Long-sought fossil mammal with transitional middle ear found
2011-04-14
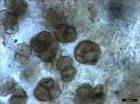
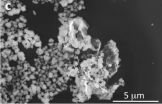
Paleontologists from the American Museum of Natural History and the Chinese Academy of Sciences announce the discovery of Liaoconodon hui, a complete fossil mammal from the Mesozoic found in China that includes the long-sought transitional middle ear. The specimen shows the bones associated with hearing in mammals— the malleus, incus, and ectotympanic— decoupled from the lower jaw, as had been predicted, but were held in place by an ossified cartilage that rested in a groove on the lower jaw. The new research, published in Nature this week, also suggests that the middle ...
City of Gold Continues to Boost Weekend Free Bingo Specials at City Bingo
2011-04-14
Free bingo site City Bingo has stepped up its devotion to providing its players with an array of weekend special and promotions. The metropolitan bingo site already offers 70% bonuses on Saturdays and 80% bonuses on Sundays and has now added The Bingo Avenue Tournament.
Players depositing at weekends had already been enjoying the aforementioned bonuses on their deposits and the introduction of their latest game is likely to keep the site buzzing. The new feature involves players picking numbers that they don't think will come up in a draw, they can swap any points accrued ...
An advance for a newborn vaccine approach
2011-04-14
Infectious disease is a huge cause of death globally, and is a particular threat to newborns whose immune systems respond poorly to most vaccines. A new approach developed at Children's Hospital Boston, using an adjuvant (an agent to stimulate the immune system) along with the vaccine, shows promise in a study of blood from Gambian infants. Results will appear in the open-access journal PLoS ONE on April 13.
The ability to immunize newborns would close their window of vulnerability to serious infections during the first months of life, such as respiratory syncytial ...
Understanding Your Breast Reconstruction Options: Autologous Tissue
2011-04-14
If you have been diagnosed with breast cancer that requires surgery, the time to consider reconstruction options is now, even before you schedule your mastectomy or lumpectomy. Because the type of mastectomy procedure you receive can have a significant impact on your reconstruction options, failing to consider your options early can limit them later.
Getting breast reconstruction is optional, it is not required, and some women find that life without breasts is freeing. However, if you would prefer to maintain your feminine appearance, breast reconstruction is a far ...
Biological arms races in birds result in sophisticated defenses against cuckoos
2011-04-14
VIDEO:
The film clip shows a nest of the most frequent host of the cuckoo finch, the tawny-flanked prinia, which has an extravagantly diverse range of eggs. The prinia parent has...
Click here for more information.
New research reveals how biological arms races between cuckoos and host birds can escalate into a competition between the host evolving new, unique egg patterns (or 'signatures') and the parasite new forgeries.
Brood parasitic birds such as cuckoos lay eggs ...
What Should I Do After a Car Accident in Georgia?
2011-04-14
The moments immediately following a serious auto accident can be overwhelming and scary, especially if someone suffers serious personal injury or death. Oftentimes, people are in a state of shock and not thinking clearly following a horrific car accident, but the moments immediately following the accident are critical to the outcome of a personal injury claim that may be filed later.
For this reason, even though you will be overwhelmed and frightened, it is important that you take certain steps after a car accident and never admit fault at the scene of the accident ...
Plasma nanoscience needed for green energy revolution
2011-04-14
A step change in research relating to plasma nanoscience is needed for the world to overcome the challenge of sufficient energy creation and storage, says a leading scientist from CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering and the University of Sydney, Australia.
Professor Kostya (Ken) Ostrikov of the Plasma Nanoscience Centre Australia, CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering, has highlighted, in IOP Publishing's Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, the unique potential of plasma nanoscience to control energy and matter at fundamental levels to produce cost-effective, ...
Correcting Severe Dental Problems
2011-04-14
The modern cosmetic dentist is increasingly able to correct severe dental problems more comfortably and in less time. Treatment options are available for everything from repairing or replacing a tooth to realigning your jaw. It is important to pay attention to any discomfort as it may be a sign of an undiscovered issue.
Preventing and Treating Tooth Erosion
Frequent visits to your dentist combined with healthy oral hygiene at home are the best preventions for dental problems. Serious infection can occur from a damaged tooth that goes undetected. While teeth naturally ...
Stillbirths: The invisible public health problem
2011-04-14
Some 2.6 million third trimester stillbirths worldwide occur every year, according to the first comprehensive set of stillbirth estimates, published today within a special series in the medical journal The Lancet.
Every day more than 7,300 babies are stillborn. A death occurs just when parents expect to welcome a new life.
Ninety-eight percent of stillbirths occur in low and middle-income countries. Wealthier nations are not immune with 1 in 200 pregnancies resulting in a stillbirth - two thirds occurring in the last trimester of pregnancy, a rate that has stagnated ...
Child Custody and Child Support Considerations
2011-04-14
Parenting time and child custody are necessary considerations in divorce agreements where children are involved. This is a particularly difficult process and can result in lengthy legal battles. Ultimately, the courts will determine what is in the best interest of the child. This may require expert testimony from a Child and Family Investigator appointed by the court, or from friends and relatives of the parents and children.
Considerations in Custody Battles
The court will consider several factors when determining the best interest of a child. This can include things ...
Loch fossils show life harnessed sun and sex early on
2011-04-14
Remote lochs along the west coast of Scotland are turning up new evidence about the origins of life on land.
A team of scientists exploring rocks around Loch Torridon have discovered the remarkably preserved remains of organisms that once lived on the bottom of ancient lake beds as long as a billion (1000 million) years ago.
These fossils illuminate a key moment in the history of evolution when life made the leap from tiny, simple bacterial (prokaryote) cells towards larger, more complex (eukaryotic) cells which would make photosynthesis and sexual reproduction possible.
The ...
Experimental treatment for COPD in development
2011-04-14
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health have developed a non-steroid based strategy for improving the lung's innate immune defense and decreasing inflammation that can be a problem for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In a study published in the April 13 edition of the journal Science Translational Medicine, the Johns Hopkins researchers targeted the Nrf2 pathway using sulforaphane, an ingredient that is present in broccoli in a precursor form, to enhance the Nrf2 pathway in the lung that mediates the uptake of bacteria. ...
Rules of the Road for California Motorcyclists
2011-04-14
California's temperate climate, long stretches of highway and sunny days make it a motorcyclist's dream. Riders can take to the streets all year long, feeling the wind in their hair and enjoying the freedom that can only be felt on a bike. Of course, as gas prices and temperatures continue to climb, more and more motorcycles will be on the road. Before summer riding season gets in full swing, though, it is important for California motorcyclists to know the rules of the road, including two laws unique to motorcycles.
What Is Different for Motorcycles Versus Passenger ...
Higher CCSVI prevalence confirmed in MS, but meaning of findings remains unclear
2011-04-14
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- A just released study on the relationship between multiple sclerosis (MS) and chronic cerebral venous insufficiency (CCSVI), a narrowing of the extracranial veins that restricts the normal outflow of blood from the brain, found that CCSVI may be a result of MS, not a cause.
The study, conducted by University at Buffalo researchers, appears in the current issue of Neurology, the journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Robert Zivadinov, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology in the UB School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences and president of ...
Your flaws are my pain
2011-04-14
Today, there is increasing exposure of individuals to a public audience. Television shows and the internet provide platforms for this and, at times, allow observing others' flaws and norm transgressions. Regardless of whether the person observed realizes their flaw or not, observers in the audience experience vicarious embarrassment.
For the first time, such vicarious embarrassment experiences as well as their neural basis have been investigated in research published in the open-access, peer-reviewed journal PLoS ONE. The research was led by Sören Krach and Frieder M. ...
Study: To students, music piracy and shoplifting are worlds apart
2011-04-14
What's the difference between stealing a CD from a music store and ripping off music online? The music industry and law enforcers say that there is none: Theft is theft, whether it's physical or digital.
College students participating in a newly published study, however, said that while they were unlikely to shoplift and viewed that behavior as immoral, they were not exactly motivated to follow the laws governing digital music piracy -- a finding that underscores the difficulties of enforcing such laws and to find new ways to discourage the theft of all types of digital ...
New fracture resistance mechanisms provided by graphene
2011-04-14
TUCSON, Ariz. and TROY, N.Y. (April 13, 2011) -- A team of researchers from the University of Arizona and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have increased the toughness of ceramic composites by using graphene reinforcements that enable new fracture resistance mechanisms in the ceramic.
The research, lead by Assistant Professor Erica L. Corral from the Materials Science and Engineering Department at the University of Arizona in Tucson, and Professor Nikhil Koratkar from the Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute ...
Sharing the Road -- Lane Sharing and Lane Splitting in Southern California
2011-04-14
Considering the long expanses of picturesque roads and highways in Southern California, it's no surprise that California streets, roads and highways beckon to motorcyclists and their passengers. But the same roads and highways can be gruelish during heavy traffic.
To get through traffic jams more quickly, some motorcyclists lane share -- that is, they use the same lane as cars and trucks that are stopped in traffic. Others bikers sometimes resort to lane splitting -- driving between traffic lanes to pass stopped vehicles.
Lane splitting and lane sharing by bikers ...
Supreme Court Okays Retaliation Suit by Close Relations under Title VII
2011-04-14
The U.S. Supreme Court recently reinstated a retaliation case where a woman's fiance was fired after she had filed a discrimination claim with the EEOC. The Court had to decide if the firing was retaliation and if the fiance was permitted to file a case under Title VII. The Justices answered yes to both questions.
The Retaliation Claim
The Supreme Court had to analyze the facts to determine if the firing was, in fact, retaliation.
The Court described the facts as follows: "Until 2003, both petitioner Eric Thompson and his fiancee, Miriam Regalado, were employees ...
Queen's researchers pioneer needle-free test for premature babies
2011-04-14
Scientists at Queen's University Belfast have pioneered a new needle-free test to take the sting out of medicine testing in premature babies. The research will not only lead to greater accuracy in prescribing, but will also significantly reduce the trauma of such tests for newborn infants and their families.
In the first published research project worldwide on this new approach to testing medicines in children, the findings were announced in leading US medical journal Pediatrics.
The study, which involves the use of blood spots obtained from a simple heel-prick, took ...
Experts at Experimental Biology examine dietary cholesterol, egg intake and heart disease risk
2011-04-14
Park Ridge, IL (April 13, 2011) – This week at Experimental Biology (EB) 2011 in Washington, D.C., long-standing beliefs about dietary cholesterol intake and cardiovascular disease risk were examined as part of a scientific symposium and a variety of poster presentations. Experts from leading institutions discussed existing and emerging science regarding dietary cholesterol intake and its association with heart disease risk, dispelling some commonly heard myths.
Established research has shown that saturated fat intake may be more likely to raise a person's blood cholesterol ...
Low doses of penta-brominated diphenyl ether flame retardants alter gene expression
2011-04-14
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are chemicals that have been widely used as flame retardants and are now classified as persistent organic pollutants. Health concerns in humans have arisen based primarily on studies with laboratory animals exposed to high levels of PBDEs. Three commercial mixtures of PBDEs have been manufactured in or imported into the United States which include penta-, octa-, and deca-brominated diphenyl ethers (BDEs). Of particular concern has been the penta-BDEs used primarily in foams in computers, televisions, mattresses, pillows, carpets, ...
HIV rate in SF could be cut sharply with expanded treatment, study predicts
2011-04-14
If HIV-infected adults in San Francisco began taking antiretroviral treatments as soon as they were diagnosed, the rate of new HIV infections among men who have sex with men would be cut by almost 6o percent over five years, according to a new study by scientists at the University of California, San Francisco.
In San Francisco, men who have sex with men comprise more than three quarters of the population of people living with HIV and more than three quarters of new HIV infections occur in this group. The study looked specifically at the impact of treatment upon rates ...
Bankruptcy Filings Rise As Stigma Falls
2011-04-14
The statistic is breathtaking: "More Americans filed for bankruptcy last year in the United States than in the entire decade of the 1960s," reports an article on MSN Money. The slowness of the recovery combined with the mountain of debt has put more people in the position of filing for bankruptcy than ever.
With the recession, more people have had problems paying their bills, in part, due to the fact they have more debt. From 1990 to 2003, credit card lending increased from $173 to $683 billion. Much of the lending was for subprime credit cards, which grew even faster ...
Children victims of most eye injuries from aerosols
2011-04-14
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Children were the victims in more than half of the emergency room visits for eye injuries related to aerosol cans between 1997 and 2009, according to a new study by researchers at Brown University. More could be done, they said, to prevent injury from the pressurized and often harsh chemical contents of the common products.
The youngest children, ages 0 to 4, were the most likely to be hurt with an estimated 2,830 emergency room visits during the study timeframe, according to the study published in advance online March 30 in the American ...
[1] ... [7560]
[7561]
[7562]
[7563]
[7564]
[7565]
[7566]
[7567]
7568
[7569]
[7570]
[7571]
[7572]
[7573]
[7574]
[7575]
[7576]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.