Measles commentary in Annals of Internal Medicine
2014-04-24
1. Measles outbreaks prompt concern about physician knowledge gaps
Vaccination refusal and importation of the disease has led to increased incidence of measles in the United States. Before widespread vaccination, approximately 500,000 measles cases occurred annually, resulting in 500 deaths and 48,000 hospitalizations. Vaccination programs helped to eradicate endemic measles by the year 2000, reducing the median number of cases per year to 60. But in just the first three months of 2014, 106 measles cases were reported, prompting health officials to become concerned. Measles ...
Plants send out signals attracting harmful bacteria, MU study finds
2014-04-24
COLUMBIA, Mo. – When bacteria attack plants, they often inject harmful proteins into the host plants' cells to weaken and suppress natural defenses. However, in some plants, bacteria attack once they've recognized the plant cells as a potential host. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have identified and replicated the process that allows the bacteria—known mostly for attacking tomatoes—to invade its host. This discovery could lead to natural anti-infective treatments that work with food-producing plants to enhance resistance to harmful bacteria in the field.
"When ...
Genome yields insights into golden eagle vision, smell
2014-04-24
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Purdue and West Virginia University researchers are the first to sequence the genome of the golden eagle, providing a bird's-eye view of eagle features that could lead to more effective conservation strategies.
Their study calls into question long-held assumptions about golden eagle vision, indicating that the raptors may not be as sensitive to ultraviolet light as previously thought. The genome also suggests that golden eagles could have a sharper sense of smell than researchers realized.
Additionally, the genome provides thousands of genetic ...
International collaboration unravels novel mechanism for neurological disorder
2014-04-24
HOUSTON – (April 24, 2014) – A team of international scientists led by Baylor College of Medicine has discovered a novel gene (CLP1) associated with a neurological disorder affecting both the peripheral and central nervous systems. Together with scientists in Vienna they show that disturbance of a very basic biological process, tRNA biogenesis, can result in cell death of neural progenitor cells. This leads to abnormal brain development and a small head circumference as well as dysfunction of peripheral nerves.
The study published today in the current issue of the journal ...
Researchers create comprehensive map of human B cell development
2014-04-24
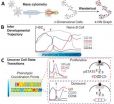
New York, NY - In the April 24, 2014 edition of Cell, a team of researchers led by Dana Pe'er at Columbia University and Garry Nolan at Stanford University describes a powerful new method for mapping cellular development at the single cell level. By combining emerging technologies for studying single cells with a new, advanced computational algorithm, they have created the most comprehensive map ever made of human B cell development. Their approach will greatly improve researchers' ability to investigate development in cells of all types, make it possible to identify rare ...
Surprising new insights into the PTEN tumor suppressor gene
2014-04-24
BOSTON – Ever since it was first identified more than 15 years ago, the PTEN gene has been known to play an integral role in preventing the onset and progression of numerous cancers. Consequently, when PTEN is either lost or mutated, malignant cells can grow unchecked and cancer can develop.
Now a team led by investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) helps explain more precisely how PTEN exerts its anti-cancer effects and how its loss or alteration can set cells on a cancerous course. The new study, which reveals that PTEN loss and PTEN mutations are ...
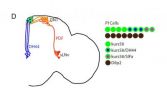
Researchers pinpoint protein crucial for development of biological rhythms in mice
2014-04-24
Johns Hopkins researchers report that they have identified a protein essential to the formation of the tiny brain region in mice that coordinates sleep-wake cycles and other so-called circadian rhythms.
By disabling the gene for that key protein in test animals, the scientists were able to home in on the mechanism by which that brain region, known as the suprachiasmatic nucleus or SCN, becomes the body's master clock while the embryo is developing.
The results of their experiments, reported online April 24 in Cell Reports, are an important step toward understanding ...
Oldest pterodactyloid species discovered, named by international team of researchers
2014-04-24
WASHINGTON—An international research team, including a George Washington University (GW) professor, has discovered and named the earliest and most primitive pterodactyloid—a group of flying reptiles that would go on to become the largest known flying creatures to have ever existed—and established they flew above the earth some 163 million years ago, longer than previously known.
Working from a fossil discovered in northwest China, the project—led by University of South Florida (USF) paleontologist Brian Andres, James Clark of the GW Columbian College of Arts and Sciences ...
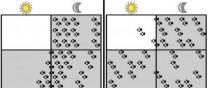
Fruit fly study identifies brain circuit that drives daily cycles of rest, activity
2014-04-24
PHILADELPHIA - Amita Sehgal, PhD, a professor of Neuroscience at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, describes in Cell a circuit in the brain of fruit flies that controls their daily, rhythmic behavior of rest and activity. The new study also found that the fly version of the human brain protein known as corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) is a major coordinating molecule in this circuit. Fly CRF, called DH44, is required for rest/activity cycles and is produced in cells that receive input from the clock cells in the fly brain. In mammals, CRF ...
Scientists find way to target cells resistant to chemo
2014-04-24
Scientists from The University of Manchester have identified a way to sensitise cancer cells to chemotherapy - making them more open to treatment.
The study published today in Cell Reports, could pave the way for the development of drugs to target cells that have become resistant to treatment.
The research team made the discovery whilst exploring the possible mechanisms behind resistance to chemotherapy drugs like Paclitaxel, often used to treat breast and colon cancer.
Dr Andrew Gilmore, who led the research team at The University of Manchester, is part of both the ...
New type of protein action found to regulate development
2014-04-24
Johns Hopkins researchers report they have figured out how the aptly named protein Botch blocks the signaling protein called Notch, which helps regulate development. In a report on the discovery, to appear online April 24 in the journal Cell Reports, the scientists say they expect the work to lead to a better understanding of how a single protein, Notch, directs actions needed for the healthy development of organs as diverse as brains and kidneys.
The Johns Hopkins team says their experiments show that Botch uses a never-before-seen mechanism, replacing one chemical group ...
Researchers discover new genetic brain disorder in humans
2014-04-24
A newly identified genetic disorder associated with degeneration of the central and peripheral nervous systems in humans, along with the genetic cause, is reported in the April 24, 2014 issue of Cell.
The findings were generated by two independent but collaborative scientific teams, one based primarily at Baylor College of Medicine and the Austrian Academy of Sciences, the other at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, the Academic Medical Center (AMC) in the Netherlands and the Yale University School of Medicine.
By performing DNA sequencing ...
Scientists reprogram blood cells into blood stem cells in mice
2014-04-24
BOSTON (April 24, 2014)—Researchers at Boston Children's Hospital have reprogrammed mature blood cells from mice into blood-forming hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), using a cocktail of eight genetic switches called transcription factors. The reprogrammed cells, which the researchers have dubbed induced HSCs (iHSCs), have the functional hallmarks of HSCs, are able to self-renew like HSCs, and can give rise to all of the cellular components of the blood like HSCs.
The findings mark a significant step toward one of the most sought-after goals of regenerative medicine: the ...
To mark territory or not to mark territory: Breaking the pheromone code
2014-04-24
LA JOLLA, CA— April 24, 2014 —A team led by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) has deciphered the surprisingly versatile code by which chemical cues help trigger some of the most basic behaviors in mice.
The findings shed light on the evolution of mammalian behaviors—which include human behaviors—and their underlying brain mechanisms.
"How does an individual respond differently to the environment based on experience? How does it distinguish itself from others? These are some of the fundamental questions that a study like this one helps us address," ...
Genetic legacy from the Ottoman Empire: Single mutation causes rare brain disorder
2014-04-24
An international team of researchers have identified a previously unknown neurodegenerative disorder and discovered it is caused by a single mutation in one individual born during the Ottoman Empire in Turkey about 16 generations ago.
The genetic cause of the rare disorder was discovered during a massive analysis of the individual genomes of thousands of Turkish children suffering from neurological disorders.
"The more we learn about basic mechanisms behind rare forms of neuro-degeneration, the more novel insights we can gain into more common diseases such as Alzheimer's ...
Oops! Researchers find neural signature for mistake correction
2014-04-24
Culminating an 8 year search, scientists at the RIKEN-MIT Center for Neural Circuit Genetics captured an elusive brain signal underlying memory transfer and, in doing so, pinpointed the first neural circuit for "oops" ? the precise moment when one becomes consciously aware of a self-made mistake and takes corrective action.
The findings, published in Cell, verified a 20 year old hypothesis on how brain areas communicate. In recent years, researchers have been pursuing a class of ephemeral brain signals called gamma oscillations, millisecond scale bursts of synchronized ...
Large-scale identification and analysis of suppressive drug interactions
2014-04-24
TORONTO – Baker's yeast is giving scientists a better understanding of drug interactions, which are a major cause of hospitalization and illness world-wide.
When two or more medications are taken at the same time, one can suppress or enhance the effectiveness of the other. Similarly, one drug may magnify the toxicity of another. These types of interactions are a major cause of illness and hospitalization. However, there are severe practical limits on the practical scope of drug studies in humans. Limits come in part from ethics and in part from the staggering expense. ...
Skin layer grown from human stem cells could replace animals in drug and cosmetics testing
2014-04-24
An international team led by King's College London and the San Francisco Veteran Affairs Medical Center (SFVAMC) has developed the first lab-grown epidermis – the outermost skin layer - with a functional permeability barrier akin to real skin. The new epidermis, grown from human pluripotent stem cells, offers a cost-effective alternative lab model for testing drugs and cosmetics, and could also help to develop new therapies for rare and common skin disorders.
The epidermis, the outermost layer of human skin, forms a protective interface between the body and its external ...
Scripps Research Institute scientists find new point of attack on HIV for vaccine development
2014-04-24
LA JOLLA, CA— April 24, 2014 —A team led by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) working with the International AIDS Vaccine Initiative (IAVI) has discovered a new vulnerable site on the HIV virus. The newly identified site can be attacked by human antibodies in a way that neutralizes the infectivity of a wide variety of HIV strains.
"HIV has very few known sites of vulnerability, but in this work we've described a new one, and we expect it will be useful in developing a vaccine," said Dennis R. Burton, professor in TSRI's Department of Immunology and Microbial ...
Three-banded panther worm debuts as a new model in the study of regeneration
2014-04-24
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (April 24, 2014) – Closely resembling plump grains of wild rice set in motion, the three-banded panther worms swimming in disposable containers in Whitehead Institute Member Peter Reddien's lab hardly seem like the next big thing in regeneration. And yet, these little-studied organisms possess the ability to regenerate any part of their bodies and are amenable to molecular studies in the lab, making them a valuable addition to a field keen on understanding how mechanisms controlling regeneration have evolved over millennia and how they might be activated ...
Engineered E. coli produces high levels of D-ribose as described in Industrial Biotechnology journal
2014-04-24
New Rochelle, NY, April 24, 2014—D-ribose is a commercially important sugar used as a sweetener, a nutritional supplement, and as a starting compound for synthesizing riboflavin and several antiviral drugs. Genetic engineering of Escherichia coli to increase the bacteria's ability to produce D-ribose is a critical step toward achieving more efficient industrial-scale production of this valuable chemical, as described in an article in Industrial Biotechnology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the Industrial Biotechnology ...
Oxygen diminishes the heart's ability to regenerate, researchers discover
2014-04-24
DALLAS – April 24, 2014 – Scientific research at UT Southwestern Medical Center previously discovered that the newborn animal heart can heal itself completely, whereas the adult heart lacks this ability. New research by the same team today has revealed why the heart loses its incredible regenerative capability in adulthood, and the answer is quite simple – oxygen.
Yes, oxygen. It is well-known that a major function of the heart is to circulate oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. But at the same time, oxygen is a highly reactive, nonmetallic element and oxidizing agent ...
New study helps to explain why breast cancer often spreads to the lung
2014-04-24
New research led by Alison Allan, PhD, a scientist at Western University and the Lawson Health Research Institute, shows why breast cancer often spreads or metastasizes to the lung.
Breast cancer is the number one diagnosed cancer and the number two cause of cancer-related deaths among women in North America. If detected early, traditional chemotherapy and radiation have a high success rate, but once the disease spreads beyond the breast, many conventional treatments fail. In particular, the lung is one of the most common and deadly sites of breast cancer metastasis ...
Parents of severely ill children see benefits as caregivers, says study
2014-04-24
Benefits often coexist with the negative and stressful outcomes for parents who have a child born with or later diagnosed with a life-limiting illness, says a recent study led by a researcher at the University of Waterloo.
While the challenges are numerous and life-changing and stress levels high, the vast majority of parents who participated in the Waterloo-led research reported positive outcomes as well, a phenomenon known as posttraumatic growth. The findings appear in the most recent issue of the American Journal of Orthopsychiatry.
"What is pivotal is the meaning ...
'Double-duty' electrolyte enables new chemistry for longer-lived batteries
2014-04-24
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., April 24, 2014 — Researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a new and unconventional battery chemistry aimed at producing batteries that last longer than previously thought possible.
In a study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, ORNL researchers challenged a long-held assumption that a battery's three main components -- the positive cathode, negative anode and ion-conducting electrolyte -- can play only one role in the device.
The electrolyte in the team's new battery design has ...
[1] ... [3670]
[3671]
[3672]
[3673]
[3674]
[3675]
[3676]
[3677]
3678
[3679]
[3680]
[3681]
[3682]
[3683]
[3684]
[3685]
[3686]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.