth metropolitan area continues to miss safety levels set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and is unlikely to meet EPA goals anytime soon, according to new research from The University of Texas at Arlington.
Purnendu “Sandy” Dasgupta, professor of chemistry and biochemistry and the Hamish Small Chair of Ion Analysis at The University of Texas at Arlington, said the region’s low population density, lack of widespread public transportation and reliance on cars contribute to its poor air quality. Its ozone values have exceeded safety levels set by the EPA for the last 20 years.
“Compared ...
Many owners see little value in storing their firearms securely
2023-11-28
With more than 400 million privately owned firearms in circulation across the United States, gun violence prevention efforts have emphasized secure firearm storage as a method for preventing injury and death. But some owners may not see the value in doing so, according to Rutgers researchers.
Despite evidence that secure storage can effectively reduce the risk of suicide and unintentional shootings, many firearm owners typically keep at least one firearm stored loaded and unlocked, quickly accessible in case of home invasion. ...
PCORI approves $80.5 million for health research using novel approaches to tackle social and clinical care factors that contribute to maternal health inequities
2023-11-28
WASHINGTON, D.C. – The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) today announced funding awards totaling $80.5 million to support four new, ambitious patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER) studies focused on both the health care and social factors that contribute to inequities in maternal morbidity and mortality. The trials are among 30 CER studies and related projects recently approved for PCORI funding.
Awarded through an innovative PCORI funding opportunity known as Partner for its focus on partnering research institutions and community organizations ...
Ohio State receives $14 million to study optimal aspirin therapy in pregnancy
2023-11-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A research team at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine has been approved for a $14 million award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) to study whether a higher daily dose of aspirin is more effective in decreasing the risk of dangerous blood pressure complications among some pregnant people.
During pregnancy, people are at risk of developing preeclampsia and gestational hypertension. Both disorders are characterized by high blood pressure and bring with them the potential for injury to the brain, lungs, kidneys and liver. These hypertensive disorders ...
University of Colorado Department of Medicine cardiologist lands $7 million funding award for nationwide study on improving heart-failure treatment
2023-11-28
Larry Allen, MD, chief of the Division of Cardiology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, will receive a funding award for a nationwide study that he hopes will lead to more heart-failure patients getting the life-saving medications they need.
The $7 million in support, announced Nov. 28, is from the nonprofit Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), the leading U.S. funder of comparative clinical effectiveness research centered on patients.
Allen, a professor of cardiology in the CU Department of Medicine, says the funding award includes $2.5 million in direct support to CU, another $2.5 million to four other ...
PCORI approves $225 million in funding for dozens of health research studies and related projects
2023-11-28
WASHINGTON, D.C. – The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) today announced the approval of funding awards totaling $225 million, which include $207 million to support 20 new patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER) studies. By comparing various approaches to care, these studies will help fill evidence gaps related to maternal illness and death, adolescent mental health, delirium in older adults, cardiovascular disease and a range of other high-burden health conditions.
Four awards include support for large patient-centered CER studies in which community organizations and research institutions as coequal partners will tackle ...
Opioids vs. NSAIDS: which are safest and most effective for treating pain following surgery?
2023-11-28
LOS ANGELES (November 28, 2023)—Thousands of adolescents and young adults have outpatient surgery every day and are sent home with pain medication. Although the need for medication is clear, the best way to treat the pain is not. A new study led by investigators at the University of Michigan and Children’s Hospital Los Angeles will compare two treatment regimens—one that uses a regimen of non-opioid medication and another that adds a low-dose opioid—to determine the safest and most effective way to treat pain in adolescents and young adults recovering from common outpatient surgeries.
In the past, opioids ...
Slash-and-burn agriculture can increase forest biodiversity
2023-11-28
The slash-and-burn agriculture practiced by many Indigenous societies across the world can actually have a positive impact on forests, according to a new study done in Belize.
Researchers found that in areas of the rainforest in which Indigenous farmers using slash-and-burn techniques created intermediate-sized farm patches – neither too small nor too large – there were increases in forest plant diversity.
This contradicts what had long been the standard view in the past, promoted by the ...
[1] ... [1518]
[1519]
[1520]
[1521]
[1522]
[1523]
[1524]
[1525]
1526
[1527]
[1528]
[1529]
[1530]
[1531]
[1532]
[1533]
[1534]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.