High-impact clinical trials generate promising results for improving kidney health: Part 2
2024-10-26
The results of numerous high-impact phase 3 clinical trials that could affect kidney-related medical care will be presented in-person at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23–27.
Hyponatremia, or a chronically low blood salt level, is the most common electrolyte disorder in hospitalized patients, and is associated with higher risks of death and re-hospitalization. In a recent trial, 2,173 hospitalized patients with hyponatremia from 9 centers across Europe were assigned to undergo either targeted correction of blood salt levels according to guidelines or to receive routine care for hyponatremia. The primary outcome was the combined ...
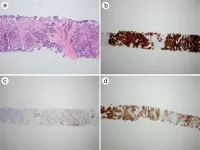
Expression of carbonic anhydrase IX as a novel diagnostic marker for differentiating pleural mesothelioma from non-small cell lung carcinoma
2024-10-26
Background and objectives
Mesothelioma is an aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis. Histological diagnosis of mesothelioma using limited tissue samples can be challenging. Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) is a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in a variety of solid tumors. This study aimed to investigate the clinical utility of CAIX expression in the differential diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma from non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).
Methods
Unstained tissue microarray slides composed of 56 cases of pleural mesothelioma and 82 cases of NSCLC were subjected to immunohistochemical staining using a mouse anti-human antibody against CAIX.
Results
Of the 38 epithelioid mesothelioma ...
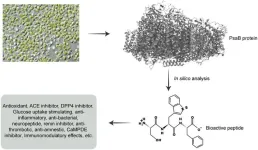
In silico assessment of photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2 (PsaB) from Chlorella vulgaris (green microalga) as a source of bioactive peptides
2024-10-26
Background and objectives
Chlorella vulgaris is a green, photosynthetic microalga in the phylum Chlorophyta. The goal of our study was to perform a bioinformatics analysis of Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2, one of its photosynthesis-related proteins, and to hunt for potent bioactive peptides.
Methods
To generate peptides and estimate the safety and efficacy of each bioactive peptide, we employed the tools BIOPEP-UWM™, PeptideRanker, DBAASP, and ToxinPred. PepDraw was used to understand the physicochemical properties ...
Association between TLR10 rs10004195 gene polymorphism and risk of Helicobacter pylori infection
2024-10-26
Background and objectives
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection can cause multiple secondary digestive disorders. Some studies have found that polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor (TLR) genes, including TLR10 rs10004195, may be associated with increased susceptibility to H. pylori infection. Despite conflicting reports, we conducted a meta-analysis to clarify the relationship between these factors.
Methods
We conducted an exhaustive review, encompassing all relevant literature up to February 2024, using databases ...
The usefulness of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry in the diagnosis of onychomycosis in patients with nail psoriasis
2024-10-26
Background and objectives
Nail psoriasis is common in patients with plaque psoriasis and is associated with morbidity, including onychomycosis, which can complicate psoriasis treatments and be difficult to differentiate. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry is a fast and simple technique for identifying microorganisms through protein analysis. This study aimed to determine the sensitivity and specificity of MALDI-TOF for diagnosing onychomycosis in patients with nail psoriasis, by using conventional mycological and histological methods as the reference standard.
Methods
A prospective study was conducted on 88 patients with ...
Liver characterization of a cohort of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency patients with and without lung disease
2024-10-26
Background and Aims
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the misfolding and accumulation of the mutant variant of alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) within hepatocytes, which limits its access to the circulation and exposes the lungs to protease-mediated tissue damage. This results in progressive liver disease secondary to AAT polymerization and accumulation, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) due to deficient levels of AAT within the lungs. Our goal was to characterize the unique effects of COPD secondary to AATD on liver disease and gene expression.
Methods
A ...
Anti-hepatitis b virus treatment with tenofovir amibufenamide has no impact on blood lipids: A real-world, prospective, 48-week follow-up study
2024-10-26
Background and Aims
The effect of tenofovir amibufenamide (TMF) on blood lipid profiles in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) remains unclear. This study aimed to explore whether TMF affects blood lipids during 48 weeks in patients with CHB.
Methods
A total of 91 patients with CHB undergoing TMF treatment for 48 weeks were divided into two groups: Lipid Normal (n = 42) and Lipid Abnormal (n = 49), based on baseline blood lipid levels. Lipid indices, virological responses, and biochemical indicators were compared between the two groups. Clinical observations were ...
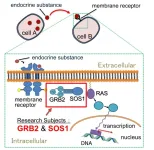
Scientists uncover workings of “batons” in biomolecular relay inside cells
2024-10-26
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have uncovered new insights into how the proteins GRB2 and SOS1 in cells pass signals from membrane receptors to nuclei. They used nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to study how and which specific regions of GRB2 and SOS1 bind to each other, especially how they trigger liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). Issues with signal transduction are a major cause of cancers: understanding how it works may lead to radical new treatments.
Biological ...
Do certain diabetes drugs increase the risk of acute kidney injury in patients taking anti-cancer therapies?
2024-10-26
San Diego, CA (October 25, 2024) — Glucagon-like peptide-1-receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) are medications that are increasingly prescribed for patients with type 2 diabetes and congestive heart failure. Reports of GLP-1RA–associated acute kidney injury (AKI) have emerged, but the risk of GLP-1RA–associated AKI among patients on anti-cancer drugs is unclear. Surprisingly, new research suggests that taking GLP-1RA is not associated with an increased risk of AKI in patients receiving anti-cancer therapies. The findings will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
For the study, investigators analyzed ...
Researchers integrate multiple protein markers to predict health outcomes in individuals with chronic kidney disease
2024-10-26
San Diego, CA (October 25, 2024) — Prior efforts to identify novel kidney biomarkers as risk factors for chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression have typically evaluated proteins individually, which limits their prognostic power. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases’ (NIDDK’s) CKD Biomarkers Consortium of investigators recently developed and tested novel dimensions of kidney health by combining a set of 17 urine and plasma biomarkers that ...
How the novel antibody felzartamab impacts IgA nephropathy
2024-10-26
San Diego, CA (October 25, 2024) — IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is an autoimmune kidney disease driven by immune cells that express a protein called CD38 on their surface. A recent Phase 2 trial revealed that felzartamab, an investigational anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, helps to reduce proteinuria and maintain patients’ kidney function. Investigators evaluated the molecular mechanisms underlying felzartamab’s potential efficacy in IgAN. The findings will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
It is hypothesized that CD38+ cells ...
Heart and kidney outcomes after canagliflozin treatment in older adults
2024-10-26
San Diego, CA (October 25, 2024) — Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors reduce the risk of cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes, but it is unclear whether their effects differ based on patients’ age. A recent analysis of clinical trial data reveals that the SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin benefited patients across all age categories. The findings will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23 – 27.
The analysis pooled individual participant data from the CANVAS Program and CREDENCE trial and assessed efficacy and safety according to baseline age. ...
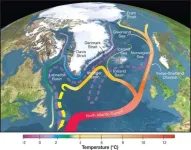
Slowing ocean current could ease Arctic warming -- a little
2024-10-25
The Arctic is warming at three to four times the global average. However, new research suggests the slowing of a key ocean current could reduce projected Arctic warming by up to 2 degrees Celsius by the end of the century.
For years, scientists have warned that unchecked Arctic warming could lead to devastating consequences, threatening wildlife and ushering in an era of more frequent and extreme weather events. Amid concerns for these types of outcomes, a study led by UC Riverside offers some limited relief.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, examined ...
Global, national, and regional trends in the burden of chronic kidney disease among women
2024-10-25
San Diego, CA (October 25, 2024) — A recent analysis reveals that the number of chronic kidney disease (CKD) cases in women around the globe nearly tripled in the past three decades. Also, type 2 diabetes and hypertension were the leading causes of CKD-related deaths in women. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
The analysis drew from the Global Burden of Disease study 2021, a comprehensive effort to quantify health loss across the world over time. The study includes information from 204 countries and territories.
From 1990 to 2021, the average annual percentage ...
Scientific discovery scratching beneath the surface of itchiness
2024-10-25
Ever had an itchy nose or, worse, an unreachable spot on your back that drives you mad? Now imagine an itch that refuses to go away, no matter how hard or long you scratch. That persistent itch, or pruritus, may actually be one of the skin’s first lines of defense against harmful invaders, according to neuroimmunologist Juan Inclan-Rico of the University of Pennsylvania.
“It’s inconvenient, it’s annoying, but sensations like pain and itch are crucial. They’re ever-present, especially when it comes to skin infections,” says Inclan-Rico, a postdoctoral researcher in the Herbert Lab at ...
SFSU psychologists develop tool to assess narcissism in job candidates
2024-10-25
It feels like narcissism is everywhere these days: politics, movies and TV, sports, social media. You might even see signs of it at work, where it can be particularly detrimental. Is it possible to keep a workplace free of destructive, manipulative egotists?
More and more organizations have come to San Francisco State University’s experts in organizational psychology asking for help doing just that. In response, University researchers developed a tool for job interviews to assess narcissistic grandiosity among potential job candidates. San Francisco State Psychology Professors Kevin Eschleman and Chris ...
Invisible anatomy in the fruit fly uterus
2024-10-25
You have likely not spent much time thinking about the uterus of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster. But then, neither have most scientists, even though Drosophila is one of the most thoroughly studied lab animals. Now a team of biologists at the University of California, Davis, has taken the first deep look at the Drosophila uterus and found some surprises, which could have implications not just for understanding insect reproduction and potentially, pest control, but also for understanding fertility in humans.
The work is published Oct. 25 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Drosophila have been a favorite subject for ...
Skeletal muscle health amid growing use of weight loss medications
2024-10-25
A recent commentary published in The Lancet journal highlights the critical importance of skeletal muscle mass in the context of medically induced weight loss, particularly with the widespread use of GLP-1 receptor agonists. These medications, celebrated for their effectiveness in treating obesity, have raised concerns regarding the potential for substantial muscle loss as part of the weight loss process.
Dr. Steven Heymsfield, professor of metabolism and body composition, and Dr. M. Cristina Gonzalez, adjunct and visiting professor in metabolism-body composition, both of Pennington Biomedical Research Center, joined colleagues Dr. Carla Prado of the University ...
The Urban Future Prize Competition awards top prizes to Faura and Helix Earth Technologies and highlights climate adaptation solutions with the inaugural Future Resilience Prize
2024-10-25
NYU Tandon School of Engineering's Urban Future Lab named the winners of its 2024 Future Resilience and Future Solutions prizes, at its 8th annual Urban Future Summit on October 24, 2024 at the Brooklyn Navy Yard in New York City. Through the generous support of The New York Community Trust, MUFG Bank, Mitsubishi Corporation (Americas), the Urban Future Lab continues to catalyze groundbreaking solutions for the climate crisis and this year, they’ve expanded their focus to include adaptation as a critical piece of the puzzle.
After an afternoon of pitches, the jury, comprised of industry experts and ...
Wayne State researcher secures two grants from the National Institute on Aging to address Alzheimer’s disease
2024-10-25
DETROIT – A Wayne State University School of Medicine faculty member has been awarded a total of $2.3 million by the National Institute on Aging of the National institutes of Health for two new, concurrent projects that both address questions related to Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive, age-related degenerative brain disease characterized by memory problems, impaired judgment, cognitive issues and changes in personality.
Joongkyu Park, Ph.D., assistant professor of pharmacology and of neurology, is the principal investigator on “Local protein synthesis ...
NFL’s Bears add lifesavers to the chain of survival in Chicago
2024-10-25
CHICAGO, October 22, 2024— The American Heart Association and the Chicago Bears brought cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) training to the Illinois High School Association (IHSA) Girls Flag Football State Finals on Saturday, Oct. 19. More than 150 youth athletes, coaches and league administrators learned lifesaving skills building their confidence and capabilities to respond in the event of a cardiac emergency. According to American Heart Association data, 9 out of every 10 people who experience cardiac arrest outside of a hospital die, in part ...
High-impact clinical trials generate promising results for improving kidney health: Part 1
2024-10-25
The results of numerous high-impact phase 3 clinical trials that could affect kidney-related medical care will be presented in-person at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23–27.
Finerenone—a selective non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist—has been shown to have kidney protective effects in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD) with type 2 diabetes, but its effects on kidney outcomes in patients with heart failure with and without diabetes and/or CKD are not known. To investigate, researchers analyzed data from 6,001 participants enrolled in the FINEARTS-HF trial, a global, randomized ...
Early, individualized recommendations for hospitalized patients with acute kidney injury
2024-10-25
About The Study: Among patients hospitalized with acute kidney injury, recommendations from a kidney action team did not significantly reduce the composite outcome of worsening acute kidney injury stage, dialysis, or mortality, despite a higher rate of recommendation implementation in the intervention group than in the usual care group.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, F. Perry Wilson, MD, email francis.p.wilson@yale.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.22718)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
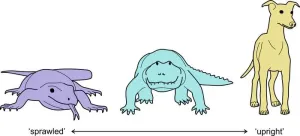
How mammals got their stride
2024-10-25
Mammals, including humans, stand out with their distinctively upright posture, a key trait that fueled their spectacular evolutionary success. Yet, the earliest known ancestors of modern mammals more resembled reptiles, with limbs stuck out to their sides in a sprawled posture.
The shift from a sprawled stance, like that of lizards, to the upright posture of modern mammals, as in humans, dogs, and horses, marked a pivotal moment in evolution. It involved a major reorganization of limb ...
Cancer risk linked to p53 in ulcerative colitis
2024-10-25
Researchers in the lab of Michael Sigal at the Max Delbrück Center and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have elucidated the role of the p53 gene in ulcerative colitis. The study, published in Science Advances, suggests a potential new drug target to stop disease progression to cancer.
A team of researchers led by Kimberly Hartl, a graduate student at the Berlin Institute for Medical Systems Biology of the Max Delbrück Center (MDC-BIMSB) and Charité – Universitätsmedizin, have shed new light on the role of the p53 tumor suppressor gene ...
[1] ... [851]
[852]
[853]
[854]
[855]
[856]
[857]
[858]
859
[860]
[861]
[862]
[863]
[864]
[865]
[866]
[867]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.