Method for determining possible stress marker in blood samples
2015-05-11
(Press-News.org) A research collaboration between the universities of Oslo and Aarhus has resulted in the development of a new method with diagnostic potential. The new method that combines phase extraction with an enzymatic reaction may eventually be used for an improved and faster screening analysis of isatin as a potential indicator of stress and neurological disorders.
Isatin is a small organic molecule found in low concentrations in different tissues and is excreted with the urine via the blood stream. Isatin is supposedly a degradation product from the neurotransmitters, e.g. dopamine and serotonine.
The level of isatin is elevated in patients suffering from stress and in patients suffering from Parkinson's disease. The level of isatin is also elevated among pregnant women.
Isatin is an inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B, an enzyme that catalyses the initial degradation of dopamine and serotonine. This inhibitory effect makes isatin act as an antidepressant, and it relieves the symptoms of patients suffering from Parkinson's.
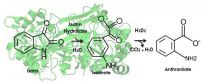
Collaborators from the University of Oslo are the prime mover in the development of this highly specific method to determine the concentration of isatin in samples of blood and urine, using the bacterial enzyme isatin hydrolase in combination with a two-phase extraction. Isatin hydrolase catalyses the conversion of isatin into isatinate, which is followed by a chemical conversion of isatinate into the fluorescent compound anthranilate.
The method can be refined further by substituting the chemical step by an enzyme that is able to convert isatinate into anthranilate.
Within several bacterial species, isatin is formed via the degradation of indole 3-acetic acid, but the origin of isatin in humans are not known. The researchers' method to detect isatin might be useful in future experiments to establish the source-tissue and precursors for isatin formation.
INFORMATION:
Link to the scientific article in ACS (American Chemical Society) Chemical Neuroscience:
Theis Sommer, Kaare Bjerregaard-Andersen, Stine Marie Simensen, Jan K. Jensen, Bjarne Jochimsen,
Patrick J. Riss, Michael Etzerodt og J. Preben Morth
Enzymatic Detection and Quantification Assay of Isatin, a Putative Stress Biomarker in Blood.
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/ipdf/10.1021/cn500346x
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-11
WASHINGTON, May 11, 2015 -- More than 25 million people rely on Adderall™ and other similar drugs to help treat narcolepsy, depression and attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). But how does amphetamine, the active ingredient in Adderall™, work? This week, Reactions explains how amphetamine helps you focus. Check out the video here: https://youtu.be/MeJRBsghMt8.
INFORMATION:Subscribe to the series at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
The American Chemical Society is ...
2015-05-11
Physicians treating hospitalized patients for conditions unrelated to the kidneys should pay close attention to common blood and urine tests for kidney function in order to prevent incidental injury to the organs that help cleanse the body of toxins, new Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health-led research suggests.
The findings, published this month in two studies in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases, suggest that while being older, male, African-American or having diabetes are risk factors for developing acute kidney injury, the strongest risk factor is ...
2015-05-11
An international group of scientists has proposed that fallout from hundreds of nuclear weapons tests in the late 1940s to early 1960s could be used to mark the dawn of a new geological age in Earth history - the Anthropocene.
The study, led by Dr Colin Waters of the British Geological Survey, published new research in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. The research involved 10 members of the Anthropocene Working Group that is chaired by Professor Jan Zalasiewicz of the Department of Geology at the University of Leicester and Gary Hancock, a world expert on plutonium ...
2015-05-11
May 11, 2015 - What are the most influential studies on surgery of the lower (lumbar) spine? The "top 100" research papers in lumbar spine are counted down in a special review in the May 15 issue of Spine, published by Wolters Kluwer.
Dr. Samuel K. Cho and colleagues of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, performed a literature review to analyze and quantify the most important research papers on lumbar spine surgery. Their results raise some interesting "questions, trends and observations"--including the finding that the two most-cited studies ...
2015-05-11
The water flea has genetically adapted to climate change. Biologists from KU Leuven, Belgium, compared 'resurrected' water fleas -- hatched from 40-year-old eggs -- with more recent specimens. The project was coordinated by Professor Luc De Meester from the Laboratory of Aquatic Ecology, Evolution and Conservation.
The water flea has genetically adapted to climate change. Biologists from KU Leuven, Belgium, compared 'resurrected' water fleas - hatched from forty-year-old eggs - with more recent specimens. The project was coordinated by Professor Luc De Meester from the ...
2015-05-11
What does space experimentation have in common with liquid cocktails? Both help in understanding what happens when multiple fluids are mixed together and subjected to temperature change - a phenomenon ubiquitous in nature and industrial applications such as oil fluids contained in natural reservoirs. The latest experimental data performed in zero gravity on the International Space Station is now available in the newly published Topical Issue of EPJ E. The results constitute the first set of highly accurate and broadly validated data on the thermodiffusion effects that occur ...
2015-05-11
MADISON -- Mike Graham knows that fluid dynamics can reveal much about how the flow of blood helps and hinders individual blood cells as they go about their work.
Graham, the Vilas Distinguished Achievement Professor and Harvey D. Spangler Professor of Chemical and Biological Engineering at UW-Madison, established a theoretical basis for these ideas by creating complex computer stimulations that show how relatively stiff white blood cells and platelets interact with more flexible red blood cells. As the different cells collide during blood flow, white cells tend to be ...
2015-05-11
Volcanoes are considered chaotic systems. They are difficult to model because the geophysical and chemical parameters in volcanic eruptions exhibit high levels of uncertainty. Now, Dmitri V. Alexandrov and colleagues from the Ural Federal University in Ekaterinburg, in the Russian Federation, have further extended an eruption model -- previously developed by other scientists -- to the friction force at work between the volcanic plug and volcanic conduit surface. The results, published in EPJ B, provide evidence that volcanic activity can be induced by external noises that ...
2015-05-11
Chinese scientists have reared beef rich in the beneficial fatty acids associated with fish oils. The study in Springer's journal Biotechnology Letters also highlights the scientific challenges that remain.
The team from Northwest A&F University and the National Beef Cattle Improvement Centre, both in Yangling (Shaanxi), successfully introduced a gene into foetal cells from Luxi Yellow cattle, a Chinese breed with a high beef yield. The fat1 gene, isolated from a nematode worm, codes for desaturase enzymes that are involved in the conversion of n-6 to n-3 polyunsaturated ...
2015-05-11
How much food your dining companion eats can have a big influence on how much you consume, a UNSW Australia-led study concludes.
This psychological effect, known as social modelling, leads people to eat less than they normally would if alone when their companion consumes a small amount of food.
Study lead author, Associate Professor Lenny Vartanian of the UNSW School of Psychology, says that in social situations the appropriate amount of food to eat can be unclear.
"Internal signals like hunger and feeling full can often be unreliable guides. In these situations people ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Method for determining possible stress marker in blood samples


