(Press-News.org) MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass. -- Some of the universe's most massive galaxies may have formed billions of years earlier than current scientific models predict, according to surprising new research led by Tufts University. The findings appear in the Astrophysical Journal published online Nov. 24 in advance of print publication on Dec. 10, 2010.
"We have found a relatively large number of very massive, highly luminous galaxies that existed almost 12 billion years ago when the universe was still very young, about 1.5 billion years old. These results appear to disagree with the latest predictions from models of galaxy formation and evolution," said Tufts astrophysicist Danilo Marchesini, lead author on the paper and assistant professor of physics and astronomy at the Tufts School of Arts and Sciences. "Current understanding of the physical processes responsible in forming such massive galaxies has difficulty reproducing these observations."
Collaborating with Marchesini were researchers from Yale University, Carnegie Observatories, Leiden University, Princeton University, the University of Kansas and the University of California-Santa Cruz.
The newly identified galaxies were five to ten times more massive than our own Milky Way. They were among a sample studied at redshift 3≤z END
Massive galaxies formed when universe was young
New findings disagree with current models
2010-11-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Early intervention essential to success for at-risk children: Queen's University study
2010-11-25
Children living in disadvantaged neighbourhoods are more likely to succeed if they participate in a community-based prevention program, according to findings released recently from a multi-year research study based at Queen's University.
Children participating in the Better Beginnings, Better Futures (BBBF) project showed improved social and academic functioning. The project also impacted positively on families and on neighbourhoods.
"The results from our study indicate that the project has been a success," says Queen's psychology professor emeritus Ray Peters, the ...
Short, on-chip light pulses will enable ultrafast data transfer within computers
2010-11-25
Electrical engineers generated short, powerful light pulses on a chip – an important step toward the optical interconnects that will likely replace the copper wires that carry information between chips within today's computers. University of California, San Diego electrical engineers recently developed the first ultra compact, low power pulse compressor on a silicon chip to be described in the scientific literature. Details appeared online in the journal Nature Communications on November 16.
This miniaturized short pulse generator eliminates a roadblock on the way to ...
Quartz crystal microbalances enable new microscale analytic technique
2010-11-25
A new chemical analysis technique developed by a research group at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) uses the shifting ultrasonic pitch of a small quartz crystal to test the purity of only a few micrograms of material. Since it works with samples close to a thousand times smaller than comparable commercial instruments, the new technique should be an important addition to the growing arsenal of measurement tools for nanotechnology, according to the NIST team.
As the objects of scientific research have gotten smaller and smaller—as in nanotechnology ...
New guidance issued for first responders collecting suspected biothreat agents
2010-11-25
Suspicious packages and powders have triggered more than 30,000 responses by U.S. law enforcement agencies across the country since 2001. These events are expensive, time-consuming and potentially dangerous. To help first responders at all levels of government deal safely and more effectively with suspected biothreat agents, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and a broad team of federal, state and local agencies and other organizations worked together to update an existing standard for sample collection and develop overall guidance for when to collect ...
Cholera and vaccine experts urge United States to stockpile vaccine
2010-11-25
As the cholera epidemic in Haiti continues to rage, public health workers are focusing their efforts on treating the tens of thousands who have already been hospitalized with cholera-like symptoms and providing clean water and adequate sanitation to control the disease's spread.
Could the United States be doing more to help the situation? In an editorial published in the November 24, 2010, issue of the New England Journal of Medicine, vaccine and infectious disease specialists Matthew Waldor of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Peter Hotez of George Washington University ...
Can cacti 'escape' underground in high temperatures?
2010-11-25
In the scorching summer heat of the Chihuahuan Desert in southwest Texas, air temperatures can hover around 97°F (36°C) while at the surface of the soil temperatures can exceed 158°F (70°C). Encountering these extreme temperatures, plants must utilize creative methods to not only survive but thrive under these difficult and potentially lethal conditions.
This new work by Dr. Gretchen North and colleagues, published in the December issue of American Journal of Botany (http://www.amjbot.org/cgi/reprint/ajb.1000286v1), sheds light on how one desert resident, the cactus ...
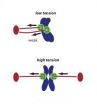
Finger-trap tension stabilizes cells' chromosome-separating machinery
2010-11-25
Scientists have discovered an amazingly simple way that cells stabilize their machinery for forcing apart chromosomes. Their findings are reported Nov. 25 in Nature.
When a cell gets ready to split into new cells, this stable set-up permits its genetic material to be separated and distributed accurately. Otherwise, problem cells – like cancer cells— arise.
The human body contains more than a trillion cells, and every single cell needs to have the exact same set of chromosomes. Mistakes in moving chromosomes during cell division can lead to babies being born with ...
Merrill Corporation Provides Lextranet Certification
2010-11-25
Merrill Corporation (www.merrillcorp.com), a leading global provider of technology-enabled services, today announced its Lextranet Certification Program for contract attorney reviewers. Lextranet is a single, secure and scalable online review and hosting platform that provides on-demand access for easy review of small or large document collections. The program will enhance Merrill's integrated hosting and review offering by ensuring that reviewers have the knowledge and skills necessary to maximize the features built into Lextranet.
"As a result of the training, document ...
Food Truck Marketing: The Brainchild Group Goes Mobile, Literally
2010-11-25
The Brainchild Group, a collection of marketing professionals and foodies, is excited to announce the launch of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and Social Media Marketing campaigns for food trucks around the world. You asked for it, and it's finally here.
The Brainchild Group is best known for implementing revolutionary, catchy online marketing campaigns for a variety of businesses ranging from mom-and-pop shops to top restaurants to Fortune 500 companies. Such expertise is combined with a true passion for food to produce marketing campaigns that connect and interact ...
All Crib Mattresses Launches New Informative Site To Help Parents Choose A Safe Crib Mattress
2010-11-25
All Crib Mattresses is pleased to announce the launch of a new website devoted to helping parents choose a safe crib mattress. Daniela Kelly, owner of the site, says, "A large portion of crib mattresses are unsafe and can even cause death. This is why I started this site, to help parents make a better decision."
The website offers information about different types of mattresses for cribs and breaks them down into price groups that make it easier for parents to select a high quality, affordable crib mattress. It even makes recommendations for the best crib mattress on ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Massive galaxies formed when universe was youngNew findings disagree with current models