A sea change for ocean resource management
2015-03-11
SAN DIEGO, Calif. (March 11, 2015)-- Ocean ecosystems around the world are threatened by overfishing, extensive shipping routes, energy exploration, pollution and other consequences of ocean-based industry. Data exist that could help protect these vulnerable ecosystems, but current management strategies often can't react quickly enough to new information, said San Diego State University biologist Rebecca Lewison.
She and colleagues from several other academic, governmental and non-governmental organizations endorse a new approach called "dynamic ocean management" in a ...
Study shows even injured kidneys can be used for transplants
2015-03-11
New Haven, Conn. -- Kidneys from deceased donors that have acute injuries are frequently discarded instead of being used for transplant. However, a Yale-led study finds that such kidneys may be more viable than previously thought, and should be considered to meet the growing demand for organ transplants.
Donated kidneys with acute injury are often discarded for fear of poor outcomes such as delayed function and even premature kidney transplant failure. Given the growing need for transplant organs, the Yale-led team embarked on the largest multicenter observational study ...
Swine flu outbreak in India raises concern
2015-03-11
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Since December, an outbreak of swine flu in India has killed more than 1,200 people, and a new MIT study suggests that the strain has acquired mutations that make it more dangerous than previously circulating strains of H1N1 influenza.
The findings, which appear in the March 11 issue of Cell Host & Microbe, contradict previous reports from Indian health officials that the strain has not changed from the version of H1N1 that emerged in 2009 and has been circulating around the world ever since.
With very little scientific data available about the new ...
Repairing the cerebral cortex: It can be done
2015-03-11
This news release is available in French. A team led by Afsaneh Gaillard (Inserm Unit 1084, Experimental and Clinical Neurosciences Laboratory, University of Poitiers), in collaboration with the Institute of Interdisciplinary Research in Human and Molecular Biology (IRIBHM) in Brussels, has just taken an important step in the area of cell therapy: repairing the cerebral cortex of the adult mouse using a graft of cortical neurons derived from embryonic stem cells. These results have just been published in Neuron.
The cerebral cortex is one of the most complex structures ...
UCLA study shows feasibility of blood-based test for diagnosing Alzheimer's Disease
2015-03-11
UCLA researchers have provided the first evidence that a simple blood test could be developed to confirm the presence of beta amyloid proteins in the brain, which is a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease.
Although approximately 5 million Americans are living with Alzheimer's, no reliable blood-based test currently exists for the neurodegenerative disorder that is the sixth-leading cause of death in the United States. Using blood-based biomarkers -- a signature of proteins in the blood that indicate the presence of a disease -- to diagnose Alzheimer's could be a key advance.
"Blood-based ...
Concurrent chemoradiation treatment at high-volume facilities improves survival for NSCLC
2015-03-11
DENVER - Patients treated with definitive concurrent chemotherapy and radiation therapy (CCRT) for stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have longer overall survival when treated by highly experienced facilities, whether or not they are academic or community cancer centers.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer related death in the US with 159,000 deaths and 224,000 diagnoses each year, with NSCLC accounting for 85% of the cases. The stage of lung cancer is determined based on the size of the tumor, the extent and location of lymph node involvement, and whether ...
Underlying subfertility may affect ART birth outcomes, BU study finds
2015-03-11
Birth outcomes for babies whose mothers used assisted reproductive technology (ART) are better in some cases, and worse in others, than for subfertile women who did not use ART, according to a first-of-its-kind study led by Boston University School of Public Health researchers.
Those findings, published online in the journal Fertility and Sterility, suggest that underlying subfertility, distinct from the use of ART, may account for some of the elevated risks in birth outcomes attributed to the use of in vitro fertilization and other ART procedures.
Researchers found ...
Meta-study shows that the experience of time is altered in depression
2015-03-11
This news release is available in German. Time perception is highly subjective and usually depends on the relevant situation so that, for instance, your sense of how fast or slow time is passing can be influenced by whether you are waiting for something or if a deadline is approaching. Patients suffering from depression appear to experience time differently than healthy individuals. Statements made by corresponding patients indicate that for them time seems to pass extremely slowly or even stands still. Psychologists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have ...
Tracking sea turtles across hundreds of miles of open ocean
2015-03-11
AMHERST, Mass. - Scientists have long known that leatherback sea turtles travel thousands of miles each year through open ocean to get from foraging habitats to nesting beaches and tropical wintering grounds, but how the wanderers find their way has been "an enduring mystery of animal behavior," says marine biologist Kara Dodge. "Adult turtles can pinpoint specific nesting beaches even after being away many years," she notes.
Sea turtles' ability to identify and maintain appropriate headings affect migration distance, duration and, for reproductively-active adults, breeding ...
Graphene: A new tool for fighting cavities and gum disease?
2015-03-11
Dental diseases, which are caused by the overgrowth of certain bacteria in the mouth, are among the most common health problems in the world. Now scientists have discovered that a material called graphene oxide is effective at eliminating these bacteria, some of which have developed antibiotic resistance. They report the findings in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Zisheng Tang and colleagues point out that dentists often prescribe traditional antibiotics to get rid of bacteria that cause tooth decay or gum disease. But with the rise in antibiotic resistance, ...
Gender and race influences when teens start drinking, smoking and doing drugs
2015-03-11
Cigarette use among white teenagers is substantially higher than among black and Hispanic teenagers, especially at 18 years old, according to Penn State researchers.
Alcohol and marijuana use are also higher in white teenagers, and the numbers continue to increase until age 20. Throughout their 20s, blacks and Hispanics are more likely to pick up a cigarette-smoking habit, while the numbers start to decrease for whites.
At 18.5 years old, 44 percent of whites surveyed smoked cigarettes, 27 percent of Hispanics did and 18 percent of blacks. However at 29 years old, ...
Researchers develop tool to understand how the gut microbiome works
2015-03-11
HEIDELBERG, 11 March 2015 - Researchers at Harvard Medical School and Columbia University in the United States have developed a way to study the functions of hard-to-grow bacteria that contribute to the composition of the gut microbiome. The new method is published in the journal Molecular Systems Biology.
"Our method, TFUMseq, is a powerful tool for understanding how the wealth of microbes that we harbour in our bodies are so successful at colonizing us. It provides a general high-throughput approach to identify genes that enhance the fitness of microbes over time as ...
Uncovering the effects of cooking, digestion on gluten and wheat allergens in pasta
2015-03-11
Researchers trying to understand wheat-related health problems have found new clues to how the grain's proteins, including gluten, change when cooked and digested. They report in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry that boiling pasta releases some of its potential allergens, while other proteins persist throughout cooking and digestion. Their findings lend new insights that could ultimately help celiac patients and people allergic to wheat.
Gianfranco Mamone and colleagues point out that pasta is one of the most popular foods in Europe and the U.S. Most people ...
Silk could be new 'green' material for next-generation batteries
2015-03-11
Lithium-ion batteries have enabled many of today's electronics, from portable gadgets to electric cars. But much to the frustration of consumers, none of these batteries last long without a recharge. Now scientists report in the journal ACS Nano the development of a new, "green" way to boost the performance of these batteries -- with a material derived from silk.
Chuanbao Cao and colleagues note that carbon is a key component in commercial Li-ion energy storage devices including batteries and supercapacitors. Most commonly, graphite fills that role, but it has a limited ...
British Psychological Society report challenges received wisdom about mental illness
2015-03-11
21st March 2015 will see the US launch of the British Psychological Society's Division of Clinical Psychology's ground-breaking report 'Understanding Psychosis and Schizophrenia'.
The report, which will be launched at 9am at the Cooper Union, Manhattan, NYC by invitation of the International Society for Psychological and Social approaches to Psychosis (ISPS), challenges received wisdom about the nature of mental illness and has led to widespread media coverage and debate in the UK.
Many people believe that schizophrenia is a frightening brain disease that makes ...
Brain waves predict our risk for insomnia
2015-03-11
This news release is available in French. Montreal, March 11, 2015 -- There may not yet be a cure for insomnia, but Concordia University researchers are a step closer to predicting who is most likely to suffer from it -- just in time for World Sleep Day on March 13.
In his study published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, Thien Thanh Dang-Vu, from Concordia's Center for Studies in Behavioral Neurobiology and PERFORM Center, explores the impact of stress on sleep. Although researchers already know that stressful events can trigger insomnia, the experiment reveals ...
How 3-D bioprinting could address the shortage of organ donations
2015-03-11
Three-dimensional bioprinting has come a long way since its early days when a bioengineer replaced the ink in his desktop printer with living cells. Scientists have since successfully printed small patches of tissue. Could it someday allow us to custom-print human organs for patients in need of transplants? An article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, explores the possibility.
Matt Davenport, an associate editor at C&EN, points out that for every organ donor in 2012, there were more than eight patients on ...
New mothers more satisfied after giving birth in a public hospital
2015-03-11
Women who give birth in a public hospital are more confident parents compared to women who have babies privately, a new Australian study has found.
A joint study by Queensland University of Technology and the University of Queensland, surveyed more than 6400 mums in Queensland, and found women who birth in the public sector were more likely to receive after-hospital health care, in turn boosting their confidence as a new parent, than women in the private system.
Associate Professor Yvette Miller from QUT's Faculty of Health and one of the authors of the study published ...
Cochrane Review of effectiveness of point of care diagnostics for schistosomiasis
2015-03-11
Researchers from the Cochrane Infectious Disease Group, hosted at LSTM, have conducted an independent review to assess how well point of care tests detect Schistosoma infections in people living in endemic regions.
Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, is a parasitic disease classified as a neglected tropical diseases (NTD), which is common in tropical and subtropical regions. The traditional means of testing for the disease is microscopy, which is lab based. Point-of-care tests and urine reagent tests are quicker and easier to use than microscopy in the field, and ...
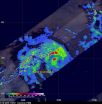
TRMM sees large and more powerful Cyclone Pam, warnings posted
2015-03-11
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite saw powerful towering thunderstorms in Tropical Cyclone Pam, indicating the storm was strengthening as it moved through the Solomon Islands. Pam has now triggered warnings in the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu and New Zealand.
In the Solomon Islands, a tropical cyclone warning was in effect today, March 11, for Temotu, Malaita and Makira provinces. A tropical cyclone watch was in effect for Rennell and Bellona, Central, Isabel, Western, Guadalcanal and the Choiseul provinces.
In Vanuatu, a tropical cyclone warning ...
Finding strengths -- and weaknesses -- in hepatitis C's armor
2015-03-11
Using a specially selected library of different hepatitis C viruses, a team of researchers led by Johns Hopkins scientists has identified tiny differences in the pathogens' outer shell proteins that underpin their resistance to antibodies. The findings, reported in the January 2015 issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, suggest a reason why some patients' immune systems can't fend off hepatitis C infections, and they reveal distinct challenges for those trying to craft a successful vaccine to prevent them. Due to concerns about the rising costs of newly available ...
Researchers develop 'visual Turing test'
2015-03-11
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Researchers from Brown and Johns Hopkins universities have come up with a new way to evaluate how well computers can divine information from images. The team describes its new system as a "visual Turing test," after the legendary computer scientist Alan Turing's test of the extent to which computers display human-like intelligence.
"There have been some impressive advances in computer vision in recent years," said Stuart Geman, the James Manning Professor of Applied Mathematics at Brown. "We felt that it might be time to raise the ...
Study explains control of cell metabolism in patient response to breast cancer drugs
2015-03-11
La Jolla, Calif., March 9, 2015 - Researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) have discovered a mechanism that explains why some breast cancer tumors respond to specific chemotherapies and others do not. The findings highlight the level of glutamine, an essential nutrient for cancer development, as a determinant of breast cancer response to select anticancer therapies, and identify a marker associated with glutamine uptake, for potential prognosis and stratification of breast cancer therapy.
"Our study indicates that a protein called RNF5 ...
Naproxen plus acid-blocking drug shows promise in preventing bladder cancer
2015-03-11
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- The anti-inflammatory class of drugs NSAIDs have shown great promise in preventing cancers including colon, esophagus and skin. However, they can increase the risks of heart attacks, ulcers and rare but potentially life-threatening bleeds.
A new study suggests there may be ways to reduce these dangerous side effects.
Collaborators from the University of Michigan, the National Cancer Institute and the University of Alabama looked at naproxen, which is known to have a lower cardiovascular risk than other NSAIDs. Naproxen, like most NSAIDs and aspirin, ...
Deadly to cancer cells only
2015-03-11
Parvoviruses are a class of viruses that normally infect rodents; in humans, they do not cause any disease symptoms. However, they are able to infect and kill cancer cells. The details behind this biological selectivity on the part of the viruses have not been understood until now. "Since the viruses might soon play a role in cancer medicine, it is important to know why they replicate exclusively in tumor cells in humans," says virologist Dr. Jürg Nüesch from the German Cancer Research Center (Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, DKFZ).
In order to complete their ...
[1] ... [3094]
[3095]
[3096]
[3097]
[3098]
[3099]
[3100]
[3101]
3102
[3103]
[3104]
[3105]
[3106]
[3107]
[3108]
[3109]
[3110]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.