Top Performing Internet Marketers to Hold Exclusive Legacy Event
2012-02-27
Well-known internet marketers, Aaron and Sophia Rashkin along with members of the Loyal 9 Revolution have scheduled the "Legacy" on March 24 and 25, at the offices of the Loyal 9 in New Jersey.
The Legacy is an extremely focused event and follows the AFL Freedom Mastermind 2 that took place in late January at the Rashkin home office in beautiful Parker, Colorado. That 2 and 1/2 day live training experience brought together 12 inspired entrepreneurs from around the world to teach them the mindset and the successful internet marketing strategies used by these ...
Study IDs new marine protected areas in Madagascar
2012-02-27
NEW YORK (February 24, 2012) – A new study by the University of California, Berkeley, Wildlife Conservation Society, and others uses a new scientific methodology for establishing marine protected areas in Madagascar that offers a "diversified portfolio" of management options – from strict no-take zones to areas that would allow fishing.
The methodology looks at existing information on the country's climate, along with dependence on fisheries and marine resources, and applies three different planning approaches to establish priorities for management along the entirety of ...
Protecting the climate by reducing fluorinated greenhouse gas emissions
2012-02-27
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which have been used in recent years in increasing quantities as substitutes for CFCs, are also climatically very active and many are also extremely long-lived. In the renowned journal Science an international team of researchers recommends that the most potent of these gases also be regulated. This could save the positive «side effect» of the Montreal Protocol for the global climate.
It is regarded as the most successful international environmental agreement and has, to date, been ratified by 196 countries – the Montreal Protocol on Substances ...
Experts in pediatric heart disease present research at Cardiology 2012 conference
2012-02-27
Pediatric cardiology researchers and clinicians from almost 50 centers from across the U.S. and around the world are gathering at the Cardiology 2012 Conference sponsored by The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia on Feb. 22-26 in Orlando, Fla. The news briefs below summarize 11 research abstracts selected by the conference organizers as featured presentations. The researchers leading these presentations comprise 6 physicians and 5 nurses.
New Early Warning Algorithm Detects Children's Early Cardiac Deterioration Before Inpatient Arrest
Most cardiopulmonary arrests in ...
OAI: Florida Auto Insurance Bill Gets Final Committee's Approval
2012-02-27
A controversial bill that would make big changes to Florida's car insurance coverage system should soon be on its way to a vote by the full House after getting the OK from the third and final committee to review it, according to OnlineAutoInsurance.com.
If the bill is signed into law, drivers who go to run their next Florida insurance quote comparison could be in for a bit of a surprise.
That's because the bill would, among other things, nix the current system in which motorists rely on personal injury protection (PIP) policies to pay for their medical bills following ...
Evolution of earliest horses driven by climate change
2012-02-27
When Sifrhippus sandae, the earliest known horse, first appeared in the forests of North America more than 50 million years ago, it would not have been mistaken for a Clydesdale.
It weighed in at around 12 pounds--and it was destined to get much smaller over the ensuing millennia.
Sifrhippus lived during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), a 175,000-year interval of time some 56 million years ago in which average global temperatures rose by about 10 degrees Fahrenheit.
The change was caused by the release of vast amounts of carbon into the atmosphere and ...
Green fuel versus black gold
2012-02-27
A life cycle assessment of growing crops for fuel as opposed to refining and using fossil fuels has revealed that substitution of gasoline by bioethanol converted from energy crops has considerable potential for rendering our society more sustainable, according to a Japanese study published in the International Journal of Foresight and Innovation Policy.
Kiyotada Hayashi of the National Agriculture and Food Research Organisation in Tsukuba and colleagues explain how biomass derived from sugarcane, sugar beet and other crops, has emerged as one of the most promising renewable ...
Doctors find new way to predict recurrent stroke
2012-02-27
New research from the University of Calgary's Hotchkiss Brain Institute (HBI) shows that using a CT (computerised tomography) scan, doctors can predict if patients who have had a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or minor stroke, with neurological symptoms such as weakness or speech issues, are at risk for another more severe stroke. This vital information can help doctors decide if stronger medications should be used to prevent future episodes, or if a patient can be safely sent home.
Currently, doctors can use a brain MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan to predict ...
How heavy and light isotopes separate in magma
2012-02-27
In the crash-car derby between heavy and light isotopes vying for the coolest spots as magma turns to solid rock, weightier isotopes have an edge, research led by Case Western Reserve University shows.
This tiny detail may offer clues to how igneous rocks form.
As molten rock cools along a gradient, atoms want to move towards the cool end. This happens because hotter atoms move faster than cooler atoms and, therefore, hotter atoms move to the cool region faster than the cooler atoms move to the hot region.
Although all isotopes of the same element want to move towards ...
A biodiversity discovery that was waiting in the wings -- wasp wings, that is
2012-02-27
From spaghetti-like sea anemones to blobby jellyfish to filigreed oak trees, each species in nature is characterized by a unique size and shape. But the evolutionary changes that produce the seemingly limitless diversity of shapes and sizes of organisms on Earth largely remains a mystery. Nevertheless, a better understanding of how cells grow and enable organisms to assume their characteristic sizes and shapes could shed light on diseases that involve cell growth, including cancer and diabetes.
Providing new information about the evolution of the diversity of sizes and ...
In the genes, but which ones?
2012-02-27
For decades, scientists have understood that there is a genetic component to intelligence, but a new Harvard study has found both that most of the genes thought to be linked to intelligence are probably not in fact related to it, and identifying intelligence's specific genetic roots may still be a long way off.
Led by David I. Laibson '88, the Robert I. Goldman Professor of Economics, and Christopher F. Chabris '88, PhD '99, Assistant Professor of Psychology at Union College, a team of researchers examined a dozen genes using large data sets that included both intelligence ...
A million chances to save a life
2012-02-27
PHILADELPHIA -- Would you be able to find an automated external defibrillator if someone's life depended on it? Despite an estimated one million AEDs scattered around the United States, the answer, all too often when people suffer sudden cardiac arrests, is no.
In a Perspective piece published online this week in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality Outcomes, two researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania outline the tremendous potential associated with greater utilization of AEDs in public places and a method to find ...
Light-emitting nanocrystal diodes go ultraviolet
2012-02-27
LOS ALAMOS, New Mexico, February 24, 2012—A multinational team of scientists has developed a process for creating glass-based, inorganic light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that produce light in the ultraviolet range. The work, reported this week in the online Nature Communications, is a step toward biomedical devices with active components made from nanostructured systems.
LEDs based on solution-processed inorganic nanocrystals have promise for use in environmental and biomedical diagnostics, because they are cheap to produce, robust, and chemically stable. But ...
Astrophysicists from Clemson University and Europe unmask a black hole
2012-02-27
CLEMSON — A study of X-rays emitted a long time ago in a galaxy far, far away has unmasked a stellar mass black hole in Andromeda, a spiral galaxy about 2.6 million light-years from Earth.
Two Clemson University researchers joined an an international team of astronomers, including scientists at Germany's Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, in publishing their findings in a pair of scientific journals this week.
Scientists had suspected the black hole was possible since late 2009 when an X-ray satellite observatory operated by the Max Planck Institute ...
The emotional oracle effect
2012-02-27
NEW YORK – February 24, 2012 – A forthcoming article in the Journal of Consumer Research by Professor Michel Tuan Pham, Kravis Professor of Business, Marketing, Columbia Business School; Leonard Lee, Associate Professor, Marketing, Columbia Business School; and Andrew Stephen, PhD '09, currently Assistant Professor of Business Administration, Joseph M. Katz Graduate School of Business, University of Pittsburgh, finds that a higher trust in feelings may result in more accurate predictions about a variety of future events. The research will also be featured in Columbia Business ...
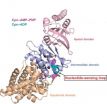
Correct protein folding
2012-02-27
The gold standard for nanotechnology is nature's own proteins. These biomolecular nanomachines – macromolecules forged from peptide chains of amino acids - are able to fold themselves into a dazzling multitude of shapes and forms that enable them to carry out an equally dazzling multitude of functions fundamental to life. As important as protein folding is to virtually all biological systems, the mechanisms behind this process have remained a mystery. The fog, however, is being lifted.
A team of researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley ...
Statins linked with lower depression risk in heart patients
2012-02-27
Patients with heart disease who took cholesterol-lowering statins were significantly less likely to develop depression than those who did not, in a study by Mary Whooley, MD, a physician at the San Francisco VA Medical Center and a professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco.
The study was published electronically in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry (February 21, 2012).
Whooley and her research team evaluated 965 heart disease patients for depression, and found that the patients who were on statins were significantly less likely to be clinically ...
Study proposes new measure of world equity market segmentation
2012-02-27
NEW YORK – February 24, 2012 – A recent study in the Review of Financial Studies proposes a new, valuation-based measure of equity market segmentation. Equity market segmentation occurs when stocks of similar risk in different countries are priced differently. The study, by Columbia Business School Professor Geert Bekaert, Chazen Senior Scholar at The Jerome A. Chazen Institute of International Business at Columbia Business School and the Leon G. Cooperman Professor of Finance and Economics, uncovers the factors that cause variation in market segmentation, both through ...
Rethinking the social structure of ancient Eurasian nomads: Current Anthropology research
2012-02-27
Prehistoric Eurasian nomads are commonly perceived as horse riding bandits who utilized their mobility and military skill to antagonize ancient civilizations such as the Chinese, Persians, and Greeks. Although some historical accounts may support this view, a new article by Dr. Michael Frachetti (Washington University, St. Louis) illustrates a considerably different image of prehistoric pastoralist societies and their impact on world civilizations more than 5000 years ago.
In the article, recently published in the February issue of Current Anthropology, Frachetti argues ...
New research points to erosional origin of linear dunes
2012-02-27
Boulder, Colorado, USA - Linear dunes, widespread on Earth and Saturn's moon, Titan, are generally considered to have been formed by deposits of windblown sand. It has been speculated for some time that some linear dunes may have formed by "wind-rift" erosion, but this model has commonly been rejected due to lack of sufficient evidence. Now, new research supported by China's NSF and published this week in GSA BULLETIN indicates that erosional origin models should not be ruled out.
The linear dunes in China's Qaidam Basin have been proposed to have formed as self-extending ...
GSA Bulletin: Alaska, Russia, Tibet, the Mississippi River, and the Great Green River Basin
2012-02-27
Boulder, CO, USA - New GSA BULLETIN science published online 24 Feb. includes work on the Chugach Metamorphic Complex of southern Alaska; news and data from the first non-Russian science team to make a helicopter over-flight of Shiveluch volcano in Kamchatka, Russia, after its large 2005 eruption; and a study by a team from the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory that proposes a new calibration model for the Eocene segment of the Geomagnetic Polarity Time Scale (GPTS).
Large-scale, short-lived metamorphism, deformation, and magmatism in the Chugach metamorphic complex, ...
Study shows significant state-by-state differences in black, white life expectancy
2012-02-27
A UCLA-led group of researchers tracing disparities in life expectancy between blacks and whites in the U.S. has found that white males live about seven years longer on average than African American men and that white women live more than five years longer than their black counterparts.
But when comparing life expectancy on a state-by-state basis, the researchers made a surprising discovery: In those states in which the disparities were smallest, the differences often were not the result of African Americans living longer but of whites dying younger than the national ...
Training parents is good medicine for children with autism behavior problems
2012-02-27
Children with autism spectrum disorders who also have serious behavioral problems responded better to medication combined with training for their parents than to treatment with medication alone, Yale researchers and their colleagues report in the February issue of Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry.
"Serious behavioral problems interfere with everyday living for children and their families," said senior author on the study Lawrence Scahill, professor at Yale University School of Nursing and the Child Study Center. "Decreasing these serious ...
Study extends the 'ecology of fear' to fear of parasites
2012-02-27
Here's a riddle: What's the difference between a tick and a lion? The answer used to be that a tick is a parasite and the lion is a predator. But now those definitions don't seem as secure as they once did.
A tick also hunts its prey, following vapor trails of carbon dioxide, and consumes host tissues (blood is considered a tissue), so at least in terms of its interactions with other creatures, it is like a lion — a very small, eight-legged lion.
Ecologists are increasingly finding it useful to think of parasites, such as ticks, as micro-predators and have been mining ...
Hamid Soleimanian, Los Angeles Bankruptcy Attorney, is Now Offering Free Consultation for All Bankruptcy Cases
2012-02-27
Business bankruptcy filings, such as those associated with Washington Mutual and Eastman Kodak, tend to make front page news. Every day, though, and with far less fanfare, consumers across the country are seeking debt relief through personal bankruptcy. Los Angeles bankruptcy lawyer Hamid Soleimanian is now offering free consultations for all bankruptcy cases.
As many as 1.36 million Americans filed for bankruptcy during 2011, according to the U.S. Bankruptcy Court. In fact, business bankruptcies have fallen by as much as 20 percent, while total filings are down just ...
[1] ... [6712]
[6713]
[6714]
[6715]
[6716]
[6717]
[6718]
[6719]
6720
[6721]
[6722]
[6723]
[6724]
[6725]
[6726]
[6727]
[6728]
... [8810]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.