BioOne announces Subscribe to Open Pilot
2023-12-04
WASHINGTON D.C. – BioOne, the leading nonprofit aggregator in the biological, ecological, and environmental sciences, today announces a bold plan to offer up to 80 society titles as part of a Subscribe to Open (S2O) pilot beginning in January 2026.
This decision, unanimously endorsed by the BioOne Board of Directors, follows 18 months of careful feasibility analysis and extensive interviews with BioOne’s community of society and library partners in search of an equitable and sustainable path to open.
BioOne will work with its publishing community throughout 2024 to encourage participation in the pilot, ...
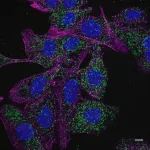
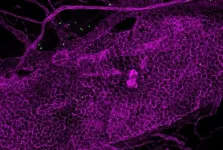
Unveiling a new era of imaging: Boston University engineers lead breakthrough microscopy techniques
2023-12-04
When microscopes struggle to pick up faint signals, it’s like trying to spot subtle details in a painting or photograph without your glasses. For researchers, this makes it difficult to catch the small things happening in cells or other materials. In new research, Boston University Moustakas Chair Professor in Photonics and Optoelectronics, Dr. Ji-Xin Cheng and collaborators are creating more advanced techniques to make microscopes better at seeing tiny sample details, without needing special dyes. Their results, published in Nature Communications and Science Advances respectively, are helping scientists visualize and understand their samples in an easier ...
New wearable communication system offers potential to reduce digital health divide
2023-12-04
Wearable devices that use sensors to monitor biological signals can play an important role in health care. These devices provide valuable information that allows providers to predict, diagnose and treat a variety of conditions while improving access to care and reducing costs.
However, wearables currently require significant infrastructure – such as satellites or arrays of antennas that use cell signals – to transmit data, making many of those devices inaccessible to rural and under-resourced communities.
A group of University of Arizona researchers has set out to change that with a wearable monitoring device system that can send ...
In hotter regions, mammals seek forests, avoid human habitats
2023-12-04
The cool of the forest is a welcome escape on a hot day. This is especially true for mammals in North America’s hottest regions, according to a study from the University of California, Davis. The study indicates that, as the climate warms, preserving forest cover will be increasingly important for wildlife conservation.
The study, published today in the journal PNAS, found that North American mammals — from pumas, wolves and bears to rabbits, deer and opossums — consistently depend on forests and avoid cities, farms and other human-dominated ...
Leukemia cells activate cellular recycling program
2023-12-04
FRANKFURT. In a recent study, scientists led by Professor Stefan Müller from Goethe University’s Institute of Biochemistry II investigated a specific form of blood cancer known as acute myeloid leukemia, or AML. The disease mainly occurs in adulthood and often ends up being fatal for older patients. In about a third of AML patients, the cancer cells’ genetic material has a characteristic mutation that affects the so-called NPM1 gene, which contains the building instructions for a protein of the same name.
While it was already known that the mutated NPM1 variant (abbreviated as ...
Argonne and Idaho National Laboratories partner with CMBlu Energy for innovative long-duration energy storage project
2023-12-04
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, along with Idaho National Laboratory (INL), was chosen by the agency for a demonstration project to validate an innovative long-duration energy storage system developed by battery manufacturer CMBlu Energy. The collaborative project aims to improve microgrids in cold climates and make fast charging of electric vehicles more affordable in underserved communities.
Over the course of the project, Argonne and INL will deploy and evaluate CMBlu Energy’s Organic SolidFlow™ ...
CCNY researchers publish optical data storage breakthrough in Nature Nanotechnology
2023-12-04
Physicists at The City College of New York have developed a technique with the potential to enhance optical data storage capacity in diamonds. This is possible by multiplexing the storage in the spectral domain. The research by Richard G. Monge and Tom Delord members of the Meriles Group in CCNY’s Division of Science, is entitled “Reversible optical data storage below the diffraction limit” and appears in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
“It means that we can store many different images at the same place in the ...
Diet has a major impact on risk of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-12-04
December 4, 2023 San Francisco, CA: In a detailed study, Diet’s Role in Modifying Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease: History and Present Understanding published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, we can finally see which diets are helpful in reducing the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. The role of diet in modifying the risk of Alzheimer’s disease is discussed in detail. Diets that are more plant based, like the Mediterranean diet and traditional diets in China, Japan, and India, are shown to reduce risk, especially ...
Study shows how ethical brands fare in a recession
2023-12-04
Peer reviewed - observational study - people
A new study from the University of East Anglia reveals why some ‘eco goods’ may fare better than others as a UK recession looms.
A new study, published today, shows that when money gets tight, people are more likely to keep up more expensive ethical purchases like buying fair trade products.
The study is one of the first to look at ethical purchases using actual market data from a major UK supermarket chain.
Lead researcher Dr Jibonayan Raychaudhuri, from UEA’s School of Economics, said: “As a possible UK recession looms closer, we wanted to better understand how people’s spending ...
New technique efficiently offers insight into gene regulation
2023-12-04
Researchers from the group of Jop Kind developed a new technique called MAbID. This allows them to simultaneously study different mechanisms of gene regulation, which plays a major role in development and disease. MAbID offers new insights into how these mechanisms work together or against each other. The results were published in Nature Methods on the 4th of December.
DNA is the most important carrier of genetic information. Each cell contains approximately two meters of DNA. To ensure that all this genetic material fits into the small cell nucleus, it must be tightly packed. The DNA is therefore wrapped around a special type of protein, a histone. The ...
U of M Medical School study finds visions of nonphysical world are common among cognitively healthy Ojibwe individuals
2023-12-04
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (12/04/2023) — Visual hallucinations are common among people with Lewy body dementia and other types of dementia. Identifying visual hallucinations is an important component of a wide variety of medical and psychiatric diagnoses and treatments, but without cultural context, some patients’ symptoms can be misinterpreted or misdiagnosed.
In existing medical literature, there is almost no information regarding normal spiritual experiences in American Indian participants in the context of a neurocognitive evaluation. University of Minnesota Medical School researchers sought to understand how Ojibwe culture and spirituality affect a doctor’s assessment ...
Consistency key to corporate expressions of racial solidarity
2023-12-04
ITHACA, N.Y. – Why do some corporate expressions of solidarity with marginalized groups register as genuine, while others seem performative or even backfire?
An analysis of statements by Fortune 500 companies following the 2020 police killing of George Floyd finds that costly actions, such as donating money to social justice groups, aren’t enough to convey allyship to Black Americans. Companies must also demonstrate a consistent, long-term commitment to diversity and racial equity, according to research co-authored by James T. Carter, assistant ...
How mountains affect El Niño-induced winter precipitation
2023-12-04
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A consideration of how mountains influence El Niño and La Niña-induced precipitation change in western North America may be the ticket to more informed water conservation planning along the Colorado River, new research suggests.
The study, coinciding with a recent shift from a strong La Niña to a strong El Niño, brings a degree of precision to efforts to make more accurate winter precipitation predictions in the intermountain West by comparing 150 years of rain and snow data with historic El Niño-Southern Oscillation patterns.
Overall, the analysis shows ...
ECHO research examines nutrition data's value from pregnancy to adolescence in understanding child health
2023-12-04
Collaborative ECHO research led by Megan Bragg, PhD, RD and Kristen Lyall, ScD of the A.J. Drexel Autism Institute highlights the opportunity for researchers to access the large amount of diet information already collected from the ECHO Cohort. This research, titled “Opportunities for examining child health impacts of early-life nutrition in the ECHO Program: Maternal and child dietary intake data from pregnancy to adolescence”, is published in Current Developments in Nutrition.
This study aimed to describe dietary intake data available in the ...
Training the immune system to prevent cancer – NextGen researchers discover paradigm-shifting approach
2023-12-04
As one of the most insidious diseases in the world, cancer has few treatments that work to eradicate it completely. Now, a new ground-breaking approach pioneered by two researchers working at the University of Missouri’s Roy Blunt NextGen Precision Health building shows promising results in preventing lung cancer caused by a carcinogen in cigarettes — a discovery that immunologists Haval Shirwan and Esma Yolcu rank among the most significant of their careers.
In the new study, Shirwan and Yolcu designed a molecule — known as an immune checkpoint stimulator (SA-4-1BBL) ...
Snail-inspired robot could scoop ocean microplastics
2023-12-04
ITHACA, N.Y. – Inspired by a small and slow snail, scientists have developed a robot protype that may one day scoop up microplastics from the surfaces of oceans, seas and lakes.
The robot’s design is based on the Hawaiian apple snail (Pomacea canaliculate), a common aquarium snail that uses the undulating motion of its foot to drive water surface flow and suck in floating food particles.
Currently, plastic collection devices mostly rely on drag nets or conveyor belts to gather and remove larger plastic debris from water, but they lack the fine scale required for retrieving microplastics. These tiny particles of plastic can be ingested ...
Georgia State professor granted $5 million to identify and characterize objects in space
2023-12-04
ATLANTA — Georgia State Professor of Physics & Astronomy Stuart Jefferies has been awarded a $5 million, multi-institutional grant by the U.S. Air Force to develop techniques to detect, map and image faint objects in space.
The work could have far-reaching impacts, including strengthening national security in an increasingly congested space domain. The work will also advance the next generation of exceptionally large telescopes and improve the capabilities of astronomers studying the universe by providing images that are significantly sharper than those from existing telescopes.
“Detecting objects in the space region between where ...
Immune protein may induce dementia unrelated to high blood pressure
2023-12-04
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have found that controlling high blood pressure may not be enough to prevent associated cognitive declines. The findings point to an immune protein called cytokine IL-17 as a culprit for inducing dementia and suggest new approaches to prevent damage to brain cells.
The study, published on Dec. 4 in Nature Neuroscience, uncovered a new mechanism involving increased levels of IL-17 in the brain which suppressed blood flow to the brain and induced cognitive impairment in a preclinical model of salt-sensitive high blood pressure.
“An ...
Q&A: How can Canada best meet its commitment to protecting 30% of its land by 2030?
2023-12-04
At last year’s COP15 conference in Montreal, the Government of Canada set the goal of conserving 30 percent of the country’s land and water by 2030. In a new study in Nature Communications, a group of McGill University researchers have sought to understand how well our existing protected lands preserve Canadian species, how many species we could save if we reach our 30 by 30 targets, and what factors impact our ability to safeguard species in future conserved areas.
Lead author Isaac Eckert, a McGill PhD candidate in Biology, answered some questions about his research.
This interview has been edited and condensed for clarity.
What ...
Eating disorder hospitalizations on the rise, affecting 'atypical' groups the most
2023-12-04
Toronto, ON, December 4, 2023 – There was a disproportionate rise in pediatric eating disorder hospitalizations among males, younger adolescents, and individuals with eating disorder diagnoses other than anorexia or bulimia, according to a new study from researchers at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) and ICES.
This large, population-based study spanned a 17-year period in Ontario, Canada (2002-2019), and tracked an overall increase of 139% in eating disorder hospitalizations among children and adolescents, with a total of 11,654 hospitalizations. The number of co-occurring mental illness diagnoses for ...
Brains of newborns aren't underdeveloped compared to other primates
2023-12-04
Contrary to current understanding, the brains of human newborns aren’t significantly less developed compared to other primate species, but appear so because so much brain development happens after birth, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, found that humans are born with brains at a development level that’s typical for similar primate species, but the human brains grow so much larger and more complex than other species after birth, it gives the false impression that human newborns are underdeveloped, or “altricial.”
Lead author Dr Aida ...
Mortality and morbidity among individuals with hypertension receiving a diuretic, ace inhibitor, or calcium channel blocker
2023-12-04
About The Study: In this prespecified secondary analysis of outcomes of 32,000 participants in a randomized clinical trial and post-trial up to 23 years later among adults with hypertension and coronary heart disease risk factors, cardiovascular disease mortality was similar between all three antihypertensive treatment groups (thiazide-type diuretic, calcium channel blocker, or angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitor). ACE inhibitors increased the risk of stroke outcomes by 11% compared with diuretics, and this effect persisted well beyond the trial period.
Authors: Jose-Miguel ...
Types of on-screen content and mental health in kindergarten children
2023-12-04
About The Study: The results of this study that included nearly 16,000 kindergarten children indicated that both total screen time and different types of content were associated with mental health problems in children ages 3 to 6. Limiting children’s screen time, prioritizing educational programs, and avoiding non–child-directed programs are recommended.
Authors: Fan Jiang, M.D., Ph.D., and Yunting Zhang, Ph.D., of Shanghai Jiao Tong University in Shanghai, China, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
Maternal prenatal depressive symptoms and fetal growth during the critical rapid growth stage
2023-12-04
About The Study: Maternal depressive symptoms were associated with slower fetal growth rate in the critical rapid growth stage before delivery in this study including 2,676 mother-offspring dyads. Early screening for depressive disorders in pregnant women appears to be essential for fetal growth and later health.
Authors: Zhenmi Liu, Ph.D., and Jiaqiang Liao, Ph.D., of Sichuan University in Chengdu, China, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.46018)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
About 20% of patients listed as alive in their electronic health records were actually deceased according to California data
2023-12-04
About 20 % of patients whose medical records showed them as being alive with a serious illness were in fact deceased according to California data, leading to hundreds of unnecessary interactions such as appointment reminders, prescription refills and other kinds of wasteful outreach that strain resources and healthcare workers’ time.
The data gap is due to California law that makes these full death data available only “for purposes of law enforcement or preventing fraud,” according to a UCLA-lead research team. Even a real-time death database maintained by the National Association for Public Health ...
[1] ... [1514]
[1515]
[1516]
[1517]
[1518]
[1519]
[1520]
[1521]
1522
[1523]
[1524]
[1525]
[1526]
[1527]
[1528]
[1529]
[1530]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.