New algorithm significantly improves imaging for full-body MRIs
2011-05-05
A new study reveals an improved algorithm that can dramatically improve how radiologists capture and interpret full-body MRIs, particularly in the abdominal region.
Motion artifacts in MRIs, such as patient movement, often appear as ghosting artifacts which may obscure clinical information says Dr. Candice Bookwalter, presenting author for the study. "Almost every acquisition during an MR abdominal exam requires a breath hold to limit motion. For example, a routine liver exam includes at least nine breath holds. Even with fast imaging techniques, these breath holds are ...
AllTernative Gym Transforms the Lives of Those With Special Needs
2011-05-05
AllTernative Gym is transforming lives with its state-of-the-art fitness and therapy programs developed specifically for those with special needs. Founded by Certified Fitness Trainer and Expert, Angie Gomez, AllTernative Gym provides Adeli Suit Therapy, Fitness Training and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy.
"As a parent of a child with special needs, I truly understand what parents are looking for in a therapy center. And, I treat each child as if he were my own and each adult as if they were a family member," states Angie Gomez, founder of AllTernative Gym. Angie ...
Sonography complements physical exam in identifying juvenile inflammatory arthritis in children
2011-05-05
Juvenile Inflammatory Arthritis (JIA) is a potentially debilitating childhood disease. Early detection and treatment of active arthritis may avert long term joint damage and disability. Research has shown that sonography with power Doppler can facilitate making assessments in joint activity and sub-clinical disease, according to research being presented at the 2011 American Roentgen Ray Society's annual meeting.
The study, performed at Albert Einstein College of Medicine's Montefiore Medical Center, in Bronx, NY, compares sonography with power Doppler to physical examination ...
Ultrasound combined with pre-operative MRI is cost effective in evaluating rotator cuff tears
2011-05-05
While ultrasound is usually viewed as more cost effective, MRI is most often used to evaluate the rotator cuff. When performing a cost utility analysis, utilizing an ultrasound as the initial imaging test for rotator cuff tear, along with pre-operative MRI to identify alternative and concurrent diagnoses, can be a very effective hybrid imaging strategy, according to research being presented at the 2011 American Roentgen Ray Society's annual meeting.
The study, performed at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, NC and Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, IL, ...
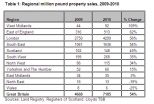
Million Pound Home Sales Rise at Fastest Rate Since 2006
2011-05-05
The number of million pound property sales in 2010 increased at the fastest rate for four years, according to research by Lloyds TSB. There were 7,185 million pound property sales in Great Britain in 2010: 54% higher than in 2009. This is the largest annual increase since 2006 (62%) and suggests a real resurgence at the very top end of the mortgage market. In total, there are now an estimated 184,0001 homes in Britain worth at least one million pounds.
Despite this significant increase, million pound property sales remain 13% below the levels they reached before the ...
Racial disparities still exist in colorectal cancer screening despite increased Medicare coverage
2011-05-05
PHILADELPHIA — Despite expanded Medicare coverage for colorectal cancer screening tests, lower rates still exist among blacks and Hispanics compared to other ethnic groups, according to research published in Cancer, Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Researchers from the University of Texas School of Public Health used data from the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER), a National Cancer Institute database, to determine the prevalence of colorectal cancer screenings among Medicare beneficiaries ...
Study suggests prolonged bottle feeding increases the risk of obesity
2011-05-05
Cincinnati, OH, May 5, 2011 -- Experts agree that obesity prevention should begin before children enter school. But due to a lack of conclusive data, health care providers often have trouble advising parents about which interventions are the most beneficial. A new study soon to be published in The Journal of Pediatrics suggests that limiting prolonged bottle use in children may be an effective way to help prevent obesity.
Dr. Robert Whitaker and Rachel Gooze of the Center for Obesity Research and Education at Temple University, and Dr. Sarah Anderson of The Ohio State ...
America's Oral Health Crisis: Closing the Gap
2011-05-05
This is the point of a new report by the Institute of Medicine (IOM), Advancing Oral Health in America, which underscores a public health crisis that has persisted more than a decade after the U.S. Surgeon General called for aggressively reversing the "silent epidemic" of America's oral health disparity. Many of the most pernicious oral health diseases are highly preventable and treatable.
The IOM study, urging the federal government to launch a new initiative on oral health, aligns with a pioneering community-based dentistry model funded by the Robert Wood ...
"Primitive Instinct" with Gregg Ritz Debuts in July on Outdoor Channel
2011-05-04
Offering amazing wildlife footage and gripping over-the-shoulder hunting scenes, Primitive Instinct transports viewers on location as Gregg gives up the comforts of home to conquer Mother Nature on her terms in places where blisters and backaches are the norm, and going home early is never an option.
Primitive Instinct offers viewers a unique look at the real Gregg Ritz: a man driven by an unwavering desire to pursue big game and big adventure regardless of the conditions. His quest for the world's most prized big game trophies amidst ever present danger, treacherous ...
Give Mom The Gift of Instant Calm With The Heavenly Acupressure Mat
2011-05-04
By simply lying on the Heavenly Acupressure Mat for 20 minutes a day moms can relieve the physical and emotional pains of everyday life.
The Heavenly Acupressure Mat is the perfect gift for mom that keeps on giving.
The Heavenly Mat uses the principles of acupressure to help relieve stress, anxiety, chronic back and neck pain, while at the same time promoting relaxation and an overall sense of well-being.
"Having an acupressure mat is like having your own personal masseuse on hand 24/7," says Benjamin Buadu, President of the Heavenly Acupressure Mat Company. ...
Excitement Builds for 8th Annual AltBuild Expo
2011-05-04
As the excitement builds for the 8th Annual AltBuild Expo at the Santa Monica Civic Center, event organizers have put the finishing touches on a number of Expo details, as well as providing a strong rationale for guests—professionals and homeowners alike—to come and experience the event.
• Over 40 speakers will present on topics as diverse as green building, "De"-construction and urban farming. Speakers include Keynoter architect Bill Worthen; water specialist Russell Ackerman; architect Wally Geer; State Senator Fran Pavley; "organic architect" Eric ...
Mold Inspection - A Safer Way of Ensuring Healthy Life
2011-05-04
Mold is one of the important problems that affect our health. It is often difficult for the homeowner to diagnosis properly the presence of mold because what you see on the surface may be 95% of the problem, or it may be only the tip of the iceberg and what you see may be just 5% of the problem. A Certified mold inspector will have a keen eye for colony growth that may go undetected for years in front of untrained eyes.
Most homeowners are unaware of the symptoms of mold exposure. A few important health problems caused by molds are listed below:
- Sneezing and coughing
- ...
Versatile pH Meter Used in the Cleanest Room in the World
2011-05-04
Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA
The Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft is one of the leading organizations for applied research in Europe. It undertakes application-oriented research of direct utility to private and public enterprise and of wide benefit to society but does not participate in basic research. The customers are industrial or service companies and the German federal and local government. The 57 Fraunhofer Institutes employ more than 15,000 staff at 40 different locations in Germany. The annual research budget totals 1.4 billion Euros. There is very intense ...
Top LA Employment Attorneys Help Secure $85,000 Settlement for Sexual Harassment Victim
2011-05-04
Expert employment and labor law attorneys of Mesriani Law Group, a leading firm in Los Angeles and southern California, have successfully secured settlement of more than $85,000 for a sexual harassment victim.
Records show that the 25-year old victim worked as Assistant Parts Manager for an auto manufacturing company in Calabasas City. According to the victim, she shared an office with one of the supervisors.
Since the day she started work, the victim claimed she was continuously subjected to repeated acts of unwanted sexual harassment from her supervisor. On one ...
Emphasizing Tana Netting's Commitment to Personal Protection and Green Entrepreneurship
2011-05-04
Tana Netting Co., Ltd. launches today the new look of its logo highlighting the company's mission to combine the development and supply of personal protection products with green business acumen. The new logo, maintaining the company's more than 25 year old heritage is an improved reflection of Tana Netting's current unique position in the global health domain.
The same mosquito image that was part of the initial SiamDutch logo and transferred to the Tana Netting logo in 2004 is still prominently present in the new attuned logo. It is projected now on top of a bright ...
Whitetail Properties Introduces Online-Only Farm Real Estate Auction Platform
2011-05-04
Whitetail Properties, a real estate listing and auction business that unites buyers and sellers through its team of farm and ranch land specialists, has just made it easier for those buyers and sellers to do business. Whitetail Properties, a real estate listing and auction business that unites buyers and sellers through its team of farm and ranch land specialists, has just made it easier for those buyers and sellers to do business. Whitetail Properties' new online-only auction platform will offer great convenience to buyers who will be able to bid on tracts of land from ...
Cypherbridge Systems announces the AK200 Design Kit at Embedded Systems Conference:
2011-05-04
Embedded Systems Conference, San Jose, California, May 3, 2011: Cypherbridge Systems today announced the availability of the AK200 Design Kit, providing a turnkey solution for the rapidly growing secure payment transaction market for Point-of-Sale Terminals.
Electric vehicle charging stations and smart parking meters are two recent examples of successful Cypherbridge implementations of the AK200 standards based approach, which eliminates proprietary proxy servers, hosting and expense, resulting in a lower system capital and maintenance cost.
President of Cypherbridge ...
Ulster County's SPCA has been named the May 2011 beneficiary for Rescue Chocolate
2011-05-04
Ulster County's Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (UCSPCA) has been named the May 2011 beneficiary for Rescue Chocolate, the vegan chocolate company which donates 100% of its profits to various animal rescue organizations.
UCSPCA runs an independent no-kill shelter. This means that the homeless animals who find their way into the sanctuary are allowed to live out their natural lives, whether or not they ever get adopted.
In addition to finding adoptive homes for homeless, abused, and neglected animals, the group's mission is to conduct cruelty investigations, ...
INVISTA's CORDURA Brand Business Unveils Chinese Interactive Web Site
2011-05-04
For the past 30 years, INVISTA's CORDURA brand team has set the standard for durable fabrics in the outdoor, workwear and military markets. As part of its effort to achieve greater consumer awareness globally, INVISTA has now launched an interactive Chinese Web site, located at http://cordura.com/sch/index.html.
With the Chinese market demonstrating rapidly growing outdoor and travel segments, the CORDURA brand team is dedicated to expanding the brand's presence and equity in these target segments within the Asia Pacific region.
"The CORDURA brand team is dedicated ...
Altec Bucket Trucks for Heavy-Duty Projects
2011-05-04
As the urban populations expand and the demands for housing, communications, and public services grow, building contractors and government agencies have foreseen the need to purchase more construction equipment and heavy-duty machineries to save on labor costs and promote safer working environments.
Bucket trucks, which have grown in popularity in the last few decades because of the growing complexities of building construction, design, and maintenance, champion the promotion of safety and work efficiency in working areas.
Generally utilized to hoist materials or ...
"Part Of The Moment'' Forever Changing The Way People Communicate With Talk Fusion Video Email
2011-05-04
Solely distributed person-to-person by Independent Associates, Talk Fusion has offered people not only a revolutionary Product, but the chance to live their dreams and achieve financial freedom. Over the last few years, we've helped millions become "Part of the Moment." Talk Fusion's legendary story began with a vision for a revolutionary product and the determination to make it happen.
In 2004, Talk Fusion Founder & CEO, Bob Reina, wanted to email a 10-sec video to friends. America Online said it couldn't be done; Bob believed it could. With the help and ...
Dr. Barbara Becker Holstein Announces The Formation of 'Authors Speaking', Designed To Bring Authors And Readers Together Through Virtual Visits
2011-05-04
Dr. Barbara Becker Holstein, nationally recognized author and positive psychologist and Don McCauley of the Free Publicity Focus Group announced today the formation of 'Authors Speaking', a social site dedicated to bringing authors and readers together.
'Authors Speaking' allows authors to make virtual visits to classrooms, libraries, bookclubs and bookstores through Skype and other forms of technology. Authors Speaking gives authors and publishers the opportunity to upload photos, bios, book covers, video and book trailers. The site also offers discussion forums, segmented ...
Uptown Markham Hits the Mark
2011-05-04
Less than four weeks since its formal launch, the first phase of Times Group Corp.'s stunning Uptown Markham master-planned community - called River Park - is enjoying spectacular sales success with 70 per cent of units sold. Eager purchaser line-ups resulted in 400 of the available 580 units being purchased at an estimated market value of more than $130 million, says Times Group Marketing Director Elmar Busch.
The extraordinary success doesn't surprise Busch, who strategically spearheaded the River Park marketing campaign. "Our original estimate was to reach 60 ...
Lee Enterprises Forms Strategic Alliance with The IMA Financial Group, Inc.
2011-05-04
Biodiesel consulting group, Lee Enterprises Consulting of Little Rock, Ark., is pleased to announce the formation of a strategic alliance with nationally known specialty insurance broker The IMA Financial Group. IMA has assigned Beau Hudson and David B. McKinney of Wichita, Kansas to work with Lee Enterprises Consulting in serving clients' insurance needs. Hudson is a Business Development professional specializing in renewable energy. McKinney pairs with prospects and clients in gathering specific information and proposing necessary coverages, working with insurance companies ...
CloudTran Delivers Capabilities Built on the Rackspace Cloud that Target Hybrid Clouds, Joins Rackspace Cloud Tools Program
2011-05-04
CloudTran, a provider of transaction processing solutions for the cloud, today announced the availability of its products built on top of the Rackspace Cloud, allowing critical business applications to now take advantage of popular cloud computing techniques. In addition, CloudTran has entered into the Rackspace Hosting (NYSE: RAX) Cloud Tools Program. This solution will dramatically reduce operating costs for these applications while providing a growth path as businesses expand operations.
"Cloud computing" allows an application to use the bundled computational ...
[1] ... [7425]
[7426]
[7427]
[7428]
[7429]
[7430]
[7431]
[7432]
7433
[7434]
[7435]
[7436]
[7437]
[7438]
[7439]
[7440]
[7441]
... [8810]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.