Multidrug-resistant bacteria: New report from Veterinary field, Osaka, Japan
2023-05-09
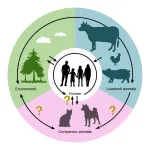
The emergence and global spread of antimicrobial resistant bacteria among companion animals (e.g., dogs and cats) pose a risk of the animals being reservoirs for cross-species transmission because of their close contact with humans.
In Japan, for the first time, a research team led by Associate Professor Mayo Yasugi from the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Veterinary Science discovered Escherichia coli resistant to both colistin and third-generation cephalosporin antibiotics in a companion dog. Outside Japan, both colistin ...
TikTok hosts the latest dance moves and bad information on liver disease
2023-05-09
CHICAGO (May 9, 2023) — Four in 10 posts about liver disease on TikTok contain misinformation, with most pushing inaccurate claims about fad diets, “detox” drinks and herbal remedies, according to a study being presented today at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2023. Results suggest that liver disease patients who seek medical information on TikTok may need help separating good information from the bad.
“People should always consult their doctor first for guidance on their specific medical condition, but we also know that getting health information and tips from social media is extremely common these days,” ...
Metabolic syndrome with heavy alcohol use may have contributed to recent surge in alcoholic liver disease-related mortality
2023-05-09
Metabolic syndrome with heavy alcohol use may have contributed to recent surge in alcoholic liver disease-related mortality
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0518
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A brief research report evaluating the relationship between metabolic syndrome (MetS) and a recent increase in alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) deaths has found that heavy alcohol use and the presence of MetS was associated with a higher risk for advanced liver disease. This association may provide some explanation ...
Low oxygen weight loss trial at Pennington Biomedical open to participants
2023-05-09
BATON ROUGE – Does altitude play a role in weight loss? Why is it easier to lose weight in Colorado versus Louisiana? Researchers at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center are seeking answers to these questions through one of the latest research trials, the “Low Oxygen and Weight Status,” or LOWS study. The LOWS study will determine whether exposure to low oxygen levels in the air, similar to those at higher altitudes, can help individuals with obesity lose weight and improve health.
The LOWS study is now open for participant enrollment. Participants will be randomized to ...
THE LANCET: An estimated one million stillbirths and newborn baby deaths could be prevented each year by implementing low-cost pregnancy interventions in low- and middle-income countries
2023-05-09
Eight low-cost and easily implementable proven interventions for pregnant women in 81 low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) could prevent an estimated 566,000 stillbirths and 5.2 million babies a year from being born preterm or small for gestational age—some with low birth weight—the impacts of which would also affect long-term health and economic output, says a new four-paper Series published in The Lancet.
Additionally, the eight interventions,
multiple micronutrient supplements
balanced protein energy supplements
aspirin
treatment of syphilis
education for smoking cessation
prevention of malaria in pregnancy
treatment ...
Under 40s with mental health problems have elevated risks of heart attack and stroke
2023-05-09
Sophia Antipolis, 9 May 2023: Adults in their 20s and 30s with mental disorders have an up to three-fold elevated likelihood of a heart attack or stroke, according to a study in more than 6.5 million individuals published today in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 Lifestyle behaviours did not explain the excess risk. One in every eight of the 20-to-39-year-old participants had some kind of mental illness including depression, anxiety and insomnia.
“Psychological problems were common in young adults and had strong ...
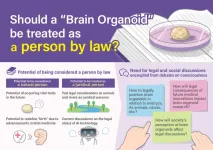
Can tiny brain tissues legally be a person? Researchers say not yet
2023-05-09
Grown in labs, human brain organoids are cultivated from stem cells, feed on nutrient broth and serve as a model of human brain development in miniature. Their growth and structure mimic portions of real brains, allowing scientists to better investigate the origins and potential treatments of neural diseases. How similar are they to actual human brains, though? Are they close enough to be considered people in their own right?
The question is complicated in myriad ethical and moral ways, but researchers based in Japan and Taiwan propose that the legal lens may prove critical when understanding the potential personhood of human ...
Study finds some MND and dementia patients share genetic defects
2023-05-09
New research has discovered that some patients with motor neuron disease (MND) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD) carry the same rare genetic defects that cause other neurodegenerative diseases.
Researchers from the Macquarie University MND Research Centre and The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research have identified the defects in the genomes of some people with non-inherited, or sporadic, MND and FTD.
MND results in the death of the neurons, or motor nerves, connecting the brain and spinal cord to the muscles. These are the cells that control our ability to move, breathe and swallow. The disease ...
Researchers develop interfacial charge modification strategy to enhance photocatalytic water oxidation
2023-05-09
Water oxidation reaction involves a four-electron and four-proton transfer process, which requires an uphill energy transformation and limits the efficiency of the overall photocatalytic water splitting reaction.
Although loading appropriate water oxidation cocatalysts can enhance the performance of water oxidation reactions, the interfacial barrier between the semiconductor and the water oxidation cocatalyst can impede the transfer and utilization of photogenerated charges.
Recently, a research team led by Profs. LI Can and LI Rengui from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) ...
Southwest Rural Health Research Center identifies key health challenges of rural America
2023-05-09
The Southwest Rural Health Research Center at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health has published a peer-reviewed paper detailing Healthy People 2030 priorities that will be most critical for rural America in the upcoming decade. These priorities were identified by rural health stakeholders across the United States. This publication comes ahead of the center’s release of Rural Healthy People 2030 — a continuation of a long-standing tradition of the Southwest Rural Health Research Center in which multidisciplinary authors ...
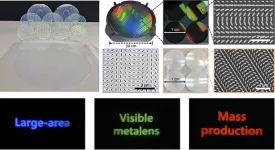
World's first mass production of metalenses for visible wavelengths
2023-05-09
Do you hate the camera bumps on the back of your smartphone? A new optical component called metalens – which was named one of the top 10 future technologies by the World Economic Forum in 2019 – may be the answer. Composed of a nanostructured array, this incredibly thin and lightweight optical device is currently the focus of much attention in the scientific community, even featured in a special issue of Nature Photonics. However, the production of metalenses requires highly precise techniques and can be expensive, posing a challenge for their scalable manufacturing.
In ...
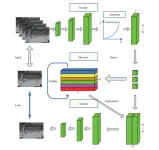
COVAD: Content-oriented video anomaly detection using a self attention-based deep learning model
2023-05-09
Video anomaly detection is a research hotspot in the field of computer vision, attracting many researchers.Video anomaly detection differs from traditional video analysis. Usually, abnormal events occur only in a small percentage of the video pixels and therefore, it is unnecessary to focus on all the video pixels as most of
them are harmless—called “the background”. Therefore, in the video feature extraction process, attention should be focused on a few detectable partial objects. Object detection is very complicated and consumes a significant amount of time during video processing. Therefore, ...
New technique enables in-vivo analysis of protein complexes
2023-05-09
As the executor of life activities, proteins exert their specific biological functions through interactions such as forming protein complexes. The localization effects, crowding effects, and organelle microenvironments within cells are crucial for maintaining the structure and function of protein complexes.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. ZHANG Lihua from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has developed a glycosidic-bond-based mass-spectrometry-cleavable cross-linker, which improves the data ...
Scientists raise concerns about popular COVID disinfectants
2023-05-09
The COVID-19 pandemic has boosted the unnecessary use of antimicrobial chemicals linked to health problems, antimicrobial resistance, and environmental harm, warn more than two dozen scientists in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science & Technology. Their critical review details how quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs) are increasingly marketed and used in home, healthcare, education, and workplace settings despite the availability of safer alternatives and in some cases limited evidence of reduced disease transmission.
“Disinfectant wipes containing ...
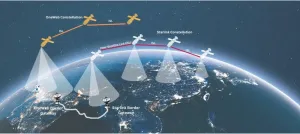
Virginia Tech, George Mason University partner to develop networking infrastructure for satellite constellations
2023-05-09
The race is on to provide high speed satellite internet to the Earth’s most remote areas. New tech companies such as Starlink, One Web, and Amazon’s Kuiper are competing with traditional, established “satcomm” companies such as Thuraya and Inmarsat to provide global high speed, low latency satellite internet across the globe. These new mega-constellations rely on tens of thousands of small low earth orbit satellites flying at a few hundred miles altitude.
Network interconnectivity is a basic building block for providing the fastest, more reliable coverage to end users. While all these mega-constellations are driven to provide high ...
Lifu Huang receives NSF CAREER award to lay new ground for information extraction without relying on humans
2023-05-08
Considering the millions of research papers and reports from open domains such as biomedicine, agriculture, and manufacturing, it is humanly impossible to keep up with all the findings.
Constantly emerging world events present a similar challenge because they are difficult to track and even harder to analyze without looking into thousands of articles.
To address the problem of relying on human effort in situations such as these, Lifu Huang, an assistant professor in the Department of Computer Science and core faculty at the Sanghani Center for Artificial Intelligence ...
LY6 gene family: potential tumor antigens and prognostic biomarkers in endometrial cancer
2023-05-08
“Importantly, the expression of several LY6 genes is elevated in UCEC [uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma] when compared to the expression in normal uterine tissue.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 8, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on May 4, 2023, entitled, “Human LY6 gene family: potential tumor-associated antigens and biomarkers of prognosis in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.”
The human Lymphocyte antigen-6 (LY6) gene family has recently gained interest for its possible role in tumor progression. In this new study, researchers Luke A. Rathbun, Anthony M. Magliocco ...
Atmospheric research provides clear evidence of human-caused climate change signal associated with CO2 increases
2023-05-08
Woods Hole, Mass. (Monday, May 8, 2023) -- New research provides clear evidence of a human “fingerprint” on climate change and shows that specific signals from human activities have altered the temperature structure of Earth’s atmosphere.
Differences between tropospheric and lower stratospheric temperature trends have long been recognized as a fingerprint of human effects on climate. This fingerprint, however, neglected information from the mid to upper stratosphere, 25 to 50 kilometers above the Earth’s surface.
“Including this information improves the detectability of a human fingerprint by a factor of five. Enhanced detectability occurs because the mid ...
UC Irvine, NASA JPL researchers discover a cause of rapid ice melting in Greenland
2023-05-08
Irvine, Calif., May 8, 2023 – While conducting a study of Petermann Glacier in northwest Greenland, researchers at the University of California, Irvine and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory uncovered a previously unseen way in which the ice and ocean interact. The glaciologists said their findings could mean that the climate community has been vastly underestimating the magnitude of future sea level rise caused by polar ice deterioration.
Using satellite radar data from three European missions, the UCI/NASA team learned that Petermann Glacier’s grounding line – where ice detaches from the land bed and begins floating in the ocean – shifts substantially ...
A new twist on chirality: researchers extend the concept of directionality and propose a new class of materials
2023-05-08
It is often desirable to restrict flows—whether of sound, electricity, or heat—to one direction, but naturally occurring systems almost never allow this. However, unidirectional flow can indeed be engineered under certain conditions, and the resulting systems are said to exhibit chiral behavior.
The concept of chirality is traditionally limited to single direction flows in one dimension. In 2021, however, researchers working with Taylor Hughes, a professor of physics at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, ...
New York’s fertility rate drops, average age of mothers rises
2023-05-08
ITHACA, NY – A decline in New York’s childbirth rate is showing no sign of reversing and many women are waiting longer to have children, according to newly compiled data from the Program in Applied Demographics (PAD) in the Cornell Jeb E. Brooks School of Public Policy.
In 2011, about 241,312 were born in New York. In 2021, that number was 210,742 – a 13% decline.
New York state’s total fertility rate (TFR) – the average number of births a woman would have in her lifetime if current patterns continue – dropped from ...
Department of Energy announces $45 million for Inertial Fusion Energy (IFE)
2023-05-08
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Today, at the celebration ceremony of the historic achievement of fusion ignition at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), the U.S. Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm announced a plan to provide up to $45 million to support Inertial Fusion Energy (IFE) research and development.
Fusion, the process that powers the sun and stars, has the potential to provide clean, safe, and reliable carbon-free energy on earth. Harnessing fusion energy is one of the greatest scientific and technological challenges of the 21st century. Fusion requires the fuel to ...
The ability to chew properly may improve blood sugar levels in patients with Type 2 diabetes
2023-05-08
For release: May 8, 2023
Contact: Mary Durlak, durlak@buffalo.edu
University at Buffalo
716-645-4595
The ability to chew properly may improve blood sugar levels in patients with Type 2 diabetes
BUFFALO, N.Y. – If you’re a health care provider treating people with Type 2 diabetes (T2D), University at Buffalo researcher Mehmet A. Eskan has this suggestion for you: check your patients’ teeth.
In a study published in PLOS ONE on April 14, Eskan demonstrates that patients with T2D who have full chewing function have a blood glucose level that is significantly lower ...
Drug industry’s carbon impact could be cut by half
2023-05-08
ITHACA, N.Y. – In a first-of-its-kind analysis, Cornell University researchers and partners found that pharmaceutical producers could reduce their environmental impact by roughly half by optimizing manufacturing processes and supply chain networks and by switching to renewable energy sources.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing is a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, similar in magnitude to the automotive industry, though it has not received anywhere near the level of academic or regulatory ...
Clearing the runway: Modeling a realistic supply chain for bio-based jet fuel
2023-05-08
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists led the development of a supply chain model revealing the optimal places to site farms, biorefineries, pipelines and other infrastructure for sustainable aviation fuel production.
The project focused on carinata, a hardy, oil-rich plant targeted as a winter bioenergy crop in Georgia. Scientists used geographical data to model facilities to grow, harvest, store, process and deliver carinata-based fuel at the lowest cost and carbon intensity.
“Our model is unique in capturing the fuel’s life-cycle carbon footprint,” said ...
[1] ... [1931]
[1932]
[1933]
[1934]
[1935]
[1936]
[1937]
[1938]
1939
[1940]
[1941]
[1942]
[1943]
[1944]
[1945]
[1946]
[1947]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.