Smoking cessation and incident cardiovascular disease
2024-11-01
About The Study: In this cohort study, smoking and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk exhibited a dose-dependent association, with light ex-smokers having a CVD risk similar to that of never-smokers relatively soon after smoking cessation. For heavy ex-smokers, greater than 25 years might be required for the residual CVD risk to align with that of never-smokers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Seung Yong Shin, MD, PhD, email theshin04@korea.ac.kr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Cannabis use during early pregnancy following recreational cannabis legalization
2024-11-01
About The Study: In this time-series study, recreational cannabis legalization implementation in California was associated with an increase in rates of cannabis use during early pregnancy, defined by both self-report and toxicology testing, driven by individuals living in jurisdictions that allowed adult-use retailers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kelly C. Young-Wolff, PhD, MPH, email kelly.c.young-wolff@kp.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.3656)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Research shows Cleveland Clinic’s therapeutic virtual yoga program can be effective for chronic low back pain
2024-11-01
Research Shows Cleveland Clinic’s Therapeutic Virtual Yoga Program Can Be Effective for Chronic Low Back Pain
Participants also reported better sleep quality and reduced use of pain medications
UNDER EMBARGO Friday, November 01, 2024, 11:00 a.m. ET, CLEVELAND: Cleveland Clinic researchers found that a 12-week therapeutic virtual yoga program for chronic low back pain can be a feasible, safe and effective treatment option. The findings are published in JAMA Network Open.
Chronic low back pain is very common — up to 20% of adults worldwide have long-lasting or recurrent lower back pain. In severe cases, ...
Closing in on Parkinson’s Disease proteins in extracellular vesicles in the blood
2024-11-01
Closing in on Parkinson’s Disease proteins in extracellular vesicles in the blood
Precision diagnostics for diseases that affect the brain and other organs brought closer by new ability to exclusively access contents of organ-derived extracellular vesicles in blood
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Brain disorders like Parkinson’s (PD) or Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) start to develop in patients much earlier than when their first clinical symptoms appear. Treating patients at these early stages could slow or even stop their ...
Regional and global experts convene in Accra, Ghana to update cancer treatment guidelines for Sub-Saharan Africa
2024-11-01
Accra, GHANA [October 29, 2024] — International oncology experts are gathering in Accra, Ghana for a series of meetings beginning today, to update cancer treatment recommendations in the NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa. This is the latest event from a longstanding collaboration between the African Cancer Coalition (ACC), American Cancer Society (ACS), and National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®), and the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI) that collectively ...
China University of Geosciences (Beijing) unveils clues to an enigmatic geological process
2024-11-01
Cratons are fascinating yet enigmatic geological formations. Known to be relatively stable portions of the Earth’s continental crust, cratons have remained largely unchanged for billions of years. Although cratons have survived many geological events, some are undergoing decratonization—a process characterized by their deformation and eventual destruction. For example, the North China Craton (NCC), an ancient continental crust block, is known to have begun extensive decratonization during the Mesozoic era, largely due to tectonic and geochemical modifications and destabilization of its base (or ‘keel’). However, explaining the mechanisms ...
Fueling greener aviation with hydrogen
2024-11-01
Despite ongoing efforts to curb CO2 emissions with electric and hybrid vehicles, other forms of transportation remain significant contributors of greenhouse gases. To address this issue, old technologies are being revamped to make them greener, such as the reintroduction of sailing vessels in shipping and new uses for hydrogen in aviation. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering have used computer modeling to study the feasibility and challenges of hydrogen-powered aviation.
“While there is a long way to go for hydrogen aviation to be realized at scale, we hope that our ...
Education, occupation, and wealth affect the risk of cognitive impairment
2024-11-01
Socioeconomic factors such as education, occupation, and wealth influence the likelihood of developing cognitive impairment or dementia in later life and whether a person is likely to recover, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Scientific Reports, followed 8,442 adults aged 50 and above in England over 10 years from 2008/09 to 2018/19, to examine how socioeconomic factors at the start of the study were associated with changes in cognitive status.
The researchers tracked how these people moved between various states: healthy, mild cognitive impairment, and dementia. They also considered the possibility ...
Revealing causal links in complex systems
2024-11-01
Getting to the heart of causality is central to understanding the world around us. What causes one variable — be it a biological species, a voting region, a company stock, or a local climate — to shift from one state to another can inform how we might shape that variable in the future.
But tracing an effect to its root cause can quickly become intractable in real-world systems, where many variables can converge, confound, and cloud over any causal links.
Now, a team of MIT engineers hopes to provide some clarity in the pursuit of causality. They developed ...
Alzheimer disease as a clinical-biological construct— an international working group recommendation
2024-11-01
About The Study: This article discusses a recent revision of the Alzheimer Association criteria to define Alzheimer disease (AD) as a purely biological entity, which raises concerns that if diagnosis of AD can be reduced to the sole presence of AD core 1 biomarkers, major uncertainty and variability in the clinical prognosis of patients diagnosed with AD may be introduced.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Bruno Dubois, MD, MSc, email bruno.dubois@aphp.fr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.3770)
Editor’s ...
Press registration now open for the EULAR 2025 Congress in Barcelona
2024-11-01
The EULAR 2025 Congress will gather the world's foremost rheumatology experts, fostering a unique environment to explore pioneering research, clinical advancements, and patient-centred innovations in rheumatology. This annual flagship event offers unparalleled access to transformative discussions and showcases the latest strides in patient care for rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs).
This year's Congress programme promises an impressive line-up, featuring must-see scientific sessions, EULAR Recommendations, and insightful abstract presentations. Esteemed speakers from across Europe and beyond ...
New research identifies ways to protect neurons from the negative effect of high-fat diet on multiple sclerosis progression
2024-11-01
NEW YORK, November 1, 2024 — Newly published research in the journal Glia has identified crucial links between dietary choices and the progression of multiple sclerosis (MS). The study, led by Patrizia Casaccia, founding director of the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center’s (CUNY ASRC) Neuroscience Initiative and Einstein Professor of Biology and Biochemistry at the CUNY Graduate Center, explored how enzymes called ceramide synthase 5 and 6 are responsible for the toxic effect ...
Boosting the nutritional value of black soldier fly larvae with biotechnology
2024-11-01
With the rapid increase in the global population, a "protein crisis" is expected in the near future, where the supply of protein will not be able to meet the rising demand. Fishmeal is the most common protein source that supports the production of livestock and aquaculture products, which are key protein sources for human consumption. However, global shortage of fishmeal and its rising prices have created an urgent need to find and secure an alternative protein source. Insects are gaining attention as novel protein sources ...
Medication decisions in pregnancy: A balancing act
2024-11-01
Most women use medication during pregnancy. Yet, selecting appropriate drugs and doses is challenging. In a new The Lancet article, physicians and researchers from the Radboud university medical center, Maastricht UMC+, Imperial College London, and the University of Liverpool introduce a shared decision-making approach combining ethical principles and a pregnant woman’s values with existing evidence. They use the example of sertraline, a commonly prescribed antidepressant in pregnancy, to illustrate the advocated decision-making process.
Although pregnant women often need medication, data on drug safety and efficacy in pregnancy remains limited. Historically seen as vulnerable research ...
Texas Tech researcher named Station Science Leader for Antarctica project
2024-10-31
Summary:
Texas Tech’s Natasja van Gestel has been named Station Science Leader by the National Science Foundation (NSF), enabling her to lead and coordinate research at Antarctica’s Palmer Station while advancing her work on climate change’s impact on glaciers. As a leader, she will oversee multiple scientific initiatives, manage resources and ensure compliance with the Antarctic Treaty’s regulations.
Why This Matters:
Climate Study: Her research contributes vital data on climate change effects in Antarctica, crucial for global climate assessments.
International Collaboration: ...
Restricting sugar consumption in utero and in early childhood significantly reduces risk of midlife chronic disease
2024-10-31
A low-sugar diet in utero and in the first two years of life can meaningfully reduce the risk of chronic diseases in adulthood, a new study has found, providing compelling new evidence of the lifelong health effects of early-life sugar consumption.
Published in Science, the study finds that children who experienced sugar restrictions during their first 1,000 days after conception had up to 35% lower risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and as much as 20% less risk of hypertension as adults. Low sugar intake by the mother prior to birth was enough to lower risks, but ...
Apixaban vs aspirin in patients with cancer and cryptogenic stroke
2024-10-31
New Orleans - Ochsner Health physicians Dr. Richard Zweifler and Dr. Joseph Tarsia are co-authors on a post hoc analysis carried out in the ARCADIA randomized clinical trial, comparing the effectiveness of apixaban versus aspirin in preventing adverse clinical outcomes in patients with a history of cancer and cryptogenic stroke. The research found no significant difference in the risk of major ischemic and hemorrhagic events between those taking apixaban and aspirin. The ...
Can magnetic pulses aimed at the brain treat insomnia?
2024-10-31
Traditional solutions for sleep disorders, including medications and cognitive behavioral therapies, often provide insufficient relief for military personnel, a problem researchers from the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson will be hoping to solve with a $3 million grant from the Department of Defense Congressionally Directed Medical Research Program.
Sleep problems are among the top health concerns of military personnel, with an estimated 85% meeting criteria for a clinically relevant sleep ...
F.M. Kirby Research Center honors 25 years of pioneering brain imaging research
2024-10-31
BALTIMORE, October 31, 2024— Kennedy Krieger Institute is proud to celebrate the 25th anniversary of the F.M. Kirby Research Center for Functional Brain Imaging at Kennedy Krieger Institute, a leader in advancements and research in understanding the human brain.
Established in 1999 in partnership with Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, the center has transformed neuroscience and medical imaging by developing cutting-edge magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques that allow researchers to examine and measure brain function and structure ...
$1.75M CDC grant funds study to boost vaccine acceptance in Arizona’s rural, border communities
2024-10-31
Researchers at the University of Arizona’s Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health received a $1.75 million Centers for Disease Control and Prevention grant to conduct a community-based, participatory research study designed to improve vaccine uptake in Arizona’s rural and border communities.
Vaccination is a highly effective public health intervention that saves millions of lives per year, yet vaccination rates have declined in recent years for a variety of reasons, ranging from safety concerns to religious and philosophical objections.
“Vaccination is a cornerstone of public health,” said co-principal investigator Tomas ...
Immune system review provides insight into more effective biotechnology
2024-10-31
Macrophage cells are the immune system’s frontline soldiers, early on the scene to protect the body from foreign invaders. These cells answer the immune system's critical question for the rest of its troops: friend or foe?
As critical responders, macrophages can perceive helpful biotechnology as threats. If not created with the right materials or mechanical forces, these devices can trigger an immune response that can cause inflammation, scar tissue or device failure.
But what is the right material or the right mechanical force? In a meta-analysis co-led ...
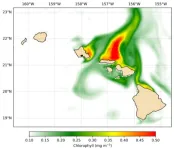
Remote control eddies: Upwelled nutrients boost productivity around Hawaiian Islands
2024-10-31
Beyond colorful coral reefs and diverse nearshore ecosystems, Pacific Ocean waters surrounding the Hawaiian Islands have comparatively little marine life and low biological productivity. New research published by University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa oceanographers showed that eddies on the leeward side of the Hawaiian Islands can supply nutrients, not only locally, but also to the opposite side of the island chain and stimulate blooms of phytoplankton, microscopic plant life that lives in the surface ocean.
The study, published in JGR Oceans, was selected by the American Geophysical Union’s editorial board as a featured article.
“While ...
Rice, Texas Medical Center institutions jointly award seed grants
2024-10-31
Rice University together with Baylor College of Medicine and the Houston Methodist Academic Institute has awarded seed grants in support of research on health equity and digital health.
Spearheaded by Rice’s Educational and Research Initiatives for Collaborative Health (ENRICH) office in collaboration with the two partnering institutions in the Texas Medical Center (TMC), the seed grant opportunity followed the Health Equity Workshop hosted earlier this year by Rice’s Digital Health Initiative.
“To achieve equitable health outcomes, a comprehensive approach is essential — one ...
Sleeping for 2: Insomnia therapy reduces postpartum depression, study shows
2024-10-31
While many people believe that poor sleep during pregnancy is inevitable, new research has determined that cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBTi) while pregnant can not only improve sleep patterns but also address postpartum depression.
Researchers from UBC’s Okanagan and Vancouver campuses, as well as the University of Calgary, discovered that delivering CBTi during pregnancy significantly reduces postpartum depressive symptoms after a baby arrives.
“Early intervention is crucial for infant and parental mental health,” says Dr. Elizabeth Keys, an Assistant Professor in UBCO’s School of Nursing and a study co-author. “Our research explores how addressing ...
How fruit flies achieve accurate visual behavior despite changing light conditions
2024-10-31
When light conditions rapidly change, our eyes have to respond to this change in fractions of a second to maintain stable visual processing. This is necessary when, for example, we drive through a forest and thus move through alternating stretches of shadows and clear sunlight. "In situations like these, it is not enough for the photoreceptors to adapt, but an additional corrective mechanism is required," said Professor Marion Silies of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU). "Earlier work undertaken by her research group had already demonstrated that such a corrective 'gain control' mechanism exists ...
[1] ... [852]
[853]
[854]
[855]
[856]
[857]
[858]
[859]
860
[861]
[862]
[863]
[864]
[865]
[866]
[867]
[868]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.