Radioprotective effects of licochalcone B: DNA protection, cytokine inhibition, and antioxidant boost
2024-10-29
Background and objectives
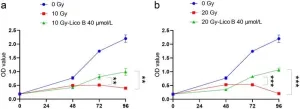
Radiation injury poses a serious threat to human health, causing complex and multifaceted damage to cells and tissues. Such injury can be caused by various factors, including nuclear accidents, medical radiation therapy, and space travel. Currently, finding effective treatment methods and drugs to mitigate the harmful effects of radiation injury on the human body is a crucial research direction. This study aimed to explore the protective effects and mechanisms of Licochalcone ...
Complete response to encorafenib + binimetinib in BRAF V600E-mutant tumor
2024-10-29
“This case report highlights the importance of full tumor genotyping to identify potentially actionable targets in rare tumors such as malignant glomus tumors.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 29, 2024 – A new case report was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on October 11, 2024, entitled “Complete response to encorafenib plus binimetinib in a BRAF V600E-mutant metastasic malignant glomus tumor.”
As highlighted in the abstract, glomus tumors (GT) are rare mesenchymal neoplasms originating in dermal arteriovenous structures involved in thermoregulation. ...
Gold bugs: Spectacular new fossil arthropod preserved in fool’s gold
2024-10-29
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 15:00 GMT / 11:00 ET TUESDAY 29 OCTOBER 2024
Gold bugs: spectacular new fossil arthropod preserved in fool’s gold
Images available via link in the notes section
A new 450-million-year-old fossil arthropod, preserved in 3D by iron pyrite (fool’s gold), has been unveiled by scientists.
The new species, Lomankus edgecombei, is distantly related to spiders, scorpions, and horseshoe crabs.
The findings have been published today (29 Oct) in the journal Current Biology.
A team of researchers led by Associate Professor Luke Parry, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Oxford, have unveiled a spectacular ...
Optimal standing positions and ventilation in airport smoking lounges
2024-10-29
WASHINGTON, Oct. 29, 2024 – While many smoking rooms in U.S. airports have closed in recent years, they are still common in other airports around the world. These lounges can be ventilated, but how much does it actually help the dispersion of smoke?
Research published in Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, shows that not all standing positions in airport smoking lounges are created equal.
Researchers from the University of Hormozgan in Iran studied nicotine particles in a simulated airport smoking room and found that the thermal environment and positioning of smokers influenced how particles ...
Ancient gene influences immunity of First Nations Peoples of Oceania
2024-10-29
AURORA, Colo. (Oct. 29, 2024) – An ancient gene mutation among First Nations inhabitants of Oceania may make them more susceptible to infectious diseases like influenza, according to a new study by scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
“We found quite a diverse set of genes in this population but there was one allele that really stood out in terms of genetic composition,” said the study’s lead author Paul Norman, PhD, professor of biomedical informatics at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. “We did some investigating, and we suspect this allele ...
The Megacheiran candidate: Fossil hunters strike gold with new species
2024-10-29
New Haven, Conn. — Paleontologists have identified fossils of an ancient species of bug that spent the past 450 million years covered in fool’s gold in central New York.
The new species, Lomankus edgecombei, is a distant relative of modern-day horseshoe crabs, scorpions, and spiders. It had no eyes, and its small front appendages were best suited for rooting around in dark ocean sediment, back when what is now New York state was covered by water.
Lomankus also happens to be bright gold — thanks to layers of pyrite ...
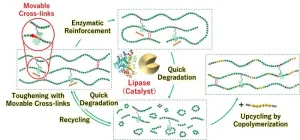
Advanced biodegradable plastics run rings around their predecessors
2024-10-29
Osaka, Japan—Achieving a sustainable society requires the development of advanced degradable plastics, or polymers, which are molecules composed of long chains of repeating units. The goal of a resource-circulating society is now one step closer thanks to the efforts of a team from Osaka University that has developed tough biodegradable plastics by including movable crosslinking groups.
In a study published this month in Chem, the researchers have revealed that developing polymers with movable crosslinks not only increases their strength but also promotes degradation by enzymes under mild conditions.
Plastics and polymers need to achieve both desirable performance ...
Suicide-related emergencies underdetected among minority, male youth, and preteens, study finds
2024-10-29
A new study by UCLA Health reveals that hospital emergency departments may be missing signs of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in children, boys and Black and Hispanic youth.
The research, published in the journal JAMA Open Network, analyzed electronic health records of nearly 3,000 children and teenagers presenting to two emergency departments in southern California for mental health reasons. Using machine learning algorithms, the researchers determined standard medical record surveillance methods miss youth with suicide-related emergencies. These methods disproportionately missed suicide-related visits among Black, Hispanic, male, and preteen youths, compared with ...
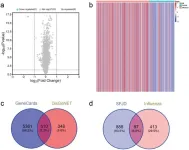
The molecular mechanism of Shufeng Jiedu capsules in the treatment of influenza: A comprehensive analysis based on network pharmacology, bioinformatics, and molecular docking
2024-10-29
Background and objectives
Shufeng Jiedu Capsules (SFJD), a traditional Chinese medicine preparation, are widely used in the clinical treatment of influenza, yet their mechanism of action remains unclear. This study aimed to systematically explore the molecular mechanism of SFJD in the treatment of influenza using network pharmacology and bioinformatics techniques.
Methods
The active ingredients of SFJD were retrieved from traditional Chinese medicine databases, and their targets were identified using the Swiss Target Prediction and TCMSP databases. Influenza disease genes were obtained from the GEO, GeneCards, and DisGeNET ...
Treating severe calcification with an atherectomy device does not improve cardiac stenting outcomes, study finds
2024-10-29
Routine use of an orbital atherectomy device to remove calcium from severely blocked coronary arteries before patients undergo cardiac stenting procedures does not improve outcomes, a Mount Sinai-led study has found.
The results of the ECLIPSE study were announced during a late-breaking trial presentation at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics Annual Meeting on Tuesday, October 29. This is the first large-scale study to study this specific device in severely calcified lesions, and the results support reserving its use for extreme cases.
“Operators across the United States currently have different thresholds ...
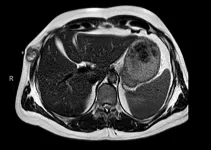
Access to patient questionnaire improves spine MRI diagnosis
2024-10-29
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Knowing a patient’s symptoms helps radiologists in lumbar spine MRI interpretation and diagnosis, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
MRI is the most important imaging exam in patients with back pain or sciatica because it shows nearly all degenerative and structural abnormalities of the spine.
However, MRI often shows spinal abnormalities in individuals who do not have symptoms. Because the same abnormalities can ...
Using AI to measure prostate cancer lesions could aid diagnosis and treatment
2024-10-29
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men, and almost 300,000 individuals are diagnosed with it each year in the U.S. To develop a consistent method of estimating prostate cancer size, which can help clinicians more accurately make informed treatment decisions, Mass General Brigham researchers trained and validated an AI model based on MRI scans from more than 700 prostate cancer patients. The model was able to identify and demarcate the edges of 85% of the most radiologically aggressive prostate lesions. Tumors with a larger volume, as estimated by the AI model, ...
Study uncovers alarming patterns in the effects of family violence
2024-10-29
A new synthesis of global evidence highlights a strong connection between family violence and long-term health consequences, significantly impacting the psychological and physical well-being of millions worldwide. This comprehensive review, the first of its kind, synthesises the findings from the most rigorous studies on child maltreatment and intimate partner violence, uncovering alarming patterns in the long-term effects of family violence.
According to the study, led by Matthias Burghart of the Max Planck Institute for the Study of Crime, Security, and Law, and Sophia ...
Emerging technology for extended preservation of organs for transplant requires new ethical & legal guidelines
2024-10-29
Leading ethics experts and researchers have co-authored a breakthrough paper calling for new governance and legal rules to guide application of emerging technology to preserve organs for transplant.
Current law and guidance are inadequate for emerging biopreservation technologies that will allow long-term storage of human organs for transplantation. The technology is much needed to address the severe time constraints that currently limit the viability of donor organs. Those constraints have contributed to a severe organ shortage, which affects patients throughout ...
Transcriptomics-based study on the mechanism of heart failure amelioration by water decoction and water-soluble alkaloids of Fuzi
2024-10-29
Background and objectives
Fuzi, the processed product of daughter roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx., is a well-known Chinese medicine for the treatment of heart failure (HF) and related cardiac diseases. This study aimed to investigate the molecular mechanism of the cardioprotective effects of Fuzi water decoction (FWD) and Fuzi water-soluble alkaloids (FWA) on the model of HF.
Methods
The HF model of rats was prepared through intravenous injection of propafenone hydrochloride. The normal group, model group, FWD-treated groups (1.25 g/kg, 2.5 g/kg, 5 g/kg) and positive group (Shenfu Injection, 3.3 mL/kg) were set up. Heart rate, LV+dp/dtmax, and ...
A novel probe technology for detecting native albumin activity as a biomarker in patients with hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical applications
2024-10-29
Background and objectives
Albumin is a major prognostic factor for patients with advanced liver disease, dependent on its concentration and biological activity. This study aimed to improve the method of active albumin detection and elucidate its predictive validity of albumin activity across hepatic disease progression and etiology.
Methods
This study synthesized a novel ratiometric fluorescent probe with an improved structure of 2′-FBPBN. The technique was used to detect native human albumin (HA) activity in 244 patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis (LC) and 66 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Clinical and laboratory data were also collected.
Results
Patients ...
A simulation study identifies robust social norms that sustain cooperation in costly reputations
2024-10-29
A groundbreaking study led by Prof. Dr. Hitoshi Yamamoto (Rissho University) and his collaborators from, Soka University, Koriyama Women’s College, and the RINRI Institute has made significant strides in the field of indirect reciprocity: a key mechanism for sustaining cooperation in human societies. Their research unveils new insights into the social norms that protect cooperative behaviour from defector invasion and reputation costs, thereby deepening our understanding of how large-scale societies maintain stability. The results of the study were published in Scientific Reports.
Indirect reciprocity is characterised by cooperative ...
Newly discovered cyanobacteria could help sequester carbon from oceans and factories
2024-10-29
An international coalition of researchers from the United States and Italy has discovered a novel strain of cyanobacteria, or algae, isolated from volcanic ocean vents that is especially adept at growing rapidly in the presence of CO2 and readily sinks in water, making it a prime candidate for biologically-based carbon sequestration projects and bioproduction of valuable commodities. This strain, nicknamed “Chonkus,” was found off the coast of the island of Vulcano in Sicily, Italy — an environment in which marine CO2 is abundant due to shallow volcanic vents. The discovery is described in a paper published ...
Making scents of aromas that differentiate beer and wine
2024-10-29
Today, people increasingly seek non-alcoholic versions of beer or wine. Despite boasting different flavors, these two drinks share many aromas, which makes it difficult to produce alcohol-free versions that mimic the real thing. Researchers in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry report on a literature analysis and experiment to characterize the chemical compounds that give beer and wine their unique fragrances. They say their findings could aid the development of flavorful, non-alcoholic substitutes.
Food and beverage researchers are working to recreate the enjoyable aromas and flavors of beer and wine in alcohol-free substitutes. However, because both beer and ...
FAU awarded DOE grant to test ocean current energy offshore Palm Beach County
2024-10-29
Imagine harnessing the power of ocean currents to generate clean, renewable energy right off the coast of Southeast Florida. Florida Atlantic University’s Southeast National Marine Renewable Energy Center (SNMREC) has been awarded an $800,000 grant from the United States Department of Energy’s Water Power Technologies Office to enable the commercial readiness of ocean energy technologies.
SNMREC, in collaboration with a team of experts including The City of Lake Worth Beach Electric Utility, 3U Technologies, 48 North Solutions, IDOM Incorporated, Braid Theory, and the European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC), ...
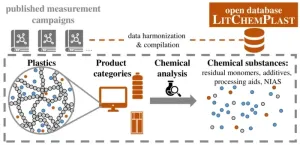
Open-access database compiles 3,500 substances measured in plastic products: Study highlights substantial knowledge gaps
2024-10-29
About this study: Plastics contain a vast number of chemicals, some of which greatly impact the environment and human health. However, information on the presence of individual substances in plastic products is oftentimes not publicly available. In a peer-reviewed study, set to be published on 29 October 2024, in Environmental Science and Technology Letters, a new publicly accessible database on chemicals measured in plastics is presented - LitChemPlast. The database contains over 3’500 substances measured in over 47'000 samples of plastic products across 372 studies.
Key findings:
• Contamination of recycled plastics:
The database shows that, due to ...
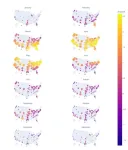
Internet activity reveals national allergy patterns
2024-10-29
Complaining about your allergies online might provide valuable data to researchers. Over 25% of Americans experience seasonal allergies, but how the prevalence of seasonal allergies varies across space and time remains obscure, in part because allergies seldom warrant visits to healthcare providers. Elias Stallard-Olivera and Noah Fierer mined Twitter (now X) posts and Google searches from 2016–2020 to extrapolate spatial and temporal allergy patterns. A natural language processing model sorted posts that indicated symptoms (e.g., “My allergies are really bad today!!”) from posts that include key words but did not indicate the presence of symptoms (e.g., “Gluten ...
New study confirms beehive fences as highly effective in reducing human-elephant conflict, but researchers warn of future risks
2024-10-29
[11:00 GMT - 29 Oct 2024] A groundbreaking, nine-year study has revealed that elephants approaching small-scale farms in Kenya avoid beehive fences housing live honey bees up to 86% of the time during peak crop seasons, helping to reduce human-elephant conflict for local farmers and boost income. Link to images and video of the project available
Key findings include:
Beehive fences are a proven success in reducing human-elephant conflict in Africa.
Savannah elephants avoid beehive fences housing live honey bees up to 86% of the time during peak crop seasons.
Across all seasons and the entire study period, the fences deterred an annual average of 76% of 3,999 ...
Tiny gold radiators fry bacteria on implants
2024-10-29
In the fight against antibiotic resistance, a new technology developed at Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, can be of great importance when, for example, hip and knee implants are surgically inserted. By heating up small nanorods of gold with near-infrared light (NIR), the bacteria are killed, and the surface of the implant becomes sterile. The researchers are now presenting a new study that increases the understanding of how the gold rods are affected by light and how the temperature in them can be measured.
Infections can occur during surgical procedures, with the risk increasing significantly when foreign materials, ...
WISH announces shortlist for Global Healthcare Innovation Awards
2024-10-29
29 October 2024. Doha, Qatar – The World Innovation Summit for Health (WISH), an initiative of Qatar Foundation, has shortlisted 12 innovators for two awards within the 2024 WISH Global Healthcare Innovation Competition. Selected from more than 150 applications, the 12 will showcase their groundbreaking innovations to global policymakers and healthcare leaders at this year’s summit in Doha, 13-14 November.
In addition to the chance to receive one of two investment awards of US$10,000, shortlisted innovators will have access to mentoring sessions with industry experts to learn ...
[1] ... [855]
[856]
[857]
[858]
[859]
[860]
[861]
[862]
863
[864]
[865]
[866]
[867]
[868]
[869]
[870]
[871]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.