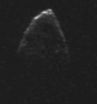
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, have made a novel discovery that may potentially protect the world from future collisions with asteroids.
The team studied near-Earth asteroid 1950 DA and discovered that the body, which rotates so quickly it defies gravity, is held together by cohesive forces called van der Waals, never detected before on an asteroid.
The findings, published in this week's edition of the science journal Nature, have potential implications for defending our planet from a massive asteroid impact.
Previous research has shown that asteroids are loose piles of rubble held together by gravity and friction. However, the UT team found that 1950 DA is spinning so quickly that it defies these forces. Ben Rozitis, a postdoctoral researcher; Eric MacLennan, a doctoral candidate; and Joshua Emery, an assistant professor in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, wanted to know what keeps the body from breaking apart.
Looking at thermal images and orbital drift to calculate thermal inertia and bulk density, the team detected the action of cohesive forces in an environment with little gravity.
"We found that 1950 DA is rotating faster than the breakup limit for its density," said Rozitis. "So if just gravity were holding this rubble pile together, as is generally assumed, it would fly apart. Therefore, interparticle cohesive forces must be holding it together."
In fact, the rotation is so fast that at its equator, 1950 DA effectively experiences negative gravity. If an astronaut were to attempt to stand on this surface, he or she would fly off into space unless he or she were somehow anchored.
The presence of cohesive forces has been predicted in small asteroids, but definitive evidence has never been seen before.
The finding provides important information for efforts aimed at stopping an asteroid from crashing into Earth.
"Following the February 2013 asteroid impact in Chelyabinsk, Russia, there is renewed interest in figuring out how to deal with the potential hazard of an asteroid impact," said Rozitis. "Understanding what holds these asteroids together can inform strategies to guard against future impacts."
This research reveals some potential techniques, such as a kinetic impactor which would deploy a massive object on a collision course with the asteroid, could exacerbate the impact's effects. For example, this technique could destabilize the cohesive forces keeping the asteroid together, causing it to break apart into several threatening asteroids headed for Earth.
This may be what occurred with the asteroid P/2013 R3, which was caught by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2013 and 2014 coming undone, possibly due to a collision with a meteor.
"With such tenuous cohesive forces holding one of these asteroids together, a very small impulse may result in a complete disruption," said Rozitis.
The researchers' findings also have implications for space exploration. For example, the European Space Agency's Rosetta spacecraft landed on Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko's surface last week and it may find a dusty surface dominated by such cohesive forces.
INFORMATION:
University of Tennessee research uncovers forces that hold gravity-defying near-earth asteroid together
Researchers at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, have made a novel discovery that may potentially protect the world from future collisions with asteroids
2014-08-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New test reveals purity of graphene
2014-08-13
Graphene may be tough, but those who handle it had better be tender. The environment surrounding the atom-thick carbon material can influence its electronic performance, according to researchers at Rice and Osaka universities who have come up with a simple way to spot contaminants.
Because it's so easy to accidently introduce impurities into graphene, labs led by physicists Junichiro Kono of Rice and Masayoshi Tonouchi of Osaka's Institute of Laser Engineering discovered a way to detect and identify out-of-place molecules on its surface through terahertz spectroscopy.
They ...
Gut flora influences HIV immune response
2014-08-13
DURHAM, N.C. – Normal microorganisms in the intestines appear to play a pivotal role in how the HIV virus foils a successful attack from the body's immune system, according to new research from Duke Medicine.
The study, published Aug. 13, 2014, in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, builds on previous work from researchers at the Duke Human Vaccine Institute that outlined a perplexing quality about HIV: The antibodies that originally arise to fight the virus are ineffective.
These initial, ineffective antibodies target regions of the virus's outer envelope called gp41 ...
Coming soon: Genetically edited fruit?
2014-08-13
Recent advances that allow the precise editing of genomes now raise the possibility that fruit and other crops might be genetically improved without the need to introduce foreign genes, according to researchers writing in the Cell Press publication Trends in Biotechnology on August 13th.
With awareness of what makes these biotechnologies new and different, genetically edited fruits might be met with greater acceptance by society at large than genetically modified organisms (GMOs) so far have been, especially in Europe, they say. This could mean that genetically edited ...
New research offers hope for HIV vaccine development
2014-08-13
(Boston)- In a scientific discovery that has significant implications for HIV vaccine development, collaborators at the Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and Duke University School of Medicine have uncovered novel properties of special HIV antibodies. The paper, published in Cell Host and Microbe, describes how some HIV antibodies experience an unusual type of mutation, a phenomenon that allows them to neutralize many different strains of HIV. These antibodies are called "broadly neutralizing antibodies," or BNAbs.
Antibodies develop from immune cells known as ...
Researchers uncover how Ebola virus disables immune response
2014-08-13
The Ebola outbreak in West Africa has brought a lot of attention to the deadly virus. According to the World Health Organization, up to 90% of those infected with Ebola die from the virus. Now, researchers publishing August 13 in the Cell Press journal Cell Host & Microbe reveal how Ebola blocks and disables the body's natural immune response. Understanding how Ebola disarms immune defenses will be crucial in the development of new treatments for the disease.
Dr. Gaya Amarasinghe and colleagues from Washington University School of Medicine along with collaborators from ...
Ebola protein blocks early step in body's counterattack on virus
2014-08-13
One of the human body's first responses to a viral infection is to make and release signaling proteins called interferons, which amplify the immune system response to viruses. Over time, many viruses have evolved to undermine interferon's immune-boosting signal, and a paper published today in the journal Cell Host & Microbe describes a mechanism unique to the Ebola virus that defeats attempts by interferon to block viral reproduction in infected cells.
The newly published study explains for the first time how the production by the virus of a protein called Ebola Viral ...
New insights into the survival and transmission strategy of malaria parasites
2014-08-13
HP1 proteins are found in most eukaryotic organisms and are important regulators of gene silencing. In short, HP1 induces heritable condensation of chromosomal regions. As a result genes located within these regions are not expressed. Importantly, since this conformation is reversible HP1-controlled genes can become activated without requiring changes in the underlying DNA sequence.
The team led by Till Voss at the Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute in collaboration with colleagues from the Nanyang Technological University in Singapore engineered a mutant parasite ...
From eons to seconds, proteins exploit the same forces
2014-08-13
HOUSTON – (Aug. 13, 2014) – Nature's artistic and engineering skills are evident in proteins, life's robust molecular machines. Scientists at Rice University have now employed their unique theories to show how the interplay between evolution and physics developed these skills.
A Rice team led by biophysicists Peter Wolynes and José Onuchic used computer models to show that the energy landscapes that describe how nature selects viable protein sequences over evolutionary timescales employ essentially the same forces as those that allow proteins to fold in less than a second. ...
Why aren't campus emergency alerts taken more seriously?
2014-08-13
Well-publicized tragedies on college campuses across the United States have prompted university officials to implement alert systems that broadcast real-time warnings via text message and e-mail to students, faculty, and staff. Such systems can be highly effective tools, but only if users take them seriously. New research to be presented at the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society 2014 Annual Meeting in Chicago illustrates some factors that can determine whether campus alert systems are attended to or disregarded.
In their paper, "Taking Emergency Warnings Seriously," ...
Researchers identify tests to diagnose invasive aspergillosis with 100 percent accuracy
2014-08-13
Philadelphia, PA, August 13, 2014 – The fungal infection invasive aspergillosis (IA) can be life threatening, especially in patients whose immune systems are weakened by chemotherapy or immunosuppressive drugs. Despite the critical need for early detection, IA remains difficult to diagnose. A study in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics compared three diagnostic tests and found that the combination of nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) and real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) detects aspergillosis with 100% accuracy.
IA is caused by the fungus Aspergillus ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] University of Tennessee research uncovers forces that hold gravity-defying near-earth asteroid togetherResearchers at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, have made a novel discovery that may potentially protect the world from future collisions with asteroids