Making a difference, belonging drives rural festival volunteers and bolsters community development
2023-11-27
AMES, Iowa — During Orange City’s three-day tulip festival each May, the northwest Iowa town attracts roughly 40,000 visitors, more than six times its population. People come for the blooms and parades, traditional Dutch food and musical theater. For the community, it’s an opportunity to celebrate its cultural heritage and give a boost to local businesses.
Volunteers are essential to the festival’s success, as they are for many rural celebrations across the Midwest. But not a lot of research has examined their motivations. To help fill this gap, researchers surveyed hundreds of volunteers from 12 festivals — including ...
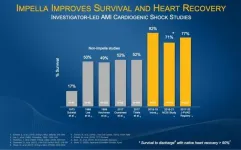
First patient enrolled in Abiomed’s RECOVER IV randomized controlled trial of Impella as a therapy for AMI cardiogenic shock
2023-11-27
DANVERS, Mass. – Nov. 27, 2023 – Abiomed, part of Johnson & Johnson MedTech[1], announces the first patient in the world has been enrolled in the landmark RECOVER IV randomized controlled trial (RCT). The on-label, two-arm trial will randomize 548 patients to assess whether Impella support prior to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is superior to PCI without Impella in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) cardiogenic shock.
Impella is the only mechanical circulatory support device for the treatment of AMI cardiogenic ...
Kavli Exploration Award backs Rice-led sustainable carbon materials research
2023-11-27
HOUSTON – (Nov. 27, 2023) – An international team of scientists led by Rice University’s Matteo Pasquali has won a $4.1 million grant to optimize carbon nanotube synthesis, a process that could help drive the green energy transition by providing more sustainable alternatives to materials dependent on heavy industry. The award is a joint effort by The Kavli Foundation, with a $1.9 million Kavli Exploration Award in Nanoscience for Sustainability, and Rice’s Carbon Hub, which contributed an additional $2.2 million.
“The energy transition is primarily a material transition,” Pasquali said. “Renewable energy ...
Mixing heat with hair styling products may be bad for your health
2023-11-27
Hair products often contain ingredients that easily evaporate, so users may inhale some of these chemicals, potentially posing health repercussions. Now, researchers have studied emissions of these volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including siloxanes, which shine and smooth hair. The scientists report in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology that using these hair care products can change indoor air composition quickly, and common heat styling techniques — straightening and curling — increase VOC levels even more.
Some ...
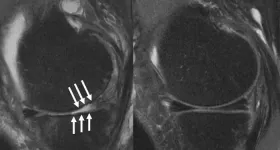
Stronger thigh muscles may prevent knee replacement surgery
2023-11-27
CHICAGO – Stronger quadriceps muscles, relative to the hamstrings, may lower the risk of total knee replacement, according to research being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Researchers said the findings could inform strength-training programs for people with advanced arthritis in the knee.
Advanced knee osteoarthritis is a major cause of pain and disability worldwide. In the U.S. alone, 14 million adults have symptomatic knee osteoarthritis, and more than half of those diagnosed are projected to eventually undergo total knee replacement surgery.
While stronger muscle groups are generally understood ...
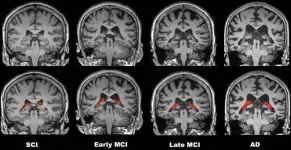
Black patients face delays in Alzheimer’s diagnosis
2023-11-27
CHICAGO – Black patients underwent medical imaging for cognitive impairment years later than white and Hispanic patients and were less frequently tested with MRI, according to research being presented this week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Previous studies have shown that Black patients are at increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia. They are less likely to have a diagnosis and are diagnosed at a more advanced stage of disease compared to white patients.
Medical ...
Patient support programs for prescription drugs are common, especially for expensive drugs
2023-11-27
About 1 in 10 prescription drugs — mainly brand-name and expensive drugs and those for rare diseases — has a manufacturer-sponsored patient support program, which usually includes financial, nursing and educational supports.
"In an era where policy-makers are grappling with escalating drug prices and budgetary impacts globally, the pharmaceutical industry promotes patient support programs as adding complementary value to a drug through supporting medication adherence and enhancing clinical outcomes, patient experience or quality of life," ...
Secrecy at Canada's pest management agency must end
2023-11-27
Health Canada increased maximum residue limits for glyphosate in some crops, such as oats and beans, in 2021 despite concerns about the health impact of glyphosate-based herbicides (GBHs). The World Health Organization's (WHO) International Agency for Research on Cancer regards these pesticides as genotoxic, meaning they can damage DNA and are likely carcinogenic.
"Health Canada's PMRA considers pesticide sales and risk evaluation data in Canada to be confidential business information, and independent researchers cannot access these data, even through the Access to Information Act. Such ...
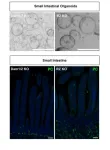
Decoding cell fate: Key mechanism in stem cell switch identified
2023-11-24
Stem cells can differentiate to replace dead and damaged cells. But how do stem cells decide which type of cell to become in a given situation? Using intestinal organoids, the group of Bon-Kyoung Koo at IMBA and the Institute for Basic Science identified a new gene, Daam1, that plays an essential role, switching on the development of secretory cells in the intestine. This finding, published on November 24 in Science Advances, opens new perspectives in cancer research.
Our bodies are, in some ways, like cars – to keep functioning, they need to be checked and repaired regularly. In the case of our bodies, ...
The Fens of eastern England once held vast woodlands, study finds
2023-11-24
The Fens of eastern England, a low-lying, extremely flat landscape dominated by agricultural fields, was once a vast woodland filled with huge yew trees, according to new research.
Scientists from the University of Cambridge studied hundreds of tree trunks, dug up by Fenland farmers while ploughing their fields. The team found that most of the ancient wood came from yew trees that populated the area between four and five thousand years ago.
These trees, which are a nuisance when they jam farming equipment during ploughing, contain a treasure trove of perfectly preserved ...
Premature death of autistic people in the UK investigated for the first time
2023-11-24
A new study led by UCL researchers confirms that autistic people experience a reduced life expectancy, however the number of years of life lost may not be as high as previously claimed.
The research, published in The Lancet Regional Health – Europe, is the first to estimate the life expectancy and years of life lost by autistic people living in the UK.
The team used anonymised data from GP practices throughout the UK to study people who received an autism diagnosis between 1989 to 2019. They ...
How do plants determine where the light is coming from ?
2023-11-23
Plants have no visual organs, so how do they know where light comes from? In an original study combining expertise in biology and engineering, the team led by Prof Christian Fankhauser at UNIL, in collaboration with colleagues at EPFL, has uncovered that a light-sensitive plant tissue uses the optical properties of the interface between air and water to generate a light gradient that is 'visible' to the plant. These results have been published in the journal Science.
The majority of living organisms (micro-organisms, plants and animals) have the ability to determine the origin of a light source, even in the absence of a sight organ comparable to the eye. This information is invaluable ...
Study provides fresh insights into antibiotic resistance, fitness landscapes
2023-11-23
E. coli bacteria may be far more capable at evolving antibiotic resistance than scientists previously thought, according to a new study published in Science on November 24.
Led by SFI External Professor Andreas Wagner, the researchers experimentally mapped more than 260,000 possible mutations of an E. coli protein that is essential for the bacteria’s survival when exposed to the antibiotic trimethoprim.
Over the course of thousands of highly realistic digital simulations, the researchers then found that 75% of all possible evolutionary paths of the E. coli protein ultimately ...
Separating out signals recorded at the seafloor
2023-11-23
Blame it on plate tectonics. The deep ocean is never preserved, but instead is lost to time as the seafloor is subducted. Geologists are mostly left with shallower rocks from closer to the shoreline to inform their studies of Earth history.
“We have only a good record of the deep ocean for the last ~180 million years,” said David Fike, the Glassberg/Greensfelder Distinguished University Professor of Earth, Environmental, and Planetary Sciences in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis. “Everything else is just shallow-water deposits. So it’s really important to understand the bias that might be present when we look ...
Dolomite crystals require cycles of saturation conditions to grow
2023-11-23
Addressing the long-standing “dolomite problem,” an oddity that has vexed scientists for nearly 200 years, researchers report that dolomite crystals require cycling of saturation conditions to grow. The findings provide new insights into how dolomite is formed and why modern dolomite is primarily found in natural environments with pH or salinity fluctuations. Dolomite – a calcium magnesium carbonate – is one of the major minerals in carbonate rocks, accounting for nearly 30% of the sedimentary carbonate minerality in Earth’s crust. However, despite its geological abundance, dolomite does not readily grow under laboratory conditions, ...
FLSHclust, a new algorithm, reveals rare and previously unknown CRISPR-Cas systems
2023-11-23
Using a new algorithm called FLSHclust (“flash clust”), researchers have discovered 188 rare and previously unknown CRISPR-linked gene modules – including a novel type VII CRISPR-Cas system – among billions of protein sequences. The approach and its findings provide novel opportunities for harnessing CRISPR systems and understanding the vast functional diversity of microbial proteins. CRISPR systems have been leveraged to develop a growing suite of novel biomolecular approaches, including CRISPR/Cas-mediated genome editing. The discovery ...
Extremely energetic cosmic ray detected, but with no obvious source
2023-11-23
An extremely energetic cosmic ray – an extragalactic particle with an energy exceeding ~240 exa-electron volts (EeV) – has been detected by the Telescope Array experiment’s surface detector, researchers report. However, according to the findings, its arrival direction shows no obvious source. Ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) are subatomic charged particles from space with energies greater than 1 EeV – roughly a million times as high as the energy reached by human-made particle accelerators. Although low-energy cosmic rays primarily emanate from the sun, the origins of rarer UHECRs are thought to be related to the most energetic phenomena in the Universe, ...
Telescope Array detects second highest-energy cosmic ray ever
2023-11-23
In 1991, the University of Utah Fly’s Eye experiment detected the highest-energy cosmic ray ever observed. Later dubbed the Oh-My-God particle, the cosmic ray’s energy shocked astrophysicists. Nothing in our galaxy had the power to produce it, and the particle had more energy than was theoretically possible for cosmic rays traveling to Earth from other galaxies. Simply put, the particle should not exist.
The Telescope Array has since observed more than 30 ultra-high-energy cosmic rays, though none approaching the Oh-My-God-level energy. No observations have yet revealed ...
'Dolomite Problem': 200-year-old geology mystery resolved
2023-11-23
Images // Video
ANN ARBOR—For 200 years, scientists have failed to grow a common mineral in the laboratory under the conditions believed to have formed it naturally. Now, a team of researchers from the University of Michigan and Hokkaido University in Sapporo, Japan have finally pulled it off, thanks to a new theory developed from atomic simulations.
Their success resolves a long-standing geology mystery called the "Dolomite Problem." Dolomite—a key mineral in the Dolomite mountains in Italy, Niagara Falls, the White Cliffs of Dover and Utah's Hoodoos—is very abundant in rocks older than 100 million years, but nearly absent in younger ...
AI recognizes the tempo and stages of embryonic development
2023-11-23
Animal embryos go through a series of characteristic developmental stages on their journey from a fertilized egg cell to a functional organism. This biological process is largely genetically controlled and follows a similar pattern across different animal species. Yet, there are differences in the details – between individual species and even among embryos of the same species. For example, the tempo at which individual embryonic stages are passed through can vary. Such variations in embryonic development are considered an important driver of evolution, as they can lead to new characteristics, thus promoting evolutionary adaptations and biodiversity.
Studying the embryonic ...
Potential new target and drug candidate for Barth syndrome
2023-11-23
In a Nature Metabolism paper published today, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh detail a potential new target and a small-molecule drug candidate for treating Barth syndrome, a rare, life-threatening and currently incurable genetic disease with devastating consequences.
Barth syndrome affects about 1 in every 300,000 to 400,000 babies born worldwide. Those with the condition have weak muscles and hearts and experience debilitating fatigue and recurrent infections.
Pitt researchers discovered that faulty mitochondria are at least partially to blame, and identified a molecular culprit that could be targeted to potentially reverse the disease course in the future.
In ...
New therapy can treat rare and hereditary diseases
2023-11-23
A lot of research has been done over many decades on diseases that are widespread in large parts of the population, such as cancer and heart disease. As a result, treatment methods have improved enormously thanks to long-term research efforts on diseases that affect many people.
However, there are many diseases that affect just a handful people. These diseases often fly under the radar and are far less researched. They include quite a few rare, hereditary diseases, such as DOOR syndrome, which is ...
Y-chromosome and its impact on digestive diseases
2023-11-23
A major breakthrough in human genetics has been achieved with the complete decoding of the human Y chromosome, opening up new avenues for research into digestive diseases. This milestone, along with advancements in third-generation sequencing technologies, is poised to revolutionize our understanding of the genetic underpinnings of digestive disorders and pave the way for more personalized and effective treatment strategies.
The Y chromosome, the smallest of the human chromosomes, has long been shrouded in mystery due to its complex repetitive structure. However, recent advancements in sequencing technologies have enabled researchers to unravel the intricate details of this genetic ...
Fractional COVID-19 booster vaccines produce similar immune response as full-doses
2023-11-23
Reducing the dose of a widely used COVID-19 booster vaccine produces a similar immune response in adults to a full-dose with fewer side effects, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and the National Centre for Communicable Diseases in Mongolia, found that a half dose of a Pfizer COVID-19 booster vaccine elicited a non-inferior immune response to a full dose in Mongolian adults who previously had AstraZeneca or Sinopharm COVID-19 shots. But it found half-dose boosting may be less effective in adults primed with the Sputnik V COVID-19 vaccine.
The research ...
Consolidator Grants: ERC unleashes €627 million in grants to fuel excellent research across Europe
2023-11-23
Iliana Ivanova, European Commissioner for Innovation, Research, Culture, Education and Youth, said: “I extend my heartfelt congratulations to all the brilliant researchers who have been selected for ERC Consolidator Grants. I'm especially thrilled to note the significant increase in the representation of women among the winners for the third consecutive year in this prestigious grant competition. This positive trend not only reflects the outstanding contributions of women researchers but also highlights the strides we are making towards a more inclusive and diverse scientific community.”
President of the European Research Council Prof. Maria Leptin said: “The new ...
[1] ... [1524]
[1525]
[1526]
[1527]
[1528]
[1529]
[1530]
[1531]
1532
[1533]
[1534]
[1535]
[1536]
[1537]
[1538]
[1539]
[1540]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.