Advanced liver fibrosis predicts liver outcomes in biopsy-proven metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
2024-10-25
Background and Aims
Data regarding risk factors and long-term outcomes of U.S. patients with biopsy-proven metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) are limited. This study aimed to investigate the role of clinical and histologic risk factors on long-term outcomes in patients with MASLD.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study of 451 adults with biopsy-proven MASLD was conducted at a U.S. academic hospital from 2012 to 2020. An experienced pathologist evaluated the index liver biopsy. Patients with a prior liver transplant or alternative etiologies of chronic liver disease were excluded. The duration ...
A new spectroscopy reveals water’s quantum secrets
2024-10-25
Water is synonymous with life, but the dynamic, multifaceted interaction that brings H2O molecules together – the hydrogen bond – remains mysterious. Hydrogen bonds result when hydrogen and oxygen atoms between water molecules interact, sharing electronic charge in the process. This charge-sharing is a key feature of the three-dimensional ‘H-bond’ network that gives liquid water its unique properties, but quantum phenomena at the heart of such networks have thus far been understood only through theoretical simulations.
Now, researchers led by Sylvie Roke, head of the Laboratory for Fundamental BioPhotonics in EPFL’s School of Engineering, ...
Sliver of cool surface water helps the ocean absorb more carbon
2024-10-25
Subtle temperature differences at the ocean surface allow more carbon dioxide (CO₂) to be absorbed, new research shows.
Scientists studied the “ocean skin” – a sliver less than 2 mm deep at the ocean surface that is fractionally cooler than the rest.
Theoretical and lab work have suggested this temperature difference should increase the amount of CO₂ absorbed by the ocean – but this had never been successfully observed at sea before.
The new study – led by researchers from the University of Exeter’s Penryn Campus in Cornwall – used precision measurements to confirm that the ...
Study: Invasive silver carp reduce movement in Chicago-area water
2024-10-25
URBANA, Ill. — Invasive silver carp have been spreading throughout the Mississippi River Basin since their introduction a half-century ago. Yet, try as they might, the fish have not advanced beyond a particular stretch of the Illinois River north of Kankakee. Research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign shows the fish are likely avoiding contaminants from the Chicago Area Waterway, which flows south before petering out around Kankakee.
A new study, published today in Scientific Reports, shows silver carp change their behavior and metabolism when introduced to water from the Illinois River north of Kankakee, representing Chicago-area water.
“When animals ...
A lung pathogen’s dilemma: infect or resist antibiotics?
2024-10-25
Imagine trying to settle into a new home while constantly being attacked. That’s what the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa faces when it infects the lungs, and it can’t both spread and protect itself from antibiotics at the same time. Nonetheless, it’s one of the top culprits in hospital-acquired infections and it’s notorious for causing long-lasting, antibiotic-resistant infections, causing damage especially in people with lung diseases like cystic fibrosis, COPD, or bronchiectasis.
To survive tough conditions, P. aeruginosa forms colonies ...
Batteries for miniature bio-integrated devices and robotics — here’s how to do it
2024-10-25
University of Oxford researchers have made a significant step towards realising miniature, soft batteries for use in a variety of biomedical applications, including the defibrillation and pacing of heart tissues. The work has been published today in the journal Nature Chemical Engineering.
The development of tiny smart devices, smaller than a few cubic millimeters, demands equally small power sources. For minimally invasive biomedical devices that interact with biological tissues, these power sources must be fabricated from soft materials. Ideally, these should ...
UCLA researchers uncover novel role of protein GPNMB in heart repair
2024-10-25
FINDINGS
UCLA scientists have identified the protein GPNMB as a critical regulator in the heart’s healing process after a heart attack.
Using animal models, they demonstrate that bone marrow-derived immune cells called macrophages secrete GPNMB, which binds to the receptor GPR39, promoting heart repair. These findings offer a new understanding of how the heart heals itself and could lead to new treatments aimed at improving heart function and preventing the progression to heart failure.
BACKGROUND
Every 40 seconds, ...
Political polarization poses health risks, new analysis concludes
2024-10-25
News coverage of the 2024 election season has often centered on how partisan division has affected our politics. But a new analysis shows that political polarization also poses significant health risks—by obstructing the implementation of legislation and policies aimed at keeping Americans healthy, by discouraging individual action to address health needs, such as getting a flu shot, and by boosting the spread of misinformation that can reduce trust in health professionals.
“Compared to other high-income countries, the United States has a disadvantage when it comes to the health of its citizens,” ...
Lymph node-like structures may trigger the demise of cancer tumors
2024-10-25
**EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL OCT. 25 AT 5 A.M. ET**
A newly described stage of a lymph node-like structure seen in liver tumors after presurgical immunotherapy may be vital to successfully treating patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, according to a study by researchers from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
The study, published Oct. 25 in Nature Immunology, provides new information about lymph node-like structures called tertiary lymphoid structures. These structures, which are highly organized ...
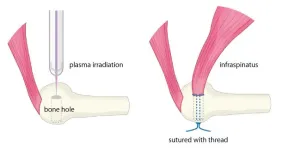
Pitchers rejoice? Plasma irradiation might prevent tendon re-tears
2024-10-25
The human body, filled with muscles and moving parts, is far from indestructible. Injuries are common, especially where tendons and bones connect. In Japan, rotator cuff tears affect approximately 1 in 4 people over age 50, and reports state that even after surgery, about 20% of cases result in re-tears. To combat this, new healing methods to bolster current clinical practices are needed.
Graduate student Katsumasa Nakazawa, Associate Professor Hiromitsu Toyoda, and then Professor Hiroaki Nakamura at Osaka Metropolitan University’s ...
The clinical significance of microvascular inflammation after kidney transplantation
2024-10-25
San Diego, CA (October 24, 2024) — Investigators recently uncovered key insights into newly defined rejection entities in kidney transplantation that may offer improved patient risk categorization post-transplant. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
Kidney transplant rejection continues to threaten the long-term success of kidney transplants, with microvascular inflammation (inflammation within capillaries) playing a pivotal role in graft failure. Due to its complex nature, this inflammation poses a major challenge in clinical practice. In response, the international Banff classification—the ...
The Lancet Public Health: New Commission calls for regulatory reform to tackle the health impacts of the rapid global expansion of commercial gambling
2024-10-24
**Embargo: 23.30 [UK time] / 06.30pm [US ET] Thursday 24th October 2024**
Peer reviewed / Literature review, systematic review and meta-analysis, opinion / People
Embargoed access to the Commission report and contact details for authors are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
The Lancet Public Health: New Commission calls for regulatory reform to tackle the health impacts of the rapid global expansion of commercial gambling
Gambling harms are far more substantial than previously understood, exacerbated by rapid global expansion ...
Scientists create cancer patients’ ‘digital twins’ to predict how well treatments may work
2024-10-24
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have shown that they can accurately re-create clinical trials of new treatments using ‘digital twins’ of real cancer patients. The technology, called FarrSight®-Twin, which is based on algorithms used by astrophysicists to discover black holes, will be presented today (Friday) at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain.
The researchers say that this approach could be used by cancer ...
New ‘mini-protein’ carries radiation dose directly to tumours without harming healthy tissues
2024-10-24
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have shown for the first time that it is possible for a specially-designed ‘mini-protein’ to deliver a radiation dose directly to tumour cells expressing a protein on their cell surfaces called Nectin-4, which is often found in a number of different cancers.
In a study presented on Friday at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain, Mike Sathekge, Professor and Head of the Nuclear Medicine Department at the University of Pretoria ...
Patients with advanced bladder cancer with alterations in the FGFR3 gene respond well to investigational drug, TYRA-300
2024-10-24
Barcelona, Spain: Patients with advanced bladder cancer that had spread to other parts of the body (metastasised) have responded well in a phase I clinical trial of an investigational drug, TYRA-300. The drug targets changes in the FGFR3 gene that drive tumour growth in about 10%-20% of these patients.
Associate Professor, Ben Tran, a medical oncologist at Peter McCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia, presented the first results as of 15 August 2024 from 41 patients enrolled in the SURF301 study in a late-breaking oral presentation at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics ...
Researchers find key genetic mutations in bowel cancer cells that lead to resistance to WRN inhibitors
2024-10-24
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have discovered key mutations in certain cancer cells that make them resistant to WRN inhibitors, a new class of anti-cancer drugs. The yet-to-be-published findings are presented on Friday at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain.
Werner helicase (WRN) inhibitors are already being evaluated in phase I clinical trials in patients with tumours that have microsatellite instability (MSI) – a condition in which the genes responsible for monitoring and repairing mistakes in DNA replication stop functioning, and errors are introduced. This is also ...
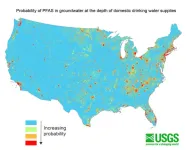
Millions in the U.S. may rely on groundwater contaminated with PFAS for drinking water supplies
2024-10-24
PEMBROKE, N.H. — Approximately 71 to 95 million people in the Lower 48 states – more than 20% of the country’s population – may rely on groundwater that contains detectable concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, also known as PFAS, for their drinking water supplies. These findings are according to a U.S Geological Survey study published Oct. 24.
The predictive model results can help members of the public, water suppliers and regulators understand the potential for PFAS contamination, guide future studies and inform strategic planning for water resources.
USGS scientists are the first to ...
Human actions cause insect color change
2024-10-24
New Zealand’s native stoneflies have changed colour in response to human-driven environmental changes, new research shows.
Just published in the journal Science, the University of Otago study provides arguably the world’s most clear-cut case of animal evolution in response to change made by humans.
Co-author Professor Jon Waters, of the Department of Zoology, says the stonefly has become a different colour due to recent deforestation.
“In natural forested regions, a native species has evolved ‘warning’ colours that mimic those of a poisonous forest species, to trick predators into ...
New AI model could make power grids more reliable amid rising renewable energy use
2024-10-24
As renewable energy sources such as wind and solar become more widespread, managing the power grid has become increasingly complex. Researchers at the University of Virginia have developed an innovative solution: an artificial intelligence model that can address the uncertainties of renewable energy generation and electric vehicle demand, making power grids more reliable and efficient.
Multi-Fidelity Graph Neural Networks: A New AI Solution
The new model is based on multi-fidelity graph neural networks (GNNs), ...
Lurie Children’s helps train pediatricians to screen toddlers for mental health risk, with equity and ethics in mind
2024-10-24
One in five children has an identified mental health problem as early as age 3. Early detection is key to earlier intervention, and it also could prevent more severe conditions down the line, such as ADHD, depression and anxiety. Pediatric primary care is an ideal setting to conduct screening for mental health risk, given that pediatricians tend to have close, ongoing relationships with young patients and their families, and broad reach to historically marginalized communities. Since mental health screening of toddlers in primary care is uncommon, it is important to train pediatricians to do so without implicit bias and in a way that prevents unintended ...
UTEP researchers develop low-cost device that detects cancer in an hour
2024-10-24
EL PASO, Texas (Oct. 24, 2024) – Researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso have created a portable device that can detect colorectal and prostate cancer more cheaply and quickly than prevailing methods. The team believes the device may be especially helpful in developing countries, which experience higher cancer mortality rates due in part to barriers to medical diagnosis.
“Our new biochip device is low-cost — just a few dollars — and sensitive, which will make accurate disease diagnosis accessible to anyone, ...
Texas A&M physicist Kevin Kelly earns American Physical Society Early Career Award
2024-10-24
Dr. Kevin J. Kelly, an assistant professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Texas A&M University and a member of the George P. and Cynthia Woods Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy, has been selected as the 2025 recipient of the American Physical Society’s Henry Primakoff Award for Early-Career Particle Physics in recognition of his contributions and promising career potential in fundamental particle physics and cosmology.
Kelly, who joined the Texas A&M faculty in 2022, works at the interface of two of the biggest outstanding mysteries in particle physics: ...
University of Maryland researcher awarded $1.8 million to study climate change’s impact on people with kidney disease
2024-10-24
Climate change is driving more extreme heat and more air pollution from wildfires, each of which put human health at risk. Now, new research funded by the federal Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and led by University of Maryland School of Public Health Professor Dr. Amir Sapkota, will study how these hazards independently and jointly impact already vulnerable groups, such as people living with end stage kidney disease (ESKD). The researchers aim to identify preventative solutions.
“During extreme heat, the damaged kidneys of people with ESKD do not regulate fluid levels very ...
Johns Hopkins Children’s Center research in mice suggests zinc supplements have potential value to directly treat short bowel syndrome
2024-10-24
Researchers from Johns Hopkins Children’s Center say they have identified a gene pathway involving the mineral zinc in mice that may someday point the way to using zinc-based supplements to directly help people with a rare disorder called short bowel syndrome (SBS).
The findings, published Oct. 7 in Nature Communications, help advance efforts toward more effective, potential treatment regimens for both children and adults with the debilitating condition.
SBS, which affects 10,000–20,000 adults and children in the United States, is marked by damage to and shortening of ...
Kalinin receives David Adler Lectureship Award
2024-10-24
Sergei Kalinin, a professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, has been named the winner of the David Adler Lectureship Award in the Field of Materials Physics by the American Physical Society. The award recognizes one outstanding contributor in the field of materials physics who is notable for high-quality research, review articles, and lecturing.
“I am deeply honored to receive the Adler Award, as it recognizes the critical transition in materials discovery that my colleagues at the University of Tennessee and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and I have championed,” ...
[1] ... [853]
[854]
[855]
[856]
[857]
[858]
[859]
[860]
861
[862]
[863]
[864]
[865]
[866]
[867]
[868]
[869]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.