Wayne State University announces creation of two research centers and institutes that aim to impact the health of Detroiters and beyond
2023-12-07
DETROIT – Wayne State University Interim Vice President for Research Timothy Stemmler, Ph.D., announced today the university’s Board of Governors approved the creation of two research initiatives that aim to improve the health and lives of the Detroit community and beyond.
Center for Emerging and Infectious Diseases
The Center for Emerging and Infectious Diseases (CEID) will contribute to the ongoing advancement of diagnostic testing, enabling rapid and accurate identification of infectious ...
New method is better able to map immune response and paves way for new treatments
2023-12-07
A new method, developed at Karolinska Institutet, KTH Royal Institute of Technology and SciLifeLab in Sweden, can identify unique immune cell receptors and their location in tissue, a study published in the journal Science reports. The researchers predict that the method will improve the ability to identify which immune cells contribute to disease processes and open up opportunities to develop novel therapies for numerous diseases.
Immune cells such as T and B cells are central to the body’s defence against both infections and tumours. Both types of immune cells express unique receptors that specifically recognise different parts of unwanted and foreign elements, such as bacteria, viruses ...
Researchers reveal uncharted liver-focused pathway in gene therapy immune responses
2023-12-07
INDIANAPOLIS— Indiana University School of Medicine researchers have uncovered vital insights regarding a liver trigger that blocks an undesired immune response from gene therapy, surprisingly resulting in the activation of specific immune cells, despite the liver's typical role in suppressing immune responses. The findings, published in Molecular Therapy, may pave the way for change in immunomodulation strategies for desired and long-lasting effects of gene therapy.
Gene therapy treatments involve replacing or introducing a healthy copy of ...
Virtualware and Kessler Foundation renew collaboration in groundbreaking spatial neglect research
2023-12-07
East Hanover, NJ – December 07, 2023 – Kessler Foundation, a leader in rehabilitation research, and Virtualware, an international leader in immersive and interactive technologies, expand their collaboration with a new agreement to further research and development aimed at advancing spatial neglect rehabilitation using virtual reality (VR) and tele-rehabilitation technology. This latest development stems from a strong, ongoing partnership initiated in 2018 between the VR innovator and the New Jersey-based disability-focused non-profit.
The intervention, ...
New HS curriculum teaches color chemistry and AI simultaneously
2023-12-07
North Carolina State University researchers have developed a weeklong high school curriculum that helps students quickly grasp concepts in both color chemistry and artificial intelligence – while sparking their curiosity about science and the world around them.
To test whether a short high school science module could effectively teach students something about both chemistry – a notoriously thorny subject – and artificial intelligence (AI), the researchers designed a relatively simple experiment involving pH levels, which reflect the acidity or alkalinity of a liquid solution.
When testing pH levels on a test strip, color conversion charts provide a handy ...
Bering secures FDA clearance for AI-based chest X-ray triage solution
2023-12-07
LONDON, DECEMBER 6, 2023 – Bering Limited, a London-based medical AI company, today announced it received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) clearance for its AI-powered chest X-Ray triage solution, ‘BraveCX’. With the FDA clearance, the company is now able to commercially provide the AI solution to medical professionals and healthcare institutions in the U.S.
Bering’s BraveCX is a radiological computer-assisted triage and notification software that analyzes adult (≥18 years old) chest X-ray (CXR) images for the presence of ...
Molecular fossils shed light on ancient life
2023-12-07
Paleontologists are getting a glimpse at life over a billion years in the past based on chemical traces in ancient rocks and the genetics of living animals. Research published Dec. 1 in Nature Communications combines geology and genetics, showing how changes in the early Earth prompted a shift in how animals eat.
David Gold, associate professor in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences at the University of California, Davis, works in the new field of molecular paleontology, using the tools of both geology and biology to study the evolution ...
Honeyguide birds learn distinct signals made by honey hunters from different cultures
2023-12-07
African honeyguide birds understand and respond to the culturally distinct signals made by local human honey hunters, suggesting cultural coevolution between species, according to a new study. Although the animal kingdom is full of interspecific mutualism, systems in which humans successfully cooperate with wild animals are rare. One such relationship involves the greater honeyguide (Indicator indicator), a small African bird known to lead humans to wild bees’ nests. Humans open the nests to collect honey, and the honeyguides eat the exposed beeswax. Human honey hunters in different parts of Africa often use ...
Two studies demonstrate on-demand quantum entanglement in ultracold molecules
2023-12-07
The controlled creation of quantum entanglement with molecules has been a long-standing challenge in quantum science. Now, in two new studies, researchers report a method for tailoring the quantum states of individual molecules to achieve quantum entanglement on demand. Their strategy presents a promising new platform for the advancement of quantum technologies such as computation and sensing. Quantum entanglement is one of the key defining features of quantum mechanics. It is central to many quantum applications. Because of their rich internal structure ...
Trees in wetter forests more sensitive to drought than trees in drier regions – a finding with policy implications
2023-12-07
Annual tree-ring growth records from more than 122 species of trees show that trees growing in wetter forests are more sensitive to increasing drought. The findings – which tackle a research question that has yielded contradictory results in the past – suggest that land management and policy focused solely on drought effects in drier regions overestimates the resilience of forests in wetter regions. Forests cover roughly 30% of Earth’s surface and, in addition to providing a host of valuable ecosystem services and harboring huge biodiversity, they play a crucial role in the planet’s carbon cycle, absorbing more atmospheric carbon than all other terrestrial ...
A new 66 million-year history of carbon dioxide offers little comfort for today
2023-12-07
A massive new review of ancient atmospheric carbon-dioxide levels and corresponding temperatures lays out a daunting picture of where the Earth’s climate may be headed. The study covers geologic records spanning the past 66 million years, putting present-day concentrations into context with deep time. Among other things, it indicates that the last time atmospheric carbon dioxide consistently reached today’s human-driven levels was 14 million years ago—much longer ago than some existing assessments indicate. It asserts that long-term climate is highly sensitive to greenhouse gas, with cascading effects that may evolve over many millennia.
The ...
Grunt or whistle: successful honey-hunters know how to communicate with wild honey-seeking birds
2023-12-07
In many parts of Africa, humans cooperate with a species of wax-eating bird called the greater honeyguide, Indicator indicator, which leads them to wild bees’ nests with a chattering call. By using specialised sounds to communicate with each other, both species can significantly increase their chances of accessing calorie-dense honey and beeswax.
Human honey-hunters in different parts of Africa use different calls to communicate with honeyguides. In a new study, researchers have discovered that honeyguide birds in Tanzania and Mozambique discriminate among honey-hunters’ calls, responding much more readily to ...
Geoscientists map changes in atmospheric CO2 over past 66 million years
2023-12-07
Embargoed: Not for Release Until 2:00 pm U.S. Eastern Time Thursday, Dec. 7 2023.
Today atmospheric carbon dioxide is at its highest level in at least several million years thanks to widespread combustion of fossil fuels by humans over the past couple centuries.
But where does 419 parts per million (ppm)—the current concentration of the greenhouse gas in the atmosphere—fit in Earth’s history?
That’s a question an international community of scientists, featuring key contributions by University of Utah geologists, is sorting out by examining a plethora of markers in the geologic record that offer ...
Ancient stars made extraordinarily heavy elements
2023-12-07
How heavy can an element be? An international team of researchers has found that ancient stars were capable of producing elements with atomic masses greater than 260, heavier than any element on the periodic table found naturally on Earth. The finding deepens our understanding of element formation in stars.
We are, literally, made of star stuff. Stars are element factories, where elements constantly fuse or break apart to create other lighter or heavier elements. When we refer to light or heavy elements, we’re talking about their atomic mass. Broadly speaking, atomic ...
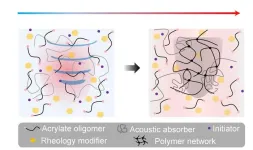
Soundwaves harden 3D-printed treatments in deep tissues
2023-12-07
DURHAM, N.C. -- Engineers at Duke University and Harvard Medical School have developed a bio-compatible ink that solidifies into different 3D shapes and structures by absorbing ultrasound waves. Because it responds to sound waves rather than light, the ink can be used in deep tissues for biomedical purposes ranging from bone healing to heart valve repair.
This work appears on December 7 in the journal Science.
The uses for 3D-printing tools are ever increasing. Printers create prototypes of medical devices, design flexible, ...
Physicists ‘entangle’ individual molecules for the first time, hastening possibilities for quantum information processing
2023-12-07
For the first time, a team of Princeton physicists have been able to link together individual molecules into special states that are quantum mechanically “entangled.” In these bizarre states, the molecules remain correlated with each other—and can interact simultaneously—even if they are miles apart, or indeed, even if they occupy opposite ends of the universe. This research was recently published in the journal Science.
“This is a breakthrough in the world of molecules because of the fundamental importance of quantum entanglement,” said Lawrence Cheuk, assistant professor of physics at Princeton ...
Wild birds lead people to honey — and learn from them
2023-12-07
Key takeaways
People in parts of Africa communicate with a wild bird, the greater honeyguide, to locate bee colonies and harvest their honey and beeswax.
A study by UCLA anthropologist Brian Wood and other authors show how this partnership is maintained and varies across cultures.
They demonstrate the bird’s ability to learn distinct vocal signals traditionally used by different honey-hunting communities.
In parts of Africa, people communicate with a wild bird — the greater honeyguide — in order to locate bee colonies and harvest their stores of honey and beeswax.
It’s a rare example of ...
Evolving trends in cosmetic breast augmentation: New data
2023-12-07
November 30, 2023 – Ongoing quality improvement data submitted by Board-certified plastic surgeons highlight current trends in surgical technique in cosmetic breast augmentation using implants, reports a study in the December issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"The findings illustrate evolving trends in breast enhancement over the past 16 years, including factors like the location of the incision and the type and positioning of implants," comments lead author Michael J. Stein, ...
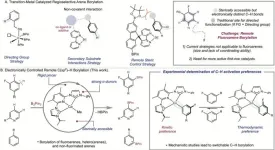
Princeton Chemistry develops catalyst for electronically controlled C–H functionalization
2023-12-07
The Chirik Group at the Princeton Department of Chemistry is chipping away at one of the great challenges of metal-catalyzed C–H functionalization with a new method that uses a cobalt catalyst to differentiate between bonds in fluoroarenes, functionalizing them based on their intrinsic electronic properties.
In a paper published this week in Science, researchers show they are able to bypass the need for steric control and directing groups to induce cobalt-catalyzed borylation that is meta-selective.
The lab’s research ...
Llama power: Tiny llama nanobodies neutralize different noroviruses. Can they improve human anti-viral therapies?
2023-12-07
Human noroviruses cause acute gastroenteritis, a global health problem for which there are no vaccines or antiviral drugs. Although most healthy patients recover completely from the infection, norovirus can be life-threatening in infants, the elderly and people with underlying diseases. Estimates indicate that human noroviruses cause approximately 684 million illnesses and 212,000 deaths annually.
“Human noroviruses are highly diverse,” said first author Dr. Wilhelm Salmen, a graduate student in Dr. B V Venkataram Prasad’s lab while he was working ...
Less ice on the road leads to more salt in the soil, air, and water
2023-12-07
When temperatures drop and roads get slick, rock salt is an important safety precaution used by individuals, businesses, and local and state governments to keep walkers, cyclists, and drivers safe. However, according to a new scientific review paper from a team of researchers at Virginia Tech and the University of Maryland, the human demand for salt comes at a cost to the environment.
Published in the journal Nature Reviews Earth & Environment with researchers Stanley Grant, Megan Rippy, and Shantanu Bhide from Virginia Tech’s Occoquan Watershed Monitoring Laboratory, ...
Very early treatment of newborns with HIV could result in medication-free remission for many babies
2023-12-07
An unexpectedly high percentage of children, who were born with HIV and started treatment within 48 hours of life, exhibit biomarkers by 2 years of age that may make them eligible to test for medication-free remission, according to a multinational study published in Lancet HIV.
“Moving away from reliance on daily antiretroviral therapy (ART) to control HIV would be a huge improvement to the quality of life of these children,” said Protocol Co-Chair and senior author Ellen Chadwick, MD, former Director of Section ...
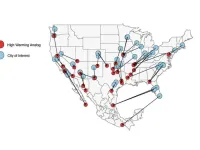
Sister climate cities, utility data predict future water, electricity demands
2023-12-07
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. – Modern-day Ciudad Mante, Mexico, could help Tampa, Florida, plan for shifting water and electricity demands due to climate change, according to an international team of researchers. Led by Renee Obringer, assistant professor of energy and mineral engineering at Penn State, the researchers used utilities data and climate analogs — contemporary cities with climates close to what other cities are predicted to experience in the future — to assess how climate change may impact residential water and electricity use across 46 cities in the United States.
Their computationally efficient model projected strong regional differences for future water and electricity ...
New target found for treatment of spinal muscular atrophy
2023-12-07
The lab of Yongchao C. Ma, PhD, at Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago uncovered a novel mechanism that leads to motor neuron degeneration in spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). This discovery offers a new target for treatment that overcomes important limitations of gene therapy and other current therapies for SMA.
SMA is a genetic disease that disrupts the nerve cells that control voluntary muscle movement. Symptoms of motor neuron degeneration could start at as early as 3 months of ...
Mass General Cancer Center researchers present key findings at American Society of Hematology (ASH) Meeting
2023-12-07
Investigators from the Mass General Cancer Center, a part of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, will present research discoveries and outcomes from clinical trials at the 2023 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting, held December 9-12, 2023 in San Diego.
ASH brings together leading experts in classical and malignant blood diseases to share the latest breakthroughs, clinical studies and research impacting the field and patient care. Mass General Cancer Center researchers will cover a wide range of topics, including ...
[1] ... [1509]
[1510]
[1511]
[1512]
[1513]
[1514]
[1515]
[1516]
1517
[1518]
[1519]
[1520]
[1521]
[1522]
[1523]
[1524]
[1525]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.