(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. -- Researchers from The Miriam Hospital have found that people with mobility impairments under age 65 have significantly higher rates of smoking than those without mobility impairments. Additionally, smokers with mobility impairments were less likely to attempt quitting than those without mobility impairments, and evidence-based, quit-smoking treatments may not be sufficient for this population. The study and its findings are published online in advance of print in the American Journal of Public Health.
Lead researcher Belinda Borrelli, Ph.D., of The Centers for Behavioral and Preventive Medicine at The Miriam Hospital, and her colleagues sought to report cigarette smoking prevalence and quit attempts among individuals with mobility impairments as they have greater health risks than the general population.
Borrelli conducted an analysis of 13,308 adults aged 21-85 years old with mobility impairments such as using special ambulatory equipment and having difficulty walking one-quarter mile without equipment. Results showed that among 21 to 44 year olds with mobility impairments, 39.2 percent were smokers, compared with only 21.5 percent of adults without mobility impairments. Among 45 to 64 year olds with mobility impairments, 31.2 percent were smokers versus 20.7 percent without mobility impairments.
The analysis also found that women ages 21 to 44 years old with mobility impairments had the highest smoking prevalence at 45.9 percent, exceeding same-aged women without mobility impairments. Men with mobility impairments had greater smoking prevalence than women with mobility impairments. Smokers with mobility impairments were also less likely to attempt quitting than smokers without mobility impairments.
"People with physical disabilities constitute 16.2 percent of the population and the majority of the population will experience physical disability at some point during their lifetime," Borrelli says. "However, the prevalence of smoking among people with disabilities was unknown prior to our paper. Our particular interest was in pinpointing smoking prevalence among those who use a device to help them get around. Literature indicates that those who use mobility aids have higher rates of depression, and in the general population, this is associated with greater smoking rates and lower likelihood of quitting smoking."
Borrelli focused on smokers with mobility impairment because in addition to being at risk for the same smoking-related health problems as the general population, this population is at risk for worsening their existing disability and underlying medical condition. Continued smoking exacerbates physical disabilities and causes or contributes to many secondary conditions including respiratory and circulatory difficulties, muscle weakness, delayed wound healing, worsening arthritis and osteoporosis. Smokers with a relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS) are three times more likely to develop a secondary-progressive disease course.
Borrelli concludes, "Our data points to the need for future research investigating why smoking prevalence is so high in this population, as well as the best methods of smoking cessation treatment for this population.
"It is not clear that evidenced-based treatments that are effective for the general population will be sufficient to help people with mobility impairments quit smoking," she adds. "We speculate that smokers with mobility impairments may need more intensive treatment given their greater risk factors for treatment failure such as high depression rates and stress levels, less physical activity and multiple medical comorbidities, coupled with high unemployment and low income. In the meantime, practicioners should recommend a combination of treatment modalities that include both psychosocial support that can be home based and pharmacological treatment."
INFORMATION:
Belinda Borrelli is a senior research scientist at The Miriam Hospital and professor of psychiatry at The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University. Other researchers in the study include Andrew Busch, Ph.D., and Shira Dunsiger also of The Miriam Hospital and Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University.
About The Miriam Hospital
The Miriam Hospital is a 247-bed, not-for-profit teaching hospital affiliated with The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University. It offers expertise in cardiology, oncology, orthopedics, men's health, and minimally invasive surgery and is home to the state's first Joint Commission-certified Stroke Center and robotic surgery program. The hospital, which received more than $23 million in external research funding last year, is nationally known for its HIV/AIDS and behavioral and preventive medicine research, including weight control, physical activity and smoking cessation. The Miriam Hospital has been awarded Magnet Recognition for Excellence in Nursing Services four times and is a founding member of the Lifespan health system. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter (@MiriamHospital) and Pinterest.
Miriam Hospital study examines smoking prevalence
First-of-its-kind study to examine the high-risk group and advise they be targeted for cessation
2014-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Obese US firefighters report receiving no weight advice from their health provider
2014-07-11
HOUSTON – (July 10, 2014) – Obese and overweight firefighters are not receiving weight management advice from their health care providers, according to new research from The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
National guidelines state that health care professionals (HCPs) should advise patients on the importance of maintaining a healthy weight. Firefighters have high rates of obesity, and cardiovascular events are the leading cause of line-of-duty deaths in firefighters. This study assessed the association of age and body mass index (BMI) ...
Many fires in New South Wales, Australia
2014-07-11
There were many fires burning in eastern New South Wales, Australia when NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead on July 11.
At 03:35 UTC on July 11 (12:35 p.m. local time/11:35 p.m. EDT on July 10), when Aqua passed over eastern New South Wales (NSW), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard captured a natural-color visible image of the region and spotted smoke (light brown) from various fires. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red.
The New South Wales, Australia Government website "NSW Rural Fire Service" ...
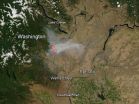
Mills Canyon fire, Washington
2014-07-11
The Mills Canyon fire started near the City of Entiat on Tuesday, July 8, 2014. Despite the efforts of local resources, the fire quickly grew to over 1,000 acres by evening. Three outbuildings were damaged. The cause of the fire is under investigation by the Washington Department of Natural Resources. The fire team is working with existing local resources in developing fire control strategies and tactics. Other cooperators include the U.S. Forest Service (USFS), Washington State Department of Natural Resources, (WA DNR), Bureau of Land Management, Chelan County Emergency ...
New simple setup for X-ray phase contrast
2014-07-11
This news release is available in German. X-ray phase-contrast imaging is a method that uses the refraction of X-rays through a specimen instead of attenuation resulting from absorption. The images produced with this method are often of much higher quality than those based on absorption. The scientists in the team of Prof. Franz Pfeiffer are particularly interested in developing new approaches for biomedical X-ray imaging and therapy – including X-ray phase-contrast imaging. One main goal is to make this method available for clinical applications such as diagnosis of ...
NASA's TRMM satellite maps Tropical Storm Neoguri's soggy path through Japan
2014-07-11
Southern Japan received a soaking from Tropical Storm Neoguri on July 9 and 10 and data from the TRMM satellite was used to create a map that shows how much rain fell in Kyushu.
Kyushu is the southwestern most and third largest island of Japan. The island is mountainous and is home to Mount Aso. Heavy rainfall from Neoguri fell on land that was already soaked in the past week from a slow moving frontal system.
Typhoon Neoguri made landfall on Kyushu early Thursday, July 10, local time after affecting the Okinawa island chain.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission ...
Virtual finger enables scientists to navigate and analyze complex 3D images
2014-07-11
SEATTLE, WASH. — July 11, 2014 — Researchers have pioneered a revolutionary new way to digitally navigate three-dimensional images. The new technology, called Virtual Finger, allows scientists to move through digital images of small structures like neurons and synapses using the flat surface of their computer screens. Virtual Finger's unique technology makes 3D imaging studies orders of magnitude more efficient, saving time, money and resources at an unprecedented level across many areas of experimental biology. The software and its applications are profiled in this week's ...
In lab studies, hydroxyethyl starch has direct harmful effects on kidney cells
2014-07-11
July 11, 2014 – The increased risk of kidney injury related to the use of hydroxyethyl starch (HES) in resuscitation fluids reflects the mass of HES molecules, according to a report in Anesthesia & Analgesia, official journal of the International Anesthesia Research Society (IARS).
The "total mass of HES molecules" explains the harmful effect of HES on cultured human renal proximal tubule cells (PTCs), concludes the laboratory study by Dr Christian Wunder and colleagues of University Hospital Würzburg, Austria. Other factors—such as differences in the origin or molecular ...
Better use of electronic health records makes clinical trials less expensive
2014-07-11
Using electronic health records to understand the best available treatment for patients, from a range of possible options, is more efficient and less costly for taxpayers than the existing clinical trial process, a new study shows.
Research led by Professor van Staa, carried out while he was a member of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) and who is now based at The University of Manchester's Health eResearch Centre, published in Health Technology Assessment (HTA) today (Friday 11 July) looked at the use of statins in 300 people with high risk of cardiovascular ...
Drone lighting
2014-07-11
Lighting is crucial to the art of photography. But lights are cumbersome and time-consuming to set up, and outside the studio, it can be prohibitively difficult to position them where, ideally, they ought to go.
Researchers at MIT and Cornell University hope to change that by providing photographers with squadrons of small, light-equipped autonomous robots that automatically assume the positions necessary to produce lighting effects specified through a simple, intuitive, camera-mounted interface.
At the International Symposium on Computational Aesthetics in Graphics, ...
Text message medicine: Texts from the ER can reduce binge drinking
2014-07-11
WASHINGTON —Young adults who screened positive for a history of hazardous or binge drinking reduced their binge drinking by more than 50 percent after receiving mobile phone text messages following a visit to the emergency department, according to a study published online yesterday in Annals of Emergency Medicine ("A Text Message Alcohol Intervention for Young Adult Emergency Department Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial").
"Each day in the U.S., more than 50,000 adults ages 18 to 24 visit ERs and up to half have hazardous alcohol use patterns," said Brian Suffoletto, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
[Press-News.org] Miriam Hospital study examines smoking prevalenceFirst-of-its-kind study to examine the high-risk group and advise they be targeted for cessation