(Press-News.org) Through the careful study of modern and early fossil tortoise, researchers now have a better understanding of how tortoises breathe and the evolutionary processes that helped shape their unique breathing apparatus and tortoise shell. The findings published in a paper, titled: Origin of the unique ventilatory apparatus of turtles, in the scientific journal, Nature Communications, on Friday, 7 November 2014, help determine when and how the unique breathing apparatus of tortoises evolved.
Lead author Dr Tyler Lyson of Wits University's Evolutionary Studies Institute, the Smithsonian Institution and the Denver Museum of Nature and Science said: "Tortoises have a bizarre body plan and one of the more puzzling aspects to this body plan is the fact that tortoises have locked their ribs up into the iconic tortoise shell. No other animal does this and the likely reason is that ribs play such an important role in breathing in most animals including mammals, birds, crocodilians, and lizards."
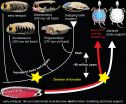
Instead tortoises have developed a unique abdominal muscular sling that wraps around their lungs and organs to help them breathe. When and how this mechanism evolved has been unknown.
"It seemed pretty clear that the tortoise shell and breathing mechanism evolved in tandem, but which happened first? It's a bit of the chicken or the egg causality dilemma," Lyson said. By studying the anatomy and thin sections (also known as histology), Lyson and his colleagues have shown that the modern tortoise breathing apparatus was already in place in the earliest fossil tortoise, an animal known as Eunotosaurus africanus.
This animal lived in South Africa 260 million years ago and shares many unique features with modern day tortoises, but lacked a shell. A recognisable tortoise shell does not appear for another 50 million years.
Lyson said Eunotosaurus bridges the morphological gap between the early reptile body plan and the highly modified body plan of living tortoises, making it the Archaeopteryx of turtles.
"Named in 1892, Eunotosaurus is one of the earliest tortoise ancestors and is known from early rocks near Beaufort West," said Professor Bruce Rubidge, Director of the Evolutionary Studies Institute at Wits University and co-author of the paper.
"There are some 50 specimen of Eunotosaurus. The rocks of the Karoo are remarkable in the diversity of fossils of early tortoises they have produced. The fact that we find Eunotosaurus at the base of the Karoo succession strongly suggest that there are more ancestral forms of tortoises still to be discovered in the Karoo," Rubidge added.
The study suggests that early in the evolution of the tortoise body plan a gradual increase in body wall rigidity produced a division of function between the ribs and abdominal respiratory muscles. As the ribs broadened and stiffened the torso, they became less effective for breathing which caused the abdominal muscles to become specialised for breathing, which in turn freed up the ribs to eventually - approximately 50 million years later - to become fully integrated into the characteristic tortoise shell.
Lyson and his colleagues now plan to investigate reasons why the ribs of early tortoises starting to broaden in the first place. "Broadened ribs are the first step in the general increase in body wall rigidity of early basal tortoises, which ultimately leads to both the evolution of the tortoise shell and this unique way of breathing. We plan to study this key aspect to get a better understanding why the ribs started to broaden."
INFORMATION:
Media enquiries:
Professor Bruce Rubidge is currently undertaking field work in the Karoo. He has intermittent communication access and can be reached on bruce.rubidge@wits.ac.za.
Dr Tyler Lyson is in Germany and can only be reached on tyler.lyson@gmail.com.
For images and a copy of the paper, kindly contact Erna van Wyk, Multimedia Communications Officer, University of the Witwatersrand on erna.vanwyk@wits.ac.za.
Being shown pictures of others being loved and cared for reduces the brain's response to threat, new research from the University of Exeter has found.
The study discovered that when individuals are briefly presented pictures of others receiving emotional support and affection, the brain's threat monitor, the amygdala, subsequently does not respond to images showing threatening facial expressions or words. This occurred even if the person was not paying attention to the content of the first pictures.
Forty-two healthy individuals participated in the study, in which ...
Last year CERN announced the finding of a new elementary particle, the Higgs particle. But maybe it wasn't the Higgs particle, maybe it just looks like it. And maybe it is not alone.
Many calculations indicate that the particle discovered last year in the CERN particle accelerator was indeed the famous Higgs particle. Physicists agree that the CERN experiments did find a new particle that had never been seen before, but according to an international research team, there is no conclusive evidence that the particle was indeed the Higgs particle.
The research team has ...
This news release is available in German. Microbiologists and molecular biologists at ETH Zurich and the University of Bonn have discovered a new agent in fungi that kills bacteria. The substance, known as copsin, has the same effect as traditional antibiotics, but belongs to a different class of biochemical substances. Copsin is a protein, whereas traditional antibiotics are often non-protein organic compounds.
The researchers led by Markus Aebi, Professor of Mycology, discovered the substance in the common inky cap mushroom Coprinopsis cinerea that grows on horse ...
An international research project, which includes researchers from the U. of Granada, has proved the need for campaigns to persuade parents of the benefits involved in having their children walk to school. This also includes work on the perception about the security of the paths their children need to follo won the way to school. This research points out, besides, the need for public administrations to actively campaign to persuade children and their families to walk more often as part of their daily routines.
Many different surveys have demonstrated that walking to school ...
Since suitable studies are lacking, it remains unclear in which sperm analysis parameters assisted reproduction using intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) can be superior to in vitro fertilization (IVF). This is the conclusion of the final report published by the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) on 6 November 2014.
Benefit assessment depending on parameters
The Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) commissioned IQWiG with the examination of two research questions: First, the researchers were to assess the benefit of ICSI in comparison with IVF ...
Eribulin (trade name: Halaven) is approved for women with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer in whom the disease has progressed despite prior drug therapy. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in a dossier assessment whether the drug offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapy in these patient groups.
According to the findings, there are both positive and negative effects. There is proof of minor added benefit for one group of patients. For other groups, there are hints or indications of lesser ...
The current classification system for colorectal cancer, which is based on genetic expression profiles, cannot be used to predict drug responses to FOLFIRI. This is the conclusion reached by a team from the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), formed by members from the Gastrointestinal Cancer Clinical Research Unit and the Structural Computational Biology Group. The study, published this week in the journal Nature Medicine, will assist oncologists in making better-informed decisions regarding how to treat their colorectal cancer patients in the clinic.
Conclusions ...
Published in Nature Biotechnology, the study showed that specially engineered lipid (fat) bodies, called liposomes, can be used to prevent bacterial toxins from killing human cells.
This could prevent unnecessary deaths from diseases such as pneumonia and sepsis. The treatment is a valuable alternative to current medications, particularly for infections that have become resistant to antibiotics.
The bacterial toxins, produced by major human pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumonia, Streptococcus pyogenes and Methicillin Resistant Staphlycoccus aureus (MRSA) were ...
During hibernation, dormice enter into 'torpor' to save energy and water. In this state, the dormice become inactive and show a marked decrease in their metabolic rate, causing their body temperature to reduce.
Torpor was then found to be a strategy used when food availability was limited. The researchers compared two groups of juveniles born late in the season - one able to feed freely and the other intermittently fasted on alternate days. The fasted dormice showed considerably greater use of torpor, enabling them to maintain high growth rates and accumulate sufficient ...
Muscle-specific protein cofilin-2 controls the length of actin filaments in muscle cells.
Sliding of myosin and actin filaments past each other provides the force for muscle contraction. In contrast to most non-muscle cells, the actin filaments in muscle sarcomeres are of precise length and relatively stable. Defects in the organization of these actin filament arrays result in various heart and muscle disorders, such as myopathies.
The research group of professor Pekka Lappalainen at Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki, has now revealed a new mechanism ...