Nearly 40% of Type 2 diabetes patients stop taking their second-line medication
2023-12-12
Two-thirds of patients discontinued their medication, switched to a different medication class or intensified their treatment
Discontinuation was higher (50%) among GLP-1 RA drugs, which are linked to gastrointestinal side effects
Findings could have implications for patients taking GLP-1 RAs to treat obesity
First large U.S. study to show such high discontinuation rates
CHICAGO --- Most patients with Type 2 diabetes will end up needing to add a second-line medication after metformin — the go-to primary drug for glucose management — ...
Black Medicare patients less likely to be referred for home health care
2023-12-12
Waltham — December 7, 2023 —
At discharge from the hospital, Black Medicare beneficiaries are less likely to be referred for home health care (HHC), compared to white patients reports a survey study in Medical Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The disparity in referral for HHC among Black Medicare patients appears greatest among those with low "readiness for discharge" scores, according to the new research, led by Olga Yakusheva, PhD, of University of Michigan School of Nursing and School of Public Health.
Does ...
NEJM AI to educate clinicians about artificial intelligence applications in medicine
2023-12-12
BOSTON, December 12, 2023 — NEJM Group, publisher of the New England Journal of Medicine, today announced the launch of its newest title, NEJM AI, a peer-reviewed, monthly journal dedicated to the latest research and application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in medicine. In addition to original research articles, the journal publishes reviews, policy perspectives and educational material for clinicians, scientists, health care leaders, policy makers, regulators, and executives with pharmaceutical, device-manufacturing and technology companies. Benchmark data sets and protocols are ...
FAU lands USDA $1 million grant to create South Florida’s first microbiome innovation center
2023-12-12
In addition to being one of the largest, most diverse metropolitan areas in the world with a population of 6.1 million, South Florida hosts more than 9.7 million acres of farmland with a revenue of more than $7 billion in recent years. However, climate change, extreme weather events, poor soils, pests and disease, and workforce shortages present unique challenges in this region.
To address a critical need to train a diverse workforce with new sets of tools and skills to confront these emerging challenges, ...
Open Science momentum grows stronger in Canada with a new commitment by its largest mental health teaching hospital
2023-12-12
The Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH), Canada’s largest mental health teaching hospital in the country is pleased to announce that it has entered into a partnership with the Tanenbaum Open Science Institute (TOSI) at McGill University’s The Neuro, joining a growing alliance Canadian institutions changing research practices in neuroscience. This important endeavour is supported by a $1M commitment from the Tanenbaum Open Science Institute and an equivalent commitment by CAMH.
As part of its commitment to Open Science, CAMH is formally adopting a set of Open Science Principles to foster collaboration and the sharing of mental health ...
A lifesaving chain, a global first: Penn Medicine sets a worldwide record with 100 kidney paired donation transplants in a year
2023-12-12
PHILADELPHIA— For thousands of people around the world waiting for a kidney, paired exchange serves as a beacon of hope. One person's willingness to undergo the act of Kidney Paired Donation (KPD) often sets in motion a chain of beautiful and selfless acts, where individuals give and receive the chance for a better life. After completing its 100th KPD transplant in a 12 month period, the Penn Transplant Institute now holds the world-wide record for the most KPD transplants in a year.
More than 90,000 people in the United States are waiting to receive a kidney transplant, with average waits to receive a kidney from a deceased donor ...
New 'atherosclerosis atlas' sheds light on heart attacks, strokes
2023-12-12
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have created an “atlas of atherosclerosis” that reveals, at the level of individual cells, critical processes responsible for forming the harmful plaque buildup that causes heart attacks, strokes and coronary artery disease.
Atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries, affects half of Americans between ages 45 and 84, and many don’t even know it, the National Institutes of Health reports. Over time, fatty plaques build up inside the arteries, where they can slow blood flow. When they break loose, they can be deadly, triggering strokes and heart attacks.
Doctors ...
Equity in cannabis research
2023-12-12
In a Perspective, researchers call for equity in cannabis research as the field rapidly expands. When marijuana was illegal across the United States, enforcement and penalties were disproportionately heaped upon communities of color. Today, cannabis remains federally illegal and unequal enforcement continues, while profits from the “green rush” of state legalization are in many cases flowing to wealthy white men. Renée Martin-Willett and an interdisciplinary team of colleagues propose a way forward for cannabis research that acknowledges this history of discrimination and misuse of institutional power and embraces ...
Civilian attacks and Ukrainian resistance
2023-12-12
During the all-out invasion of Ukraine, Russia has deliberately chosen civilian targets, such as apartment buildings, presumably with the goal of deterring Ukrainian resistance. But does such terror deter or, in contrast, motivate resistance among ordinary Ukrainians? Henrikas Bartusevičius and colleagues conducted two-wave probability surveys in Ukraine in March and April 2022, with approximately 1,000 and 800 respondents in the first and second waves, respectively. Surveys were conducted online by a local survey agency, Info Sapiens. Respondents reported the frequency of ...
Drought and the rapid rise of skateboarding
2023-12-12
When a severe drought hit California in 1977, the state ordered citizens to drastically reduce domestic water usage. Water restrictions put in place occurred after a heady mix of prosperity and radical urban planning had resulted in the construction of more than 150,000 private swimming pools in California in the 1960s. The result was a ubiquitous new landscape feature: empty concrete pools. Ulf Büntgen and colleagues document how this novel geographic resource inspired surfers to develop professional vertical skateboarding in Los Angeles and environs. Other causal factors included the development of polyurethane ...
How a drought led to the rise of skateboarding in 1970s California
2023-12-12
Why did professional skateboarding arise in southern California in the 1970s? Was it a coincidence, or was it a perfect storm of multiple factors?
It’s fairly well-known that a drought in southern California in the mid-1970s led to a ban on filling backyard swimming pools, and these empty pools became playgrounds for freestyle skateboarders in the greater Los Angeles area. But a new cross-disciplinary study from the University of Cambridge shows that beyond the drought, it was the entanglement of environmental, economic and technological factors that led to the explosive rise of professional skateboarding culture in the 1970s.
The authors say that professional ...
A new brew: Evaluating the flavor of roasted, lab-grown coffee cells
2023-12-12
It may soon be time to wake up and smell the lab-grown coffee made from cultured plant cells. But it’s not clear whether drinks from this product replicate coffee beans’ complex flavors. Now, a study in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that some of the comforting aromas and tastes of a conventional cup of coffee could be reproduced by roasting and brewing coffee cell cultures.
Coffee is one of the most popular beverages worldwide. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, 23 billion pounds of beans are expected to be produced during the 2023­­–24 growing ...
Stability in physical and political science
2023-12-12
In a Perspective, a biophysical chemist, Kenneth J. Breslauer, and his brother, a political scientist, George W. Breslauer, explore the parallelisms between the concept of stability as it is used in their respective fields. The workings of a cell or molecule are generally understood to be reducible to physics, but social and political events are thought to be structured by human agency and a generous helping of chance. However, both molecular systems and socio-political organizations can be said to exhibit stability, instability, or so-called “metastability,” a state of precarious and kinetic stability. For example, a chemical system can be metastable when molecules ...
UTSA establishes new hub to improve management of digital assets
2023-12-12
UTSA has received a two-year, $300,000 grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to establish the National DigiFoundry (NDF), a consortium that has the potential to redefine the management of digital assets such as cryptocurrencies.
To develop the NDF, UTSA will create a new Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO), a national organization that promotes engagement and collaboration between the public and private sectors. At a time when digital assets, including cryptocurrencies, have surpassed a trillion dollars in market value, this collaboration is paramount, according to John Huggins, interim executive director of UTSA’s National ...
Daily singing workout keeps songbird males attractive
2023-12-12
Every year in the Christmas season it becomes clear again that some people are amazingly skilled singers, like Mariah Carey and George Michael. Their singing can stir strong emotions.
Singing involves probably the most complex, and mostly hidden, movements humans and animal can make. To become a good singer, you need to learn how to coordinate the movements of hundreds of muscles in your body with extreme precision. Therefore, you need a lot of talent, and practice.
We all know that athletes invest a lot of time exercising their limb ...
Scientists find new, better way to develop vaccines
2023-12-12
A new paper in Biology Methods & Protocols, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that researchers in Germany have developed a new system to display epitopes in mammal cells for immunization studies. They believe that this method can help scientists greatly in immunization efforts.
Promoting blood cells to produce antibodies against a specific viral protein is an important step in developing vaccines for human use. This can be challenging for researchers because whether the subjects develop antibodies depends on how scientists design ...
Creating a future, together, for rare-disease research
2023-12-12
Osaka, Japan – Patients with rare diseases have traditionally been the subjects of medical research. However, in recent years, their role has begun to shift from ‘research participants’ to ‘experts with a lived experience’, with some being involved in study planning, design and interpretation. Additionally they may soon be involved in helping pick the most important areas to prioritize for research.
In a study published last month in the journal Research Involvement and Engagement, researchers from Osaka University created an online space, referred to as the ‘Evidence-generating Commons’, for conversation, collaboration and ...
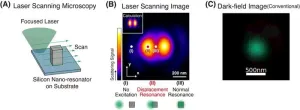
In a new light – new approach overcomes long-standing limitations in optics
2023-12-12
Osaka, Japan – When you look up at the sky and see clouds of wondrous shapes, or struggle to peer through dense, hazy fog, you’re seeing the results of ‘Mie scattering’, which is what happens with light interacts with particles of a certain size. There is a growing body of research that aims to manipulate this phenomenon and make possible an array of exciting technologies.
Now, in a study recently published in Nature Communications, a multi-institutional research team including Osaka University has overcome what were thought to be fundamental limitations of how to enhance the efficiency of Mie scattering.
Researchers in the field ...
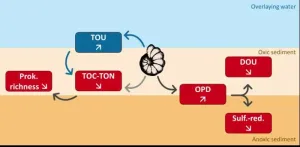
Underwater architects: The ‘burrowing effect’ of foraminifera on marine environments
2023-12-12
Dr. Dewi Langlet, a scientist at the Evolution, Cell Biology and Symbiosis Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST), studies foraminifera, single-cell organisms with shells made of calcium carbonate. He and his collaborators have shown for the first time that the burrowing of single-celled organisms in marine ecosystems affects oxygen distribution and bacterial diversity in sea sediments. Their findings have been published in the journal Biogeosciences.
Foraminifera are mostly marine organisms ...
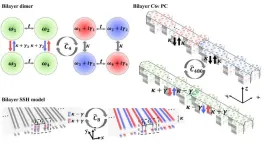
A scheme for realizing nonreciprocal interlayer coupling in bilayer topological systems
2023-12-12
The exchange of energy and environment is inevitable in any physical system, so non-Hermitian systems that can be described by non-Hermitian Hamiltonians are ubiquitous. There are two kinds of non-Hermitian Hamiltonians, describing nonreciprocal systems with anisotropic coupling, also referred to as nonreciprocal coupling, and gain-loss systems. Three physicists won the Nobel physics prize for their discovery of topological phases and transitions in 2016. Recently, an emerging interplay of topological photonics and non-Hermitian photonics has ...
Combination immunotherapy produces high response rate in early results of Sylvester trial targeting high-risk follicular lymphoma
2023-12-12
DOWNOADABLE VIDEO
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY, DEC. 11, 2023 AT 8:45 P.M. ET) – Researchers conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine say a new combination of antibody therapies produced a ‘surprisingly high’ response rate in patients with high-risk follicular lymphoma, a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Based on these initial findings – reported in an oral presentation at the 65th ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition in San Diego, California, Dec. 9-12 – the research team plans to expand the number of trial participants ...
Multicenter study at Sylvester, other academic centers shows CAR-T cell therapy safe, effective even for high-risk patients
2023-12-12
DOWNLOADABLE VIDEO IS AVAILABLE HERE
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY, DEC. 11, 2023, AT 8:45 PM ET) – CAR-T cell therapy is a safe and effective treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), even for patients regarded as high risk due to comorbidities.
That’s the conclusion of a five-year analysis of results from the U.S. Lymphoma CAR-T Cell Consortium, a group of 17 academic cancer centers in the U.S. Their findings will be presented at the American Society of Hematology’s 2023 annual meeting in San Diego, Dec. 9-12.
“CAR-T has caused a paradigm shift in the treatment of patients with diffuse large B-cell ...
Clinical trial proves that the ketogenic diet is effective at controlling polycystic kidney disease
2023-12-12
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — It’s official: The ketogenic diet proved to be effective at controlling polycystic kidney disease (PKD) in the first randomized controlled clinical trial of ketogenic metabolic therapy for PKD.
“I’m really happy about these clinical trial results,” said UC Santa Barbara biologist Thomas Weimbs, whose lab was part of an international collaboration to investigate the effect of the fasting response known as ketosis on the cysts that are the hallmark of the disease. “We now have the first evidence in humans that the cysts really don’t like ...
New drug helps narrow racial survival disparity in patients with acute myeloid leukemia
2023-12-12
SAN DIEGO – Non-Hispanic Black patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are living longer, now that new therapies are available, according to a study presented by researchers from the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine and Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center at the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition (Abstract 955).
In the past, the standard treatment for AML, a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, was intensive chemotherapy. Unfortunately, many older patients were ineligible ...
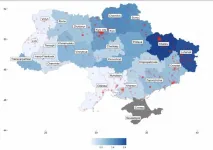
Scientific community: Ukraine may have lost 20% of its pre-war scientific research capacity
2023-12-12
Ukraine may have lost about 20% of its scientific research capacity — time directly spent by scientists on research activities — as a consequence of the Russia-Ukraine war. The findings, published in Humanities & Social Sciences Communications, also suggest that over 17% of scientists who were research active in Ukraine before the war may have left the scientific research sector by December 2022.
Since the full-scale Russian invasion of Ukraine began in February 2022, there has been disruption to many sectors of the Ukrainian economy, including the Ukrainian scientific research sector. However, it has so far proved difficult to quantify many of the key impacts of the ...
[1] ... [1502]
[1503]
[1504]
[1505]
[1506]
[1507]
[1508]
[1509]
1510
[1511]
[1512]
[1513]
[1514]
[1515]
[1516]
[1517]
[1518]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.