Texas Accounting Chair Steven Kachelmeier garners coveted award for scholarship
2024-10-22
Texas Accounting Chair Steven Kachelmeier Garners Coveted Award for Scholarship
AUSTIN, Texas — The American Accounting Association (AAA) presented its Lifetime Achievement Award for Behavioral Accounting Research to Steven Kachelmeier, a professor and chair of the Department of Accounting at The University of Texas McCombs School of Business. Kachelmeier, the Thomas O. Hicks Endowed Chair in Business, accepted this prestigious award during the weekend at the association’s 2024 Accounting ...
CABHI launches funding program that ignites innovation to advance healthy aging
2024-10-22
TORONTO, Oct. 22, 2024 – Today, the Centre for Aging + Brain Health Innovation (CABHI), powered by Baycrest launched Ignite, its new funding program to support Canadian innovators designing solutions for older persons. As Canada’s aging population rapidly grows – with nearly 20 per cent of people above the age of 65 – so too will the need for innovations that enhance the lives of older persons, including those impacted by dementia.
Canadian early-stage innovators – including researchers, point-of-care staff, and companies – are developing ...
A fully automated AI-based system for assessing IVF embryo quality
2024-10-22
A new artificial intelligence-based system can accurately assess the chromosomal status of in vitro-fertilized (IVF) embryos using only time-lapse video images of the embryos and maternal age, according to a study from investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The new system, called "BELA,” and described in a paper published Sept. 5 in Nature Communications, is the team’s latest AI-based platform for assessing whether an embryo has a normal (euploid) or abnormal (aneuploid) number of chromosomes—a key determinant of IVF success. Unlike prior AI-based approaches, BELA does not need to consider embryologists' subjective assessments of embryos. ...
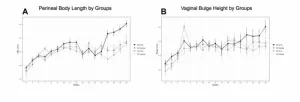
Senolytics dasatinib and quercetin for prevention of pelvic organ prolapse in mice
2024-10-22
“This study represents one of the first to evaluate the impact of senolytic agents D+Q on the clinical development of pelvic organ prolapse and expression of proteins associated with cellular senescence in a mouse model.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 22, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 19 on September 26, 2024, entitled, “Use of the senolytics dasatinib and quercetin for prevention of pelvic organ prolapse in a mouse animal model.”
Pelvic organ prolapse is a common condition among women ...
UCLA efforts to provide prostate cancer treatment in the community gets $6 million boost
2024-10-22
The UCLA Urology department has been awarded $6 million from the California Department of Health Care Services to continue providing vital care and critical services to underinsured and uninsured Californians diagnosed with prostate cancer.
For the next two years, the additional funding will support the 23-year-old IMPACT program—which stands for Improving Access, Counseling, and Treatment for Californians with Prostate Cancer—and extend the program’s reach and duration, ensuring continued support for California’s most vulnerable populations.
Led ...
Study asks: Can cell phone signals help land a plane?
2024-10-22
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Dangling from a weather balloon 80,000 feet above New Mexico, a pair of antennas sticks out from a Styrofoam cooler. From that height, the blackness of space presses against Earth’s blue skies. But the antennas are not captivated by the breathtaking view. Instead, they listen for signals that could make air travel safer.
Researchers from Sandia National Laboratories and Ohio State University are taking experimental navigation technology to the skies, pioneering a backup system to keep an airplane on course when it cannot rely on global positioning system satellites.
More than 15 miles below the floating cooler, cell phone ...
Artificial intelligence is creating a new way of thinking, an external thought process outside of our minds
2024-10-22
The interaction between humans and artificial intelligence is shaping a new thinking system, a new cognitive scheme, external to the human mind, but capable of enhancing its cognitive abilities. This is called System 0, which operates alongside the two models of human thought: System 1, characterized by intuitive, fast, and automatic thinking, and System 2, a more analytical and reflective type of thinking. However, System 0 introduces an additional level of complexity, radically altering the cognitive landscape in which ...
Reaction conditions tune catalytic selectivity
2024-10-22
UPTON, N.Y. — Chemists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have developed a new theoretical framework for more accurately predicting the behavior of catalysts. These collections of atoms lower the energy needed for countless chemical reactions. The study reveals how conditions such as temperature and pressure can change a catalyst’s structure, efficiency, and even the products it makes. The findings are published in the journal Chem Catalysis.
“Our results highlight the significant impact ...
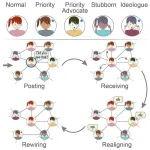
Verified users on social media networks drive polarization and the formation of echo chambers
2024-10-22
When X (formerly Twitter) changed its verification system in 2022, many foresaw its potential to impact the spread of political opinions on the platform. In a modeling study publishing October 22 in the Cell Press journal iScience, researchers show that having verified users whose posts are prioritized by the platform’s algorithms can result in increased polarization and trigger the formation of echo chambers. Because X’s new verification system allows almost anybody to become verified, this side effect could be taken advantage of by users wishing to manipulate others’ opinions, the researchers say.
“Our findings confirm ...
Get a grip: The best thumb position for disc launch speed and spin rate
2024-10-22
WASHINGTON, Oct. 22, 2024 – Disc golf is a sport growing in popularity, but there hasn’t been much research into the best techniques – until now.
Researcher Zachary Lindsey and his team studied professional and amateur disc golf players in Georgia to analyze the effect of thumb grip on disc-throwing.
“Participants were eager and excited to engage in the study, as there is clearly a thirst for scientific evidence and data to drive progress in the sport so that disc golf enthusiasts can improve their game in recreational and competitive contexts,” ...
Maternal eating disorders, BMI, and offspring psychiatric diagnoses
2024-10-22
About The Study: In this population-based cohort study including 392,000 mothers and 649,000 offspring, offspring from mothers with an eating disorder history or pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI) outside normal weight were at higher risk of psychiatric disorders. The results differed somewhat between the 2 exposures with regard to which offspring diagnoses had associations, and effect sizes were typically larger for maternal eating disorders vs BMI. These findings suggest a need to consider these 2 exposures clinically to help prevent offspring mental illness.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ida A. K. Nilsson, PhD, email ida.nilsson@ki.se.
To ...
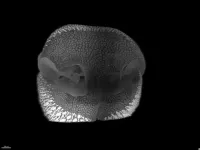
Geometric mechanics shape the dog's nose
2024-10-22
The noses of many mammals, such as dogs, ferrets and cows, feature grooves forming a multitude of polygons. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has analyzed in detail how these patterns form in the embryo using 3D imaging techniques and computer simulations. The researchers discovered that differential growth of the skin tissue layers leads to the formation of domes, which are mechanically supported by the underlying blood vessels. This work describes for the first time this morphogenetic process, which could help explain the formation of other biological structures ...
‘Visual clutter’ alters information flow in the brain
2024-10-22
New Haven, Conn. — Whether we’re staring at our phones, the page of a book, or the person across the table, the objects of our focus never stand in isolation; there are always other objects or people in our field of vision. How that visual “clutter” affects visual processing in the brain, however, is not well understood.
In a new study published Oct. 22 in the journal Neuron, Yale researchers show that this clutter alters how information flows in the brain, as does the precise location of that clutter within the wider field of vision. The findings ...
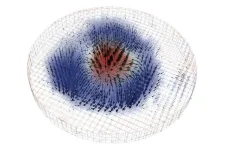
Researchers succeed in taking 3D x-ray images of a skyrmion
2024-10-22
A difficult-to-describe nanoscale object called the magnetic skyrmion might one day yield new microelectronic devices that can do much more — for example, massive data storage — all while consuming much less power.
But researchers need a more detailed understanding of skyrmions if they are ever to be used reliably in computational devices, including quantum computers. Peter Fischer, a senior researcher at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley ...
MRI can save rectal cancer patients from surgery, study suggests
2024-10-22
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can spare many patients with rectal cancer from invasive surgery that can carry lifelong side effects, new research indicates.
The findings, from UVA Cancer Center’s Arun Krishnaraj, MD, MPH, and collaborators, indicate that MRI can predict patient outcomes and the risk of the tumor reccurring or spreading for patients who have undergone chemotherapy and radiation.
That information could be extremely useful in determining the best course of treatment and deciding whether a patient can ...
Fyodor Urnov on clinical crisis in CRISPR genome editing
2024-10-22
New Rochelle, NY, October 18, 2024—An invited Guest Editorial entitled “Give Cas a Chance,” by Fyodor Urnov, PhD, Director of Technology & Translation at the Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI), anchors the October 2024 special issue of The CRISPR Journal on “CRISPR Trials.”
As guest editor of the special issue, Dr. Urnov has penned an extraordinary editorial that emphatically defines the magnitude of the crisis in the genome editing arena and offers a path forward. The inherently programmable nature of CRISPR gene editing that makes it ...
People with type 2 diabetes who eat low-carb may be able to discontinue medication
2024-10-22
WASHINGTON—Adults with type 2 diabetes on a low-carbohydrate diet may see benefits to their beta-cell function allowing them to better manage their disease and possibly discontinue medication, according to new research published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Beta-cells are endocrine cells in the pancreas that produce and release insulin, the hormone that controls blood sugar levels.
More than 38 million Americans have diabetes, and over 90% of them have ...
Air pollution linked to having a peanut allergy during childhood
2024-10-22
Exposure to higher levels of air pollution as a baby is linked to having a peanut allergy throughout childhood, according to a new study. And policies aimed at tackling poor air quality could potentially reduce the prevalence and persistence of peanut allergies, it stated.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and the University of Melbourne, found being exposed to higher levels of air pollution from infancy was associated with increased odds of developing a peanut allergy and having the allergy persist across the first 10 years of life. However, the same association was not seen for egg allergy or eczema.
Published ...
Dangers of the metaverse and VR for US youth revealed in new research
2024-10-22
The metaverse, a space where the lines between physical and digital realities blur, is rising among younger populations. As of March, 33% of teens own a virtual reality (VR) device and 13% use it weekly.
With the metaverse offering richer emotional experiences, youth may be particularly vulnerable to significant harm in these immersive spaces, underscoring the need to explore potential risks.
Unfortunately, research of online victimization in the metaverse is sorely lacking. A new study by Florida Atlantic University, in collaboration with the University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire, is one of the first to examine the ...
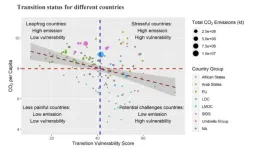
A national indicator for a just energy transition
2024-10-22
The Energy Transition Vulnerability Index (ETVI) quantifies the vulnerability of nations to adverse impacts of transitioning away from fossil fuels. The COP28 agreement has called for all countries to wind down use of fossil fuels to combat climate change—but the agreement stipulates that these transitions should not disproportionately harm historically marginalized and vulnerable stakeholders. Xunpeng Shi and colleagues create a method of quantifying energy transition vulnerability for 135 countries from 2010 to 2020. The indicator focuses on exposure—which captures the magnitude of the changes required—, ...
Cognitive effort whets the appetite for reward
2024-10-22
Mental fatigue may make rewards more desirable, according to a study in rats and humans. Exerting cognitive effort has been linked with making unhealthy choices. In the past, the link has been explained via a weaking of inhibitory control or will power. Marcello Solinas and colleagues explore the possibility that cognitive effort may also make unhealthy choices more tempting by increasing the perceived reward. Rats who completed a cognitively demanding task self-administered more cocaine than rats who did not complete a cognitive demanding task—or rats who were allowed ...
European funders and organizations partner to promote sustainable research
2024-10-22
A significant step forwards in changing research practices towards sustainability has been taken with the publication of the Heidelberg Agreement on Environmental Sustainability in Research Funding. The agreement provides a framework for research funders to play an active role and incentivize sustainable practices in research. It outlines principles for transitioning to a more sustainable research system and practical recommendations on how to implement sustainability in funding schemes.
A key focus of the Heidelberg Agreement is to ensure that research funders take a proactive approach to promoting sustainability in scientific ...
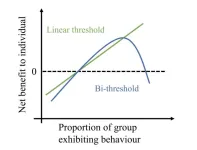
A model for the decline of trends, fads, and information sharing
2024-10-22
A model of human behavior finds that people will share information if enough—but not too many—of their contacts do so. Humans are social creatures, and many behaviors and beliefs can spread from person to person. Understanding the dynamics of behavioral diffusion can help encourage healthy or sustainable behaviors or stop the spread of misinformation. Linear threshold models assume that people will adopt a behavior when the number of their social contacts that have done so passes a threshold. Pouria Ramazi and colleagues propose an addition to the model, ...
Plastic mulch is contaminating agricultural fields
2024-10-22
Using plastic sheets for weed control, even under current best management practices, pollutes soil with macro- and micro-plastics and negatively affect critical soil functions, according to a study. The United Nations considers soil plastic contamination an environmental health and food security threat. Around the world, over 25 million acres of farmland is seasonally covered with opaque plastic films used as “mulch” to prevent weeds, retain moisture, and warm soil—a practice known ...
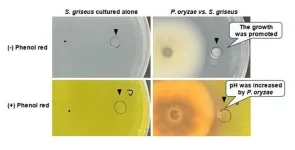
Scientists discover how fungi interact with soil actinomycetes
2024-10-22
In the world of agriculture, rice is a staple food for more than half of the global population, making its cultivation crucial for food security. However, the rice blast fungus Pyricularia oryzae (syn. Magnaporthe oryzae) poses a significant threat to rice crops, causing extensive damage and leading to substantial yield losses. Traditional methods of controlling this pathogen often rely on chemical fungicides, which can have detrimental environmental impacts and contribute to the development of resistant strains. Therefore, researchers are increasingly exploring alternative strategies that leverage natural ...
[1] ... [860]
[861]
[862]
[863]
[864]
[865]
[866]
[867]
868
[869]
[870]
[871]
[872]
[873]
[874]
[875]
[876]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.