Parent training can reduce serious behavioral problems in young children with autism
2015-04-21
A multi-site study sponsored by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) finds young children with autism spectrum disorder and serious behavioral problems respond positively to a 24-week structured parent training. The benefits of parent training endured for up to six months post intervention.
Published in the April 21 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association the study found parent training was more effective in reducing disruptive and aggressive behavior than 24 weeks of parent education. Parent training provided parents with specific strategies ...
Whiteboards of the future: New electronic paper could make inexpensive electronic displays
2015-04-21
Researchers from the University of Tokyo have revamped an old e-paper concept to make an inexpensive handwriting-enabled e-paper well suited to large displays like whiteboards. They describe the e-paper in the Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing.
Traditional ink and paper is convenient for both reading and writing. In e-paper development the writing feature has generally lagged behind. Handwriting-enabled displays mainly show up in the inexpensive, but feature-limited realm of children's toys, and in the high-end realm of touch-screen e-readers and smart ...
New gene therapy success in a rare disease of the immune system
2015-04-21
French teams from CIC Biothérapie (AP-HP/Inserm), from pediatric hematology department of Necker Hospital for Children (AP-HP), led by Marina Cavazzana, Salima Hacein Bey Albina and Alain Fischer and from Genethon led by Anne Galy (Genethon/Inserm UMR-S951), and English teams from UCL Institute of Child Health and Great Ormond Street Hospital in London led by Adrian Thrasher and Bobby Gaspar demonstrated the efficacy of gene therapy treatment for Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (WAS). Six children that were treated and followed for at least 9 months had their immune system ...
Getting better all the time: JILA strontium atomic clock sets new records
2015-04-21
BOULDER, Colo. -- In another advance at the far
frontiers of timekeeping by National Institute of
Standards and Technology (NIST) researchers, the
latest modification of a record-setting strontium atomic
clock has achieved precision and stability levels that
now mean the clock would neither gain nor lose one
second in some 15 billion years*--roughly the age of
the universe.
Precision timekeeping has broad potential
impacts on advanced communications, positioning technologies (such as GPS) and many
other technologies. Besides keeping future technologies on schedule, ...
Type 1 diabetes: First hurdle taken on the way to an insulin vaccine
2015-04-21
Scientists from the DFG Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden, TU Dresden and the Institut für Diabetesforschung, Helmholtz Zentrum München, together with researchers from Vienna, Bristol and Denver (USA) have successfully completed the first step in development of an insulin vaccine to prevent type 1 diabetes.
As reported by these diabetes researchers in the current edition of the renowned scientific journal JAMA, evaluations of the international Pre-POINT study point to a positive immune response in persons at risk for the disease who were given oral doses ...
Incidence of serious diabetes complication increases in Colorado youth
2015-04-21
AURORA, Colo. (April 21, 2015) - The incidence of a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes, called diabetic ketoacidosis, increased by 55 percent between 1998 and 2012 in youth in Colorado, according to a study by researchers from the Barbara Davis Center for Childhood Diabetes and the University of Colorado School of Medicine on the Anschutz Medical Campus.
The finding is published in the April 21 issue of JAMA.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) at the time of type 1 diabetes diagnosis has detrimental long-term effects and is characterized by dangerously high ...
Children at risk for type 1 diabetes show immune response when given oral insulin
2015-04-21
AURORA, Colo. (April 21, 2015) - Children at risk for type 1 diabetes, who were given daily doses of oral insulin, developed a protective immune response to the disease that researchers with the Barbara Davis Center for Childhood Diabetes at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus say could possibly lay the groundwork for a vaccine against the chronic illness.
The pilot study, published Tuesday, April 21, in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), was carried out in the U.S., Germany, Austria and the United Kingdom.
"This is the first time ...
Sweet potato naturally 'genetically modified'
2015-04-21
Sweet potatoes from all over the world naturally contain genes from the bacterium Agrobacterium. Researchers from UGent and the International Potato Institute publish this discovery in PNAS. Sweet potato is one of the most important food crops for human consumption in the world. Because of the presence of this 'foreign' DNA, sweet potato can be seen as a 'natural GMO.'
The researchers discovered the foreign DNA sequences of Agrobacterium while searching the genome - this is the entire DNA-code - of sweet potato for viral diseases. Instead of contributing this peculiar ...
Sex matters ... even for liver cells
2015-04-21
Female liver cells, and in particular those in menopaused women, are more susceptible to adverse effects of drugs than their male counterparts, according to new research carried out by the JRC. It is well known that women are more vulnerable when it comes to drug-induced liver effects, but it's the first time it has been shown that there are differences at cellular level. The findings are striking and clinically relevant, and emphasise the importance of considering sex-based differences in human health risk assessment.
In this study, five prevalently used drugs (diclofenac, ...
Scientists identify brain circuitry responsible for anxiety in smoking cessation
2015-04-21
WORCESTER, MA -- In a promising breakthrough for smokers who are trying to quit, neuroscientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School and The Scripps Research Institute have identified circuitry in the brain responsible for the increased anxiety commonly experienced during withdrawal from nicotine addiction.
"We identified a novel circuit in the brain that becomes active during nicotine withdrawal, specifically increasing anxiety," said principal investigator Andrew Tapper, PhD , associate professor of psychiatry. "Increased anxiety is a prominent nicotine ...
Certain interactive tools click with web users
2015-04-21
Before web developers add the newest bells and the latest whistles to their website designs, a team of researchers suggests they zoom in on the tools that click with the right users and for the right tasks.
"When designers create sites, they have to make decisions on what tools and features they use and where they put them, which takes a lot of planning," said S. Shyam Sundar, Distinguished Professor of Communications and co-director of the Media Effects Research Laboratory. "You not only have to plan where the feature will be, you also have to design what will go underneath ...
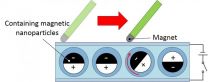
New tabletop detector 'sees' single electrons
2015-04-21
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- MIT physicists have developed a new tabletop particle detector that is able to identify single electrons in a radioactive gas.
As the gas decays and gives off electrons, the detector uses a magnet to trap them in a magnetic bottle. A radio antenna then picks up very weak signals emitted by the electrons, which can be used to map the electrons' precise activity over several milliseconds.
The team worked with researchers at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, the University of Washington, the University of California at Santa Barbara (UCSB), and ...
Global warming progressing at moderate rate, empirical data suggest
2015-04-21
DURHAM, N.C. - A new study based on 1,000 years of temperature records suggests global warming is not progressing as fast as it would under the most severe emissions scenarios outlined by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
"Based on our analysis, a middle-of-the-road warming scenario is more likely, at least for now," said Patrick T. Brown, a doctoral student in climatology at Duke University's Nicholas School of the Environment. "But this could change."
The Duke-led study shows that natural variability in surface temperatures -- caused by interactions ...
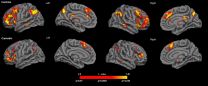
Cannabis consumers show greater susceptibility to false memories
2015-04-21
The study conducted at Sant Pau and Bellvitge hospitals, published in the American journal Molecular Psychiatry and conducted with the use of neuroimaging techniques, demonstrates for the first time that cannabis consumers have a less active hippocampus, a key structure related to the storage of memories.
Consumers of cannabis show distortions in their memories and can even come to imagine situations which differ from reality.
The study compared the memories of consumers to that of non-consumers to find differences in the retention of situations and experiences.
The ...
What happens when multiple sclerosis patients stop taking their medication?
2015-04-21
New research led by NYU Langone Medical Center examines what happens when a patient with multiple sclerosis (MS) who is clinically stable stops taking their medication.
The international, multi-site study found almost 40 percent of patients had some disease activity return when they stopped taking their meds.
The findings were presented at the American Academy of Neurology Annual Meeting held April 18-25, in Washington, D.C.
"Despite long periods of disease stability while taking medication, we found a large minority of patients who stopped experienced relapses or disability ...
Messenger RNA-associated protein drives multiple paths in T-cell development
2015-04-21
PHILADELPHIA - RNA is both the bridge between DNA and the production of proteins that carry out the functions of life and what guides which and how much protein gets made. As messenger RNA (mRNA) is transcribed from DNA to carry genetic information out of the nucleus, segments that don't code for actual proteins need to be removed from the RNA strand and the remaining pieces spliced together. Different pieces of the expressed gene (exons) are cut out, and these sections are joined together to form the final mRNA strand. Cells gain their ability to produce proteins with ...
Reflections on current state of situation awareness topic of JCEDM special issue
2015-04-21
Over the past 25 years, the construct of situation awareness (SA), or the perception and interpretation of what is happening around you, has been a catalyst for new advances in the human factors/ergonomics field, particularly in the areas of information display, automation, and training.
But recent advances also raise new questions, such as these: To what extent is SA about "awareness in the head" versus "awareness of where to look around you"? How is the process of maintaining SA affected by workload? Is it possible to have high-level SA about, for example, the progress ...
Trial shows benefit of 'BRCA-targeting' drug in prostate cancer
2015-04-21
Men with prostate cancer benefit from treatment with the pioneering drug olaparib - the first cancer drug to target inherited mutations - according to the results of a major trial presented today (Tuesday).
Olaparib was licensed in December for women with ovarian cancer and inherited BRCA mutations, but the new research suggests it could also benefit men with genomic faults within their tumours.
Researchers told the American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) conference in Philadelphia that up to 30 per cent of men with advanced prostate cancer had tumours with defects ...
Amazon rainforest losses impact on climate change, study shows
2015-04-21
Human activity has removed more than one-tenth of trees and plants from the Amazon rainforest since the 1960s, a study shows.
Widespread removal of trees has contributed to a rise in the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, increasing the potential impact of climate change, researchers say.
Deforestation of the Amazon accounted for 1.5 per cent of the increase in carbon dioxide levels seen since the mid-nineteenth century, the team says.
However, this increased the total amount of carbon found in the atmosphere only very slightly compared with fossil fuel ...
Fishing impacts on the Great Barrier Reef
2015-04-21
New research shows that fishing is having a significant impact on the make-up of fish populations of the Great Barrier Reef.
It's long been known that environmental impacts such as climate change and pollution are amongst the drivers of change on the Great Barrier Reef.
Now researchers from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE) at James Cook University have found that removing predatory fish such as coral trout and snapper, through fishing, causes significant changes to the make-up of the reef's fish populations.
"A stable and healthy reef ...
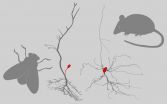
Why some neurons 'outsource' their cell body
2015-04-21
Nerve cells come in very different shapes. Researchers at the Bernstein Center Berlin now reveal why, in insects, the cell body is usually located at the end of a separate extension. Using mathematical models, they show that this increases the strength of electrical signal transmission at no additional energetic cost.
Nerve cells follow a functional design: They receive input signals over more or less ramified cell branches (dendrites), which they forward to other nerve cells along an elongated, thin cell process (axon). The cell body contains the nucleus with genetic ...
Online discussion forums good for well-being, study shows
2015-04-21
A new study has found that internet discussion forums have positive links to well-being and are even associated with increased community engagement offline, contrary to a common perception of them being outdated and prone to trolling.
Research just published in the journal Computers in Human Behavior found that online forums have benefits for both individuals and wider society and are of greater importance than previously realised.
Although seemingly eclipsed in the past decade by social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter, forums are still regularly used ...
Hurdles to US climate change action are in economics and politics, not divided science
2015-04-21
The U.S. Congress successfully hears the "supermajority" consensus on the reality and causes of climate change, according to scientists from Texas A&M University, Idaho State University, and University of Oklahoma. In a paper published in Climatic Change, the scientists suggest looking at business interests, partisan predispositions and political ideology for the hurdles to policy action.
"Different perceptions and claims among lawmakers are a major hurdle to agreeing on action to address global warming and these were thought to simply reflect scientific uncertainty," ...
More detailed findings confirm that coffee protects against breast cancer recurrence
2015-04-21
A number of research studies have shown that coffee helps to protect against breast cancer. A new study led by Lund University, has confirmed that coffee inhibits the growth of tumours and reduces the risk of recurrence in women who have been diagnosed with breast cancer and treated with the drug tamoxifen.
The study, which is a follow-up of the results the researchers obtained two years ago, was carried out at Lund University and Skåne University Hospital, in collaboration with researchers in the UK.
"Now, unlike in the previous study, we have combined information ...
Regular consumption of yogurt does not improve health
2015-04-21
Dietary recommendations support the consumption of dairy products as part of a healthy diet. However, after a Spanish study involving more than 4,000 people analysed the relationship between the regular intake of yogurt and health-related quality of life, it declared that there was no link with the improvement of the physical and mental parameters analysed.
For years various researchers have stated the benefits of eating yogurt on a regular basis although its effectiveness has never been proven. In fact, until now, few studies have specifically examined the effect of ...
[1] ... [3019]
[3020]
[3021]
[3022]
[3023]
[3024]
[3025]
[3026]
3027
[3028]
[3029]
[3030]
[3031]
[3032]
[3033]
[3034]
[3035]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.