Building safer cities with AI: Machine learning model enhances urban resilience against liquefaction
2024-10-28
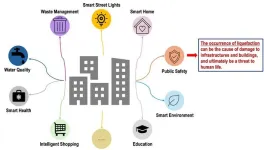
As urban areas expand, the threat of natural disasters becomes a pressing concern for city planners and disaster management authorities. In earthquake-prone countries like Japan, one of the critical risks to infrastructure is liquefaction, a phenomenon where intense shaking causes loose, water-saturated soils to lose their strength and behave like a liquid. Liquefaction can cause buildings to sink into the soil, crack foundations, and collapse roads and utilities like water lines.
Soil liquefaction accompanies every major earthquake, and the damage is significant. The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake in Japan caused liquefaction ...
Novel self-cleaning electrode developed for alkaline-earth metal peroxide synthesis
2024-10-28
Metal peroxide (MO2, M=Ca, Sr, Ba) is an alternative to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). It has excellent oxidative properties, superior chemical stability, high purity, and is easy to store and transport. It has been widely used in wastewater treatment and disinfection.
A Chinese research group has recently developed a novel self-cleaning electrode by constructing a micro-/nanostructure of a highly active catalyst with appropriate surface modification, achieving highly stable synthesis of alkaline-earth MO2.
This study was published in Nature Nanotechnology.
The current primary synthesis process of MO2 involves fast decomposition of H2O2, leading to insufficient utilization ...
New report demands greater understanding of the impact of change on academia
2024-10-28
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is today calling for greater awareness of the impact that a myriad of fast-developing technologies are having on academics and their institutions.
This follows the publication of a new report from Digital Science looking at how changing attitudes and behaviors towards research are affecting traditional research models and dynamics. Key themes to emerge from the findings relate to areas of open research, impact and evaluation, tech and AI, collaboration and research security.
The objective of the report – titled Research Transformation: Change in the era of AI, open and impact ...
Discovery of key mechanism in Huntington’s Disease could pave the way for early detection and treatment
2024-10-28
Researchers from the University of Oxford have identified a key biochemical mechanism relevant to the development of Huntington’s Disease. This discovery opens up the possibility of studying the disease before its clinical onset and eventually stopping its progression.
The study, published in Nature Metabolism, has shown for the first time the biochemical change responsible for the development of Huntington’s disease, and how blocking this change stopped disease progression.
Huntington's disease is an inherited condition that stops parts of the brain from working properly, leading to mental and physical decline that slowly ...
Humans and AI: Do they work better together or alone?
2024-10-28
The potential of human-AI collaboration has captured our imagination: a future where human creativity and AI's analytical power combine to make critical decisions and solve complex problems. But new research from the MIT Center for Collective Intelligence (CCI) suggests this vision may be much more nuanced than we once thought.
Published today in Nature Human Behaviour, “When Combinations of Humans and AI Are Useful” is the first large-scale meta-analysis conducted to better understand when human-AI combinations are useful in task completion, and when they are not. Surprisingly, the research has found that combining humans and AI to ...
Childhood attention issues and genetic factors may predict psychosis risk
2024-10-28
Researchers at UCLA Health have found that a person's risk of developing psychotic-like experiences may be influenced by both childhood attention problems and their genetic makeup.
The findings, published in Nature Mental Health, build upon a long-studied association between childhood attention problems and the likelihood of later developing schizophrenia. Using data from about 10,000 children over six years, UCLA researchers led by Dr. Carrie Bearden sought to determine how attentional variability ...
Amsterdam UMC study proves impact of rapid first shock after cardiac arrest
2024-10-28
It is well known that acting quickly in the event of a cardiac arrest is important, but what does a quick initial shock with a defibrillator mean exactly for patients' chances of survival? Researchers from Amsterdam UMC analysed the data of 3723 patients who had a cardiac arrest outside the hospital and concluded that for the first shock, every minute reduces the chance of survival by 6%. The results of this research were published today in the international journal Circulation.
"Our research shows that every minute of delay in giving the first shock has a major impact. If the first shock was given within six minutes, it was possible ...
Children’s BMI can affect their future lung function
2024-10-28
An abnormal BMI in children – be it high or low – can now be associated with impaired lung function, but if their BMI is normalised before they reach adulthood, the impairment can be offset, researchers from Karolinska Institutet report. Their results, which are based on data collected under the BAMSE project in Sweden, are presented in The European Respiratory Journal.
One in ten people have reduced lung function development in childhood and cannot achieve maximal lung capacity in adulthood, increasing the risk of serious health problems such as cardiovascular disease, lung disease and diabetes. One risk factor associated with impaired lung function development is abnormal ...
Don't worry. Study shows you're likely a more creative writer than ChatGPT. For now
2024-10-28
Imagine you decide to write a short story about a protagonist who creates an artificial human and then falls in love with it. What gender is your protagonist? What about the artificial human? Would you write a moving love story? A cautionary dystopian tale?
Would your story be more compelling than one written by ChatGPT?
Likely yes, says Nina Beguš, a researcher and lecturer in UC Berkeley's School of Information and Department of History. Leveraging her background in comparative literature ...
Heart failure mortality declining in Sweden
2024-10-28
A new study from Karolinska Institutet shows that heart failure mortality has decreased in Sweden over the last 20 years. The study has been published in the European Journal of Heart Failure.
A national study has shown that heart failure mortality has decreased in Sweden over the last two decades. Despite these improvements, the prognosis for heart failure patients remains worrying – 25 percent of those diagnosed in 2022 died within a year.
“Our results suggest that advances in heart failure treatment over the past decades have reduced heart failure mortality, both at the population level and for individual patients. ...
Understanding how mutations affect diseases
2024-10-28
Many statistical models and algorithms used by scientists can be imagined as a “black box.” These models are powerful tools that give accurate predictions, but their internal workings are not easily interpretable or understood. In an era dominated by deep learning, where an ever-increasing amount of data can be processed, Natália Ružičková, a physicist and PhD student at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), chose to take a step back. At least in the context of genomic ...
Quality control in artificial photosynthesis: validating natural antenna mimicry
2024-10-28
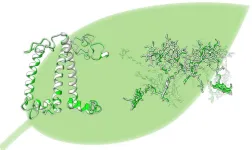
Humans can do plenty, but plants have an ability we don’t: they make energy straight from sunlight, a superpower called photosynthesis. Yet new research shows that scientists are closing that gap.
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have revealed the 3D structure of an artificial photosynthetic antenna protein complex, known as light-harvesting complex II (LHCII), and demonstrated that the artificial LHCII closely mirrors its natural counterpart. This discovery marks a significant step forward in understanding how plants harvest and manage solar energy, paving the way for future innovations in artificial ...
When science speaks in extremes
2024-10-28
“Vaccines are 100% safe, and anyone who doubts this is ignorant”: Have you ever come across messages like this during the pandemic crisis a few years ago? If you often feel that certain public debates—such as those on vaccines or the climate crisis—boil down to a black-and-white clash between two sides demanding, with harsh tones, unquestioning allegiance to their view, you're not entirely wrong. We are rightly accustomed to being warned about pseudoscientific misinformation and fake news, and much research has been devoted ...
Will the ocean suffer an epidemic?
2024-10-28
Written by a team of European experts from the marine sciences, Navigating the Future VI discusses how the biodiversity crisis is being played out in the Ocean. It notes that Ocean species large and small are far less well described than their terrestrial counterparts, making it harder to measure declines and their impacts. This publication provides governments, policymakers and funders with robust, independent scientific advice on future seas and Ocean research. With the COP16 on biodiversity already in full swing in Cali, Colombia, it is timely to reflect further on the need to better understand our Ocean biodiversity.
“Climate change ...
A single thin film perfectly absorbs all electromagnetic waves!
2024-10-28
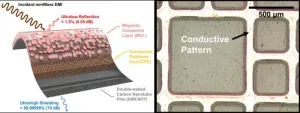
The research team of Dr. Byeongjin Park and Dr. Sang Bok Lee from the Composites & Convergence Materials Research Division at the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), has developed the world's first ultra-thin film composite material capable of absorbing over 99% of electromagnetic waves from various frequency bands (such as 5G/6G, WiFi, and autonomous driving radar) using a single material.
This electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding material is less than 0.5mm thick and is distinguished by its low reflectance ...
Teens who made history with Pythagoras’ theorem discovery publish their first academic paper with new proofs
2024-10-28
In 2022, U.S. high school students Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson astonished teachers when they discovered a new way to prove Pythagoras’ theorem using trigonometry after entering a competition at their local high school. As a result, both students were awarded keys to the city of New Orleans, and even received personal praise from Michelle Obama.
Today they become published authors of a new peer-reviewed paper detailing their discoveries, published in the journal American Mathematical Monthly.
Pythagoras’ famous 2,000-year-old ...
More social species live longer, Oxford study finds
2024-10-28
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01 GMT MONDAY 28 OCTOBER / 20:01 ET SUNDAY 27 OCTOBER 2024
More social species live longer, Oxford study finds
New research published today (28 Oct) from the University of Oxford has revealed that species that are more social live longer and produce offspring for a greater timespan. This is the first study on this topic which spans the animal kingdom, from jellyfish to humans.
What are the benefits and costs of sociality? Social organisms may enjoy benefits such as sharing resources, being better protected from predators, and having support to raise offspring. However, by living in more ...
Magicians don’t mind sharing the secrets behind tricks – if they are their own
2024-10-27
Magic is one of the oldest forms of entertainment, and much of its enchantment is said to rely on the audience not knowing how the tricks are done.
However, while magicians swear to keep their secrets forever when they embark on their profession they are happy to share the tricks of their trade in certain circumstances, a new study shows.
Illusionists who took part in major new research thought it was OK to expose their own techniques, but not those invented by others, and also believe it is acceptable to reveal the secrets behind tricks invented by someone who has since died.
They didn’t think it was right to share the workings of a magic trick just to gain public ...
No incentive for older birds to make new friends
2024-10-27
Like people, birds have fewer friends as they age, but the reasons why are unclear. New research suggests they may just have no drive to.
In humans, it’s often been assumed that older people have fewer friends because they’re pickier about who they spend their time with. There’s also the issue that there are fewer people of their own age around.
But it’s hard to pick apart the various potential causes for humans, so researchers have turned to animals. The team behind the new research, led by Imperial College London, studied an isolated population of sparrows on the island of Lundy, in the Bristol Channel.
By mapping the ...
Development and validation of a new prognostic model for predicting survival outcomes in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure
2024-10-27
Background and Aims
Early determination of prognosis in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is crucial for optimizing treatment options and liver allocation. This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with ACLF and to develop new prognostic models that accurately predict patient outcomes.
Methods
We retrospectively selected 1,952 hospitalized patients diagnosed with ACLF between January 2010 and June 2018. This cohort was used to develop new prognostic scores, which were subsequently validated in external groups.
Results
The study included 1,386 ACLF patients and identified six independent ...
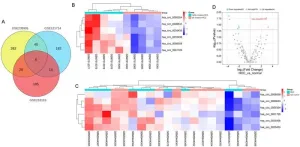
Identification and validation of the Hsa_circ_0001726/miR-140-3p/KRAS axis in hepatocellular carcinoma based on microarray analyses and experiments
2024-10-27
Background and Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most fatal malignancies. Epigenetic mechanisms have revealed that noncoding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs), are involved in HCC progression. This study aimed to construct a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in HCC and validate one axis within the network.
Methods
HCC-related transcriptome data were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus, and HCC-related genes were sourced from GeneCards to identify differentially expressed circRNAs and miRNAs. ...
New study warns that melting Arctic sea-ice could affect global ocean circulation
2024-10-27
“Our finding that enhanced melting of Arctic sea-ice likely resulted in significant cooling in northern Europe in the earth’s past is alarming,” says Mohamed Ezat from the iC3 Polar Research Hub, lead author of the new study. “This reminds us that the planet’s climate is a delicate balance, easily disrupted by changes in temperature and ice cover.”
Ice-free summer conditions are expected to occur in the Arctic Ocean from the year 2050 onwards.
Earlier this ...
Researchers test imlifidase enzyme versus plasma exchange in removing donor-specific antibodies in kidney transplant rejection trial
2024-10-27
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — For kidney transplant recipients experiencing antibody-mediated rejection, the current standard of care involves removing donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) through plasmapheresis (PLEX)—a procedure that removes antibodies from the plasma portion of the blood. Results from a recent clinical trial reveal that an investigational drug called imlifidase, which cleaves and inactivates the type of antibodies that include DSAs, is more effective than PLEX. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney ...
Preclinical studies test novel gene therapy for treating IgA nephropathy
2024-10-26
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — IgA nephropathy is an autoimmune kidney disease, and complement, a component of the innate immune system, plays a role in the condition’s pathogenesis. Investigators have developed and tested a novel gene therapy that enters kidney cells and enables them to block complement activation. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
The gene therapy, called PS-002, uses a modified virus to treat kidney cells called podocytes. Administration of PS-002 in a mouse model of IgA nephropathy reduced signs of kidney dysfunction, lowered complement ...
Trial assesses antibody therapy for chronic active antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection
2024-10-26
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — Chronic active antibody-mediated rejection (caAMR) is a common cause of allograft loss after transplantation, with no approved therapies. Clazakizumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6), stabilized kidney transplant recipients’ kidney function in a phase 2 trial. Investigators now have data from a phase 3 trial with clazakizumab. The findings from the Phase 3 IMAGINE trial, the largest placebo-controlled study in kidney transplant recipients with caAMR, will be ...
[1] ... [850]
[851]
[852]
[853]
[854]
[855]
[856]
[857]
858
[859]
[860]
[861]
[862]
[863]
[864]
[865]
[866]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.