Hair styles may contribute to scarring hair loss in African-American women
2011-04-12
Hair grooming practices, such as braids and weaves, as well as inflammation in the form of bacterial infection, may be contributing to the development of scarring hair loss in African American women, according to a report posted online today that will appear in the August print issue of Archives of Dermatology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
"Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA) is a term coined by the North American Hair Research Society to describe a scarring hair loss, centered on the vertex of the scalp, that spreads peripherally," the authors write ...
High levels of vitamin D appear to lower risk of age-related macular degeneration in young women
2011-04-12
High levels of vitamin D in the bloodstream appear to be associated with a decreased risk of developing early age-related macular degeneration among women younger than 75 years, according to a report in the April issue of Archives of Ophthalmology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
"Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a chronic, late-onset disease that results in degeneration of the macula, is the leading cause of adult irreversible vision loss in developed countries," the authors write as background information in the article. "Age-related macular degeneration affects ...
A Cloud Hosting Review Site Helps Businesses Get the Best Cloud Experience - CloudHostingReviewer.com Leads the Way
2011-04-12
The Future of Hosting Lies Not in the Sky but in the Clouds
The terms Cloud Computing and Cloud Hosting may not be very new for anyone related to the field. Experts are of the opinion that these terms define the future of Computer science and technology. In Cloud hosting, a website is not limited to a single server. A cloud hosted site is run on on multiple servers as if they were one server. Access to multiple servers gives nearly unlimited processing power and therefore a better experience.
CloudHostingReviewer.com is a website that offers in-depth reviews of top ...
Study finds physicians recommend different treatments for patients than they choose for themselves
2011-04-12
The act of making a recommendation appears to change the way physicians think regarding medical choices, and they often make different choices for themselves than what they recommend to patients, according to a survey study published in the April 11 issue of Archives of Internal Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
"Patients facing difficult decisions often ask physicians for recommendations," the authors write as background information in the study. "However, little is known regarding the ways that physicians' decisions are influenced by the act of making a recommendation."
Peter ...
Genetic study offers insight into the social lives of bees
2011-04-12
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Most people have trouble telling them apart, but bumble bees, honey bees, stingless bees and solitary bees have home lives that are as different from one another as a monarch's palace is from a hippie commune or a hermit's cabin in the woods. A new study of these bees offers a first look at the genetic underpinnings of their differences in lifestyle.
The study focuses on the evolution of "eusociality," a system of collective living in which most members of a female-centric colony forego their reproductive rights and instead devote themselves to specialized ...
Intense Peru Entices Travelers to Tour Machu Picchu 100 Years After Its Discovery
2011-04-12
Intense Peru, experts in designing unique travel experiences to Peru, recently announced a 10% savings on all Machu Picchu tours in recognition of the 100 year anniversary of the discovery of Lost City of the Incas by American archaeologist Hiram Bingham. Every year an increasing number of travelers come from different parts of the world to admire the Historic Sanctuary of Machu Picchu. Some travelers have little information and some others not only are well prepared but fill their tour guides with enthusiastic comments and questions. And the truth is that no matter how ...
Protein could improve recovery from heart attacks
2011-04-12
Angiogenesis, the development of new blood vessels, is required during embryonic development and wound healing, as well as during disease processes such as tumor growth. The signals that direct angiogensis are incompletely understood, but could represent novel targets for the development of therapies that promote or inhibit this process.
In this paper, Young-Guen Kwon and colleagues, of Yonsei University in Seoul, Korea, investigated the role of two related proteins- DKK1 and DKK2- in angiogenesis. These proteins are known to have similar functions in inhibiting a particular ...
Physicists discover new way to visualize warped space and time
2011-04-12
PASADENA, Calif.—When black holes slam into each other, the surrounding space and time surge and undulate like a heaving sea during a storm. This warping of space and time is so complicated that physicists haven't been able to understand the details of what goes on—until now.
"We've found ways to visualize warped space-time like never before," says Kip Thorne, Feynman Professor of Theoretical Physics, Emeritus, at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech).
By combining theory with computer simulations, Thorne and his colleagues at Caltech, Cornell University, ...
Potato consumption in children's meals leads to higher overall diet quality
2011-04-12
Denver, CO., April 11, 2011 – Research to be presented this week at The Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB) Conference in Washington, D.C., demonstrates that consumption of white potatoes (non-fried) by children does not displace other vegetables from children's meals. In fact, meals that contain white potatoes contain more servings of other vegetables, and are significantly higher in potassium, fiber and vitamin C. Both potassium and fiber were identified as nutrients of concern in the 2010 Dietary Guidelines, released February 2011.
"Potatoes ...
Pistachios deliver weight management support, heart health benefits
2011-04-12
Washington, D.C., April 11, 2011 – In a first-of-its-kind study with nuts, randomized controlled-feeding research conducted by the Agricultural Research Service (ARS) of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) found that fat in pistachios may not be completely absorbed by the body. The findings indicate that pistachios may actually contain fewer calories per serving than originally thought – further validating pistachios as one of the lowest calorie nuts with 160 calories per 30 gram serving (approximately 1 ounce). The study was presented today at the Experimental ...
Glaucoma patients report a wide range of emotional and psychological changes
2011-04-12
Fear of the unknown is one of the greatest issues facing patients with glaucoma - the second leading cause of blindness worldwide after cataracts - according to research in the April issue of the Journal of Advanced Nursing. People also worry about how the eye disease, which can be hereditary, will affect other members of their family.
Researchers spoke to 24 people with glaucoma, which can lead to severe restriction of the visual field and irreversible blindness if it is not detected early enough and successfully treated.
It's estimated that 4.5 million people worldwide ...
Light, chemistry, action -- a new technique to target skin cancers?
2011-04-12
Targeted photodynamic therapy can completely eradicate some models of cancer, according to the latest research by UK and Swiss scientists, published in the current issue of the British Journal of Cancer.
The team – including researchers from the University of Hull and ETH Zurich – linked light-sensitive molecules with antibodies that target tumour blood vessels. When irradiated with light, the molecules create particles known as reactive oxygen species, which in high numbers cause irreparable damage to cells.
By ensuring the light-sensitive molecules were targeted at ...
DirectRooms.com - Performances From International Cultures are Held in Aberdeen
2011-04-12
People that want to learn about the customs of different nations can head to the Aberdeen International Fun Day to see all sorts of activities. Performers will be giving an insight into the music and dance of each of their representative countries and this will include dances from Russia, India, Sweden and China. Attendees can see firsthand the steps of Bhangra dances, take part in a Tai Chi class or even listen to the melodic voices or a Gaelic choir.
The performances are designed to bridge the gap between communities and for people to learn about each other's cultures ...
How do we fight the war against cyber terrorism?
2011-04-12
The Internet has no borders, no universal legislation, and although highly social and distributed is not represented by cooperation across the globe. Given those characteristics how might nations make their plans for counter terrorism in cyberspace as active online as they are in the everyday world? A collaboration between researchers in the US and Iran hoped to address that issue and its findings are published this month in the International Journal of Internet Technology and Secured Transactions.
Incidence of online crime has grown considerably in recent years, with ...
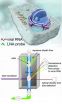
New technique tracks viral infections, aids development of antiviral drugs
2011-04-12
WASHINGTON -- Scientists at the Naval Research Laboratory Center for Bio-Molecular Science and Engineering have developed a method to detect the presence of viruses in cells and to study their growth. Targeting a virus that has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic makeup, the new technique referred to as locked nucleic acid (LNA) flow cytometry-fluorescence in situ hybridization (flow-FISH), involves the binding of an LNA probe to viral RNA.
While individual parts of the technique have been developed previously, Drs. Kelly Robertson and Eddie Chang, in collaboration ...
Silver Lining for Pan American Metals of Miami in Miami Beach: Helping You to Find Your Silver Lining
2011-04-12
Pan American Metals of Miami sees the silver lining as the dollar is crashing. Precious metals of gold, silver, paladium and platinum.
You hear stories of people making money and wonder, why can't I get a break like that? Well, this is the break. You now know something that most people won't find out until its headline news... and by that time it's too late. Let's pick up so many oz. positions.
You see finding a bag of money on the train is only part of winning... you still have to pick it up and carry it home... don't you? So what I'm saying is it is not that easy ...
Tufts biologists find another clue to the origins of degenerative diseases
2011-04-12
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass. -- For years, researchers in genome stability have observed that several neurodegenerative diseases—including Huntington's disease—are associated with cell-killing proteins that are created during expansion of a CAG/CTG trinucleotide repeat.
In research published in the March 17 online edition of the journal PLoS Genetics, Tufts University biologist Catherine Freudenreich, and then-graduate student Rangapriya Sundararajan show that cell death in yeast can also result from the process by which the cell repairs damage that occurs within a repeated ...
Connect, Collaborate, Inform and Get Business at HIA-LI 23rd Annual Business Trade Show & Conference
2011-04-12
The largest one-day Business to Business Trade Show on Long Island is only a few short weeks away. The event, hosted by HIA-LI, the recognized voice for business on Long Island, in partnership with the Long Island Forum for Technology (LIFT) and Suffolk County Community College, will feature prominent local and regional speakers, nearly 400 exhibitors from the business, technology, professional, educational and governmental segments, and an anticipated 4,000 attendees. The event is scheduled for Thursday, May 26 from 9 AM to 4 PM, at the Suffolk County Community College ...
Fatigue and sleep woes worsen neurocognitive problems in childhood cancer survivors
2011-04-12
Fatigue and sleep problems dramatically reduce the thinking and reasoning abilities of adults who survived childhood cancer, according to new research from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Researchers hope the findings will lead to new strategies for improved neurocognitive functioning in this growing population. The work was led by St. Jude Children's Research Hospital investigators.
This is the first study to show that childhood cancer survivors are particularly vulnerable to impaired memory, emotional control, organization and related neurocognitive skills due ...
Mechanism for esophageal cancer uncovered
2011-04-12
A gene thought to be associated with cancer development can be a tumor suppressor gene in mice, researchers have discovered. Understanding which genes are involved in spreading cancer could lead to future therapies.
"For cancer to spread, some genes are activated, while others that would prevent cancer growth are prevented from doing their jobs. The cancer research community has thought that the gene p120, falls into the latter category," said Douglas Stairs, Ph.D., assistant professor of pathology, who completed this research at University of Pennsylvania and is now ...
Mechanism for invasion of tumorous cells discovered by Hebrew University researchers
2011-04-12
Jerusalem, April 11, 2011 – Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have discovered a previously unknown mechanism whereby tumor cells invade normal tissues, spreading cancer through various organs.
The ability of tumor cells to invade adjacent structures is a prerequisite for metastasis and distinguishes malignant tumors from benign ones. Thus, understanding the mechanisms that drive malignant cells to invade and a possible avenue for halting that mechanism could have tremendous potential for enhancing early detection of malignant cells and for therapeutic ...
Umbilical cord blood-derived stem cells studied for lupus therapy
2011-04-12
Tampa, Fla. (April 11, 2011) – Human umbilical cord blood-derived mensenchymal stem cells (uMSCs) have been found to offer benefits for treating lupus nephritis (LN) when transplanted into mouse models of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). SLE is an autoimmune disease with "myriad immune system aberrations" characterized by diverse clinical conditions, including LN, a leading cause of morbidity and mortality for patients with SLE.
The beneficial results were reported in a study by Taiwanese researchers published in the current issue of Cell Transplantation (20:2), freely ...
Superior Lamp, Inc. is Seriously Committed to Reducing Energy Consumption
2011-04-12
Each day we are making conscious and unconscious decisions that greatly affect how much energy that we use and, therefore, how much energy is required to be produced. The cost has never been higher.
The effects of our energy consumption are all around us. Just take a look at any headline in the news today. Many are energy-driven. Each time a middle eastern country has a crisis our stock market shudders at the possibility that oil production may drop off by two or three percent. Every time a storm rises in the Gulf of Mexico, or a bill in Congress on deep water drilling ...
Research digs deep into the fracking controversy
2011-04-12
The turmoil in oil-producing nations is triggering turmoil at home, as rising oil prices force Americans to pay more at the pump. Meanwhile, there's a growing industry that's promising jobs and access to cheaper energy resources on American soil, but it's not without its controversy. Deborah Kittner, a University of Cincinnati doctoral student in geography, presents, "What's the Fracking Problem? Extraction Industry's Neglect of the Locals in the Pennsylvania Marcellus Region," at the annual meeting of the Association of American Geographers. Kittner will be presenting ...
In it to win it?
2011-04-12
Pathological gambling addiction is surprisingly common in the U.S., afflicting as many as 3.4% of all adults. Like other addictions, it is highly disabling both to the individual and to society, often leading to suicide, job loss, and criminal behavior. It affects more men than women and can become worse over time.
Scientists have found that a wide range of drugs can be effective for treating this disorder in the short term, including Naltrexone, used to treat alcohol addiction. Now, psychiatrist Prof. Pinhas Dannon of Tel Aviv University's Sackler Faculty of Medicine ...
[1] ... [7553]
[7554]
[7555]
[7556]
[7557]
[7558]
[7559]
[7560]
7561
[7562]
[7563]
[7564]
[7565]
[7566]
[7567]
[7568]
[7569]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.