Survival of the fittest? New study shows how cancer cells use cell competition to evade the body’s defenses
2023-11-22
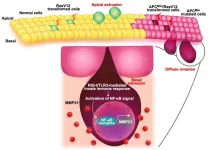
Living cells compete with each other and try to adapt to the local environment. Cells that are unable to do so are eliminated eventually. This cellular competition is crucial as the surrounding normal epithelial cells use it to identify and eliminate mutant cancer cells. Studies have reported that when activating mutants of “Ras” proteins are expressed in mammalian epithelial cells, they are pushed toward the lumen, excreted along with other bodily waste, and eliminated by competition. Epithelial cells containing Ras mutants have been reported to be removed in this manner in several organs, including the small intestine, stomach, pancreas, and lungs. ...
Danish researchers puncture 100-year-old theory of odd little 'water balloons'
2023-11-22
Quinoa and many other extremely resilient plants are covered with strange balloon-like 'bladders' that for 127 years were believed to be responsible for protecting them from drought and salt. Research results from the University of Copenhagen reveal this not to be the case. These so-called bladder cells serve a completely different though important function. The finding makes it likely that even more resilient quinoa plants will now be able to be bred, which could lead to the much wider cultivation of this sustainable ...
Novel MRI reveals brain changes in long-COVID patients
2023-11-22
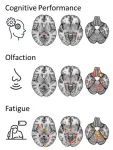
CHICAGO – People with long COVID exhibit patterns of changes in the brain that are different from fully recovered COVID-19 patients, according to research being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study comparing patients with long COVID to both a group without history of COVID-19 and a group that went through a COVID-19 infection but is subjectively unimpaired,” said one of the study’s lead authors, Alexander Rau, M.D., resident in the Departments of Neuroradiology and Diagnostic and ...
AI identifies non-smokers at high risk for lung cancer
2023-11-22
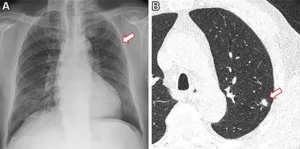
CHICAGO – Using a routine chest X-ray image, an artificial intelligence (AI) tool can identify non-smokers who are at high risk for lung cancer, according to a study being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death. The American Cancer Society estimates about 238,340 new cases of lung cancer in the United States this year and 127,070 lung cancer deaths. Approximately 10-20% of lung cancers occur in “never-smokers” – people who have never smoked cigarettes ...
This sea worm’s butt swims away, and now scientists know how
2023-11-22
A research team, led by Professor Toru Miura from the University of Tokyo, shows how the expression of developmental genes in the Japanese green syllid worms, Megasyllis nipponica, helps form their swimming reproductive unit called stolon.
Life always finds ways to surprise us. The presence of a unique reproductive mechanism of some annelid worms or segmented worms is one such surprise. In a process called stolonization, the posterior body part with gonads of the syllid worm detaches from its original body. The detached part is called the stolon, and it is full of gametes (eggs or sperms). The stolon swims around by itself and spawns when it ...
New study on experience of adopted people as they become parents
2023-11-22
Becoming a parent is a key turning point for adopted people
Parenting is always challenging, but for adopted people becoming a mum or dad can be extra demanding, as well as extra special – according to research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study is the first in to investigate the lived experiences of adopted people in the UK as they become parents.
It finds that they are affected by issues that link back to their adoption and to difficult experiences in their past – related to loss, rejection, abuse and neglect.
Because of these ...
Anti-rheumatic drugs could prevent thyroid disease
2023-11-22
Anti-rheumatic drugs used for rheumatoid arthritis might prevent the development of autoimmune thyroid disease, according to a new observational study by researchers from Karolinska Institutet published in the Journal of Internal Medicine.
It is well known that patients with rheumatoid arthritis are at increased risk of autoimmune thyroid diseases such as Hashimoto's disease and Graves' disease. While patients with RA are usually treated with immunomodulatory drugs that affect the immune system, such drugs are rarely used in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Instead, such patients are treated with thyroid hormone to compensate for the changes in normal ...
Does spaceflight increase men’s risk of erectile dysfunction?
2023-11-22
During missions into space, astronauts are exposed to high levels of galactic cosmic radiation and weightlessness. Simulation experiments in male rats indicated that these aspects of spaceflight can negatively affect vascular tissues relevant to erectile dysfunction, even after a period of long-term recovery.
The research, which is published in The FASEB Journal, indicated that vascular alterations are induced by relatively low doses of galactic cosmic radiation and to a lesser extent simulated weightlessness, primarily through increases in oxidative stress. Treatment with different antioxidants could counter some of these ...
What are the effects of workforce automation across race and gender in the United States?
2023-11-22
Advances in areas such as robotics and artificial intelligence enable the automation of a range of occupational tasks, leading to fundamental changes in the nature of work. New research published in The American Journal of Economics and Sociology indicates that the effects of job automation vary across race and gender, and without targeted interventions, will likely result in increasing inequality.
The research analyzes two distinct measures of automation job displacement risk for more than 1.4 million Americans across 385 occupations. The findings show that the intersection of race and gender has a significant effect on automation risks. For example, ...
Has the COVID-19 pandemic compromised bone health?
2023-11-22
Results from a study published in the American Journal of Human Biology suggest that the COVID-19 pandemic has had negative effects on bone tissue—including both bone mineral density in the forearm and total bone mineral content.
The study by investigators at Comenius University, in Slovakia, included 387 young adults whose bone health measurements were taken prior to the COVID-19 pandemic and 386 whose measurements were taken from September 2020 to November 2022 during the pandemic. Individuals participated in the study only once, either before or during the pandemic.
Certain lifestyle changes during the pandemic may have contributed ...
Does stem cell transplantation benefit patients with knee osteoarthritis?
2023-11-22
Cell therapy represents a potential regenerative treatment for osteoarthritis. A recent analysis of all relevant published studies indicates that stem cell transplantation from different sources is effective for treating knee osteoarthritis, the most prevalent chronic joint disease.
The review and meta-analysis, which is published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research, included 16 studies involving 875 patients with knee osteoarthritis (441 in the stem cell transplantation group and 434 in the control group). Stem cell treatment was associated with significant reductions in patient-reported pain from the third month onwards. The most significant pain relief at different postoperative months ...
Can sound stimulation lessen long-term concussion symptoms?
2023-11-22
New research indicates that acoustic stimulation of the brain may ease persistent symptoms in individuals who experienced mild traumatic brain injury in the past.
The study, which is published in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, included 106 military service members, veterans, or their spouses with persistent symptoms after mild traumatic brain injury 3 months to 10 years ago. Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive 10 sessions of engineered tones linked to brainwaves (intervention), or random ...
New partnership between ResearchGate and Pensoft to drive readership and visibility of open access journals
2023-11-22
ResearchGate, the professional network for researchers, and Pensoft, an independent open access academic publisher known worldwide for its cutting-edge publishing tools and workflows, today announced a new partnership that will see a set of Pensoft’s open access journals increase their reach and visibility through ResearchGate – increasing access and engagement with its 25 million researcher members.
Pensoft is a fully open access publisher, providing high-quality end-to-end services to its own and third-party scientific journals via its in-house developed scholarly publishing platform ARPHA.
As part of this new partnership, ...
Experts urge a united global vision, definitions and targets for ‘responsible sourcing’ of minerals needed for green transition
2023-11-22
Experts have delivered a sweeping prescription to governments, civil society and industry for a globally coordinated approach to the responsible sourcing of raw materials needed to achieve a circular green economy.
In a report, the four-year EU-funded RE-SOURCING project proposes adopting the global vision of a circular economy and reduced resource consumption by 2050 and outlines a series of interim milestones and targets for three key industrial sectors: renewable energy, mobility, and electric and electronic equipment.
The report (at https://bit.ly/3uqXlqT from ...
Rise in people discovered dead and decomposed raises concerns
2023-11-22
An exploratory study has raised concerns about the increasing number of people in England and Wales whose bodies are discovered so late that they have decomposed.
The study, published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, has highlighted potential links between growing isolation and such deaths, even before the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study was authored by a team led by Dr Lucinda Hiam of the University of Oxford and including histopathology registrar Dr Theodore Estrin-Serlui of Imperial College NHS Healthcare Trust.
The researchers analysed data from the Office for ...
Obesity may not be the only factor to link ultra-processed foods to higher risk of mouth, throat and oesophagus cancers
2023-11-22
Eating more ultra-processed foods (UPFs) may be associated with a higher risk of developing cancers of upper aerodigestive tract (including the mouth, throat and oesophagus), according to a new study led by researchers from the University of Bristol and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). The authors of this international study, which analysed diet and lifestyle data on 450,111 adults who were followed for approximately 14 years, say obesity associated with the consumption of UPFs may not be the only factor to blame. The study is published today [22 November] in the European Journal of Nutrition.
Several ...
Immunotherapy drug is well tolerated in lung cancer patients with limited physical function, study suggests
2023-11-22
For patients with advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and limited performance status, an immune checkpoint inhibitor drug called durvalumab is safe and may benefit overall survival, according to a new eClinicalMedicine study by UPMC Hillman Cancer Center researchers.
Performance status, a measure of a patient’s physical function and ability to perform daily activities, is often assessed with the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) score on a scale of 0 to 5. Higher values describe patients who spend more time confined to a bed or chair and have less ability to care for themselves. Many clinical ...
Strip searching a child without appropriate consent is “sexual abuse,” insists expert
2023-11-22
Strip searching a child without appropriate consent is “sexual abuse,” and should attract heavy sanctions—backed up by legislation—for any UK police officer who does it, insists a leading paediatrician in an opinion piece, published online in the Archives of Disease in Childhood.
Unless the officer(s) can legitimately justify their actions to an independent panel, they should be instantly dismissed and compelled to sign the Sex Offenders Register, writes paediatrician Professor Andy Bush of Imperial College, London.
He cites the “shocking number” of children ...
Skunks’ warning stripes less prominent where predators are sparse, study finds
2023-11-22
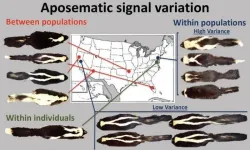
Striped skunks are less likely to evolve with their famous and white markings where the threat of predation from mammals is low, scientists from the University of Bristol, Montana and Long Beach, California have discovered.
Skunks’ iconic black and white colouration signals its toxic anal spray. However some skunks show very varied fur colour ranging from all black to thin or thick black and white bands to all white individuals. Variation is huge across the North American continent.
Findings ...
Chlorine disinfectant is no more effective than water at killing off hospital superbug
2023-11-22
One of the primary chlorine disinfectants currently being used to clean hospital scrubs and surfaces does not kill off the most common cause of antibiotic associated sickness in healthcare settings globally, according to a new study.
Research by the University of Plymouth has showed spores of Clostridioides difficile, commonly known as C. diff, are completely unaffected despite being treated with high concentrations of bleach used in many hospitals.
In fact, the chlorine chemicals are no more effective at damaging the spores when used as a surface disinfectant – than using water with no additives.
Writing in the journal Microbiology, the study’s authors ...
Rice receives $2.5M grant to support inclusive STEM education
2023-11-21
HOUSTON – (Nov. 21, 2023) – The Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) awarded Rice University with $2.5 million spanning over five years as part of its Driving Change initiative designed to connect research universities that are working to build inclusive learning environments for students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM).
“I’m honored and grateful to the Howard Hughes Medical Institute that Rice University was selected for the Driving Change initiative,” said Amy Dittmar, Howard R. Hughes Provost and executive vice president for academic affairs. “Rice has laid the groundwork for student ...
Medical AI tool from UF, NVIDIA gets human thumbs-up in first study
2023-11-21
A new artificial intelligence computer program created by researchers at the University of Florida and NVIDIA can generate doctors’ notes so well that two physicians couldn’t tell the difference, according to an early study from both groups.
In this proof-of-concept study, physicians reviewed patient notes — some written by actual medical doctors while others were created by the new AI program — and the physicians identified the correct author only 49% of the time.
A team of 19 researchers from NVIDIA and the University of Florida said ...
Getting to the root of visceral gut pain
2023-11-21
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
Researchers at Michigan State University may have discovered why visceral pain is so common in people who have experienced inflammation in their guts, including patients with irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS.
Working with mouse models, MSU physiologists showed that nervous system cells known as glia can sensitize nearby neurons, causing them to send pain signals more easily than they did prior to inflammation.
“The glia drop the threshold for activating a neuron,” said MSU Research Foundation Professor Brian Gulbransen, whose research team authored the new report in the ...
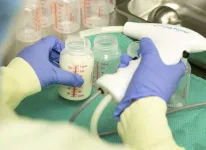
How AI could help optimize nutrient consistency in donated human breast milk
2023-11-21
A team of University of Toronto Engineering researchers, led by Professor Timothy Chan, is leveraging machine learning to optimize the macronutrient content of pooled human donor milk recipes.
The researchers introduce their data-driven optimization model in a new paper published in Manufacturing and Systems Operations Management.
Chan and his team worked with Mount Sinai Hospital’s Rogers Hixon Ontario Human Milk Bank — which provides donor milk to preterm and sick babies who are hospitalized across Ontario — as well as Dr. Debbie O’Connor, a professor at the Temerty ...
Dwarf galaxies use 10-million-year quiet period to churn out stars
2023-11-21
Contact: Morgan Sherburne, morganls@umich.edu
Images
ANN ARBOR—If you look at massive galaxies teeming with stars, you might be forgiven in thinking they are star factories, churning out brilliant balls of gas. But actually, less evolved dwarf galaxies have bigger regions of star factories, with higher rates of star formation.
Now, University of Michigan researchers have discovered the reason underlying this: These galaxies enjoy a 10-million-year delay in blowing out the gas cluttering up their environments. Star-forming regions are able to hang on to their gas and dust, allowing more stars to coalesce ...
[1] ... [1527]
[1528]
[1529]
[1530]
[1531]
[1532]
[1533]
[1534]
1535
[1536]
[1537]
[1538]
[1539]
[1540]
[1541]
[1542]
[1543]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.