Review article shows key role of Brazil in research on sugarcane for bioenergy
2023-11-27
Publications on sugarcane have increased exponentially since 2006 worldwide, and Brazil has had more articles published on the topic than any other country in the period, according to a review in BioEnergy Research.
The number of articles on the subject averaged about five per year between 1999 and 2006 but had reached 327 by 2021. Brazil has twice as many articles on sugarcane as the United States, which ranks first in the world for scientific publications in general. Brazil is also ahead of Australia, China and India, which are also major sugarcane growers.
According to the authors of the review, who are affiliated with the Laboratory of Plant Physiological Ecology (LAFIECO) ...
Cellular postal service delivers messages from non-human cells, too
2023-11-27
Messenger bubbles produced by human cells can pick up bacterial products and deliver them to other cells, University of Connecticut researchers report in the Nov. 16 issue of Nature Cell Biology. The discovery may explain a key mechanism by which bacteria, whether friendly or infectious, affect our health.
Extra-cellular vesicles (EVs) are like a postal service for our cells. Cells produce the EVs, tiny bubbles with a water-resistant shell made of fatty substances called lipids, and send them into the bloodstream. When another cell comes across an EV, it takes it inside itself ...
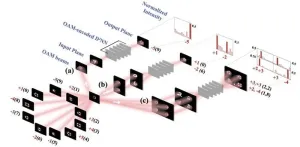
Orbital-angular-momentum-encoded diffractive networks for object classification tasks
2023-11-27
Deep learning has revolutionized the way we perceive and utilize data. However, as datasets grow and computational demands increase, we need more efficient ways to handle, store, and process data. In this regard, optical computing is seen as the next frontier of computing technology. Rather than using electronic signals, optical computing relies on the properties of light waves, such as wavelength and polarization, to store and process data.
Diffractive deep neural networks (D2NN) utilize various properties of light waves to perform tasks like image and object recognition. Such networks consist of two-dimensional pixel arrays as diffractive layers. Each pixel serves as an adjustable ...
Gig workers saw greater financial hardship during COVID-19 compared to other workers
2023-11-27
Many gig workers experienced financial hardships during the COVID-19 pandemic, including food insecurity and trouble paying bills, according to a recent study published in Work and Occupations.
“In a nutshell, our study shows gig workers were harmed more by the COVID-19 pandemic than any other workers,” said Dr. Mathieu Despard, a co-author on the paper and faculty member in UNC Greensboro’s Department of Social Work.
Despard – who collaborated closely with first author Daniel Auguste ...
CU Anschutz scientists create patch that may successfully treat congenital heart defects
2023-11-27
AURORA, Colo. (Nov. 27, 2023) – Using laboratory engineered tissue, scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have created a full thickness, biodegradable patch that holds the promise of correcting congenital heart defects in infants, limiting invasive surgeries and outlasting current patches.
The findings were published this week in the journal Materials Today.
“The ultimate goal is to make lab-grown heart tissue from a patient’s own cells that can be used to restructure the heart to correct for heart defects,” said the ...
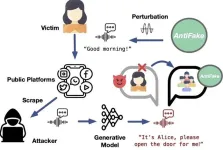
Defending your voice against deepfakes
2023-11-27
Recent advances in generative artificial intelligence have spurred developments in realistic speech synthesis. While this technology has the potential to improve lives through personalized voice assistants and accessibility-enhancing communication tools, it also has led to the emergence of deepfakes, in which synthesized speech can be misused to deceive humans and machines for nefarious purposes.
In response to this evolving threat, Ning Zhang, an assistant professor of computer science and engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University ...
Revolutionizing cancer treatment through programmable bacteria
2023-11-27
What if a single one-dollar dose could cure cancer?
A multi-university team of researchers, supported by federal funding, is developing a highly efficient bacterial therapeutic to target cancer more precisely to make treatment safer through a single $1 dose.
Traditionally, cancer therapies have been limited in their efficacy in treating patients. Some, like radiation and chemotherapy, cause harmful side effects, while others tend to result in low patient responsiveness, not to mention the cost it takes to receive treatment. Findings from the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network recorded ...
One protein is key to the spread of lung cancer. Now, a new study has found a way to stop it
2023-11-27
A new study by Tulane University has uncovered a previously unknown molecular pathway that could be instrumental to halting lung cancer in its tracks.
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. The research, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could lead to the development of a new anti-cancer drug and more personalized lung cancer treatment, said senior study author Dr. Hua Lu, the Reynolds and Ryan Families Chair in Translational Cancer at the Tulane University School of Medicine.
The study found ...
Study: Spike in premature births caused by COVID, halted by vaccines
2023-11-27
MADISON, Wis. — COVID-19 caused an alarming surge in premature births, but vaccines were key to returning the early birth rate to pre-pandemic levels, according to a new analysis of California birth records.
“The effect of maternal COVID infection from the onset of the pandemic into 2023 is large, increasing the risk of preterm births over that time by 1.2 percentage points,” says Jenna Nobles, a University of Wisconsin–Madison sociology professor. “To move the needle on preterm birth that much is akin to a disastrous ...
Why does puberty trigger us to stop growing?
2023-11-27
All animals start out as a single-celled organism and then start growing. At some point, of course, they need to stop getting bigger, but the process by which this happens is poorly understood.
New research from Alexander Shingleton at the University of Illinois Chicago and colleagues identifies a potential trigger that makes fruit flies stop growing, which has implications for understanding human development. The research is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In humans, the body’s signal to stop growing happens around puberty, though it takes several more years before growth actually ceases. It is important to better ...
Maternal vaccination against COVID-19 lowered risk of preterm births, Stanford study finds
2023-11-27
During the first two years of the pandemic, a COVID-19 infection during pregnancy increased the risk of preterm birth and NICU hospitalizations. However, by 2022, when COVID-19 vaccines were readily available in the United States, this effect disappeared – suggesting that vaccination against the coronavirus may have prevented thousands of preterm births, according to a new study led by Stanford sociologist Florencia Torche.
The study’s findings, published Nov. 27 in the journal Proceedings of the National ...
UCF receives $1.5million NSF grant to improve energy efficiency of wireless communications
2023-11-27
Wireless devices consume more than just the hours users spend scrolling through social media, streaming podcasts and TV shows, and playing games. The networks used to connect these devices also consume a large amount of energy – up to a few thousand terawatt-hours annually worldwide, which is enough to power 70,000,000 homes for one year.
UCF researcher Kenle Chen aims to enhance the energy efficiency of these systems with the support of a $1.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation’s Addressing Systems Challenges through Engineering ...
No IKAROS, no antibodies
2023-11-27
A cell nucleus is a busy place. Cellular proteins twist and pull DNA, folding the genome into intricate 3D structures that support functioning of its coding parts.
This choreography is essential for cell development, and the exact steps vary wildly between cell types. Establishing proper communication between genes and far-away control switches at the right time in the right cell is not a small feat. In fact, very few proteins have the right combination of features to organize the genome into the right structures.
In ...
New framework for using AI in health care considers medical knowledge, practices, procedures, values
2023-11-27
Health care organizations are looking to artificial intelligence (AI) tools to improve patient care, but their translation into clinical settings has been inconsistent, in part because evaluating AI in health care remains challenging. In a new article, researchers propose a framework for using AI that includes practical guidance for applying values and that incorporates not just the tool’s properties but the systems surrounding its use.
The article was written by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, The Hospital for Sick Children, the Dalla Lana School of Public Health, Columbia University, and the University of Toronto. It is published in Patterns.
“Regulatory ...
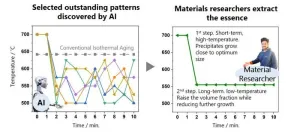
Increasing high-temperature strength of materials through collaborative efforts of AI and materials researchers
2023-11-27
1. A materials research team consisting of NIMS and Nagoya University has designed a novel two-step thermal aging schedule (i.e., non-isothermal aging or unconventional heat treatment) capable of fabricating nickel-aluminum (Ni-Al) alloys that are stronger at high temperatures than Ni-Al alloys fabricated using conventional thermal aging processes. This was achieved by using artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to identify several dozen different thermal aging schedules potentially effective in increasing alloys’ high-temperature strength. The mechanisms ...
The jigglings and wigglings of atoms reveal key aspects of COVID-19 virulence evolution
2023-11-27
Auburn, AL – Richard Feynman famously stated, “Everything that living things do can be understood in terms of the jigglings and wigglings of atoms.” This week, Nature Nanotechnology features a groundbreaking study that sheds new light on the evolution of the coronavirus and its variants of concern by analyzing the behavior of atoms in the proteins at the interface between the virus and humans. The paper, titled “Single-molecule force stability of the SARS-CoV-2–ACE2 interface in variants-of-concern,” is the result of an international collaborative ...
UCF receives 3 minority serving institution awards to promote collaborations with NASA
2023-11-27
ORLANDO, Nov. 27, 2023 – Three research projects from the University of Central Florida have been selected for NASA Minority University Research and Education Project Partnership Annual Notification (MPLAN) awards. The grants, worth up to $50,000 each, are designed to connect and promote research collaborations between Minority Serving Institutions and NASA Mission Directorates.
A total of 18 projects received Phase I funding across 15 universities. UCF received the most awards, with all three housed within the College of Engineering and Computer Science. Dean Michael Georgiopoulos ...
Stem cell-based treatment controls blood sugar in people with Type 1 diabetes
2023-11-27
An innovative stem cell-based treatment for Type 1 diabetes can meaningfully regulate blood glucose levels and reduce dependence on daily insulin injections, according to new clinical trial results from the University of British Columbia (UBC) and Vancouver Coastal Health (VCH).
“This is a significant step toward a functional cure for Type 1 diabetes,” said Dr. David Thompson, principal investigator at the Vancouver trial site, clinical professor of endocrinology at UBC and director of the Vancouver General Hospital Diabetes Centre. ...
Wave Devouring Propulsion: a revolutionary green technology for maritime sustainability
2023-11-27
A new form of wave devouring propulsion (WDP) could power ships and help to cut greenhouse gas emissions in the maritime industry.
Academics from Cranfield University have worked on the concept of using wave energy for propulsion, and designed an inventive method of achieving greater thrust from the power of the waves by harnessing a vessel’s submerged flapping foils in an innovative way.
Inspiration from whale fins
Taking inspiration from the power of a whale's fins, the team studied the structure and movement of the tail fin to unravel how it effectively uses wave energy for propulsion. Through simulations and experiments, they developed ...
Algorithmic recommendation technology or human curation? Study of online news outlet in Germany suggests both
2023-11-27
Recommender systems are machine learning applications in online platforms that automate tasks historically done by people. In the news industry, recommender algorithms can assume the tasks of editors who select which news stories people see online, with the goal of increasing the number of clicks by users, but few studies have examined how the two compare.
A new study examined how users of an online news outlet in Germany reacted to automated recommendations versus choices made by human editors. On average, the algorithm outperformed the person, but the person did better under certain conditions. The study’s authors suggest a combination of human curation and automated recommender ...
BU study finds breast density discussions with clinicians varied significantly by race/ethnicity and literacy level
2023-11-27
(Boston)—Breast density information aims to increase awareness of breast density and its risks and inform future breast screening decisions. Breast density notifications (BDN) advise women to discuss breast density with their clinicians, but prior research shows less than half of women in the general population have those conversations and little is known about the content of conversations that do occur.
A new study by researchers from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School ...
Alien haze, cooked in a lab, clears view to distant water worlds
2023-11-27
Scientists have simulated conditions that allow hazy skies to form in water-rich exoplanets, a crucial step in determining how haziness muddles observations by ground and space telescopes.
The research offers new tools to study the atmospheric chemistry of exoplanets and will help scientists model how water exoplanets form and evolve, findings that could help in the search for life beyond our solar system.
“The big picture is whether there is life outside the solar system, but trying to answer that kind of question requires really detailed modeling of all different types, specifically in planets with lots of water,” said co-author ...
Deoxygenation levels similar to today’s played a major role in marine extinctions during major past climate change event
2023-11-27
Scientists have made a surprising discovery that sheds new light on the role that oceanic deoxygenation (anoxia) played in one of the most devastating extinction events in Earth’s history. Their finding has implications for current day ecosystems – and serves as a warning that marine environments are likely more fragile than apparent.
New research, published today in leading international journal Nature Geosciences, suggests that oceanic anoxia played an important role in ecosystem disruption and extinctions in marine environments during the Triassic–Jurassic mass extinction, ...
Fish IgM structure sheds light on antibody evolution, study finds
2023-11-27
Antibodies—proteins that are produced by our immune system to protect us—are crucial for recognizing and getting rid of unwanted substances, or antigens, in our body. Although their role is universal, antibody structure varies in different animals. In a new study, researchers have analyzed the antibody Immunoglobulin M in rainbow trout to shed some light on why these proteins may have evolved over time.
In humans, IgM consists of five repeating units that are held together by a joining chain, resulting in a star shape. Consequently, IgM can bind to multiple antigens at the ...
Wind and solar projects can profit from bitcoin mining
2023-11-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – Bitcoin mining is often perceived as environmentally damaging because it uses huge amounts of electricity to power its intensive computing needs, but a new study demonstrates how wind and solar projects can profit from bitcoin mining during the precommercial development phase — when a wind or solar farm is generating electricity, but has not yet been integrated into the grid.
The findings suggest some developers could recoup millions of dollars to potentially invest in future renewable energy projects.
The ...
[1] ... [1522]
[1523]
[1524]
[1525]
[1526]
[1527]
[1528]
[1529]
1530
[1531]
[1532]
[1533]
[1534]
[1535]
[1536]
[1537]
[1538]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.